Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY-GRAVITATION-Exercise 13.1
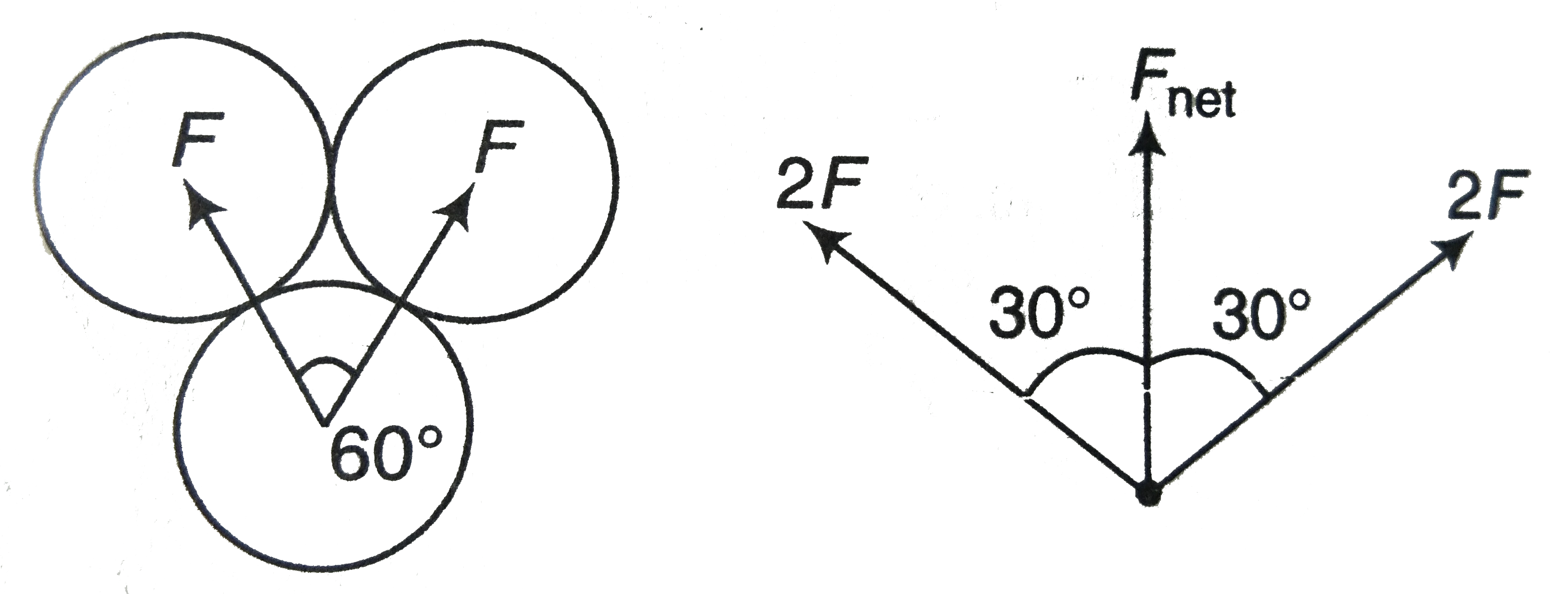
- Three uniform spheres each having a mass M and radius a are kept in su...
Text Solution
|
- Four particles having masses, m, 2m, 3m, and 4m are placed at the four...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles of masses 1.0 kg and 2.0 kg are placed at a separation o...
Text Solution
|
- Three points A , B and C each of mass are placed in a line with AB=BC=...
Text Solution
|
- Spheres of the same metarial and same radius r are touching each other...
Text Solution
|