Cyclotron. It is a device to produce high speed fi.e., high energy) positively charged particles like protons, deutrons and a-particles.
Principle. It is based upon the principle that a charged particle moving at right angles to a uniform magnetic field is acted upon by a force perpendicular to its direction of motion and follow a circular path.
Construction. It consists of two semicircular hollow metal boxes `D_1 and D_2` called dees. D.s are separated by a small gap and are connected to terminals of high frequency oscillator providing alternating potential of nearly 10,000 V and millions hertz frequency. Whole of the apparatus is placed in a metal box containing gas at low pressure and placed between the poles of a strong electromagnetic field perpendicular to the plane of D.s.
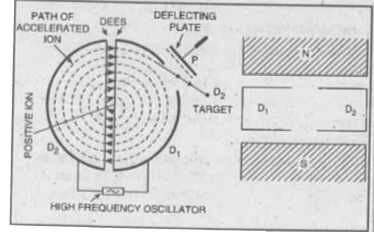
Theory. Let a positive ion (`""_1H^1, ""_1H^2, ""_1He^3 or ""_2He^4`) be located in the gap when D is negatively and `D_2` positively charged, the positive ion will get accelerated, towards `D_1`. Since magnetic field is uniform and acting at right angle to the plane of D.s, the ion traverses a circular path in `D_1`. When the ion emerges out into the gap after completing a semicircle in `D_1`. If during the time taken to cover semicircle, the electric field gets reversed, the ion further gets accelerated towards `D_2`. It enters `D_2` with greater speed and moves in `D_2` in a bigger semicircle. The process is represented time and again and each time ion gets an addition kick in the proper direction.
The ion becomes faster and faster until it reaches the periphery of the D.s where it is brought out of the chamber by means of deflecting plate P charged to a very high negative potential and is made for bombarding the target.
Consider the ion to carry a charge q and of mass m. If v is the speed of the ion when it is moving in circular path of radius r, then
`(mv^2)/(r) = Bqv`
`or v/r = (Bq)/m`
Since B, and m are constant v `prop` r greater the speed, bigger the radius.
Time taken to complete half rotation = `(pir)/v = pi (m/(Bq))`
Time taken to complete one rotation `=2t = (2 pi m)/(Bq)`
Frequency, `v = 1/T = (Bq)/(2 pi m)`
