Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
RAY OPTICS
PRADEEP|Exercise (NCERT)Exercise With Solution|38 VideosRAY OPTICS
PRADEEP|Exercise Higher Thinking Order|5 VideosRAY OPTICS
PRADEEP|Exercise Long Answer (d)|6 VideosPROPERTIES OF BULK MATTER
PRADEEP|Exercise Multiple choice questions|7 VideosSYSTEMS OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION
PRADEEP|Exercise Assertion- Reason Type questions|20 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PRADEEP-RAY OPTICS-(NCERT)Long Answer
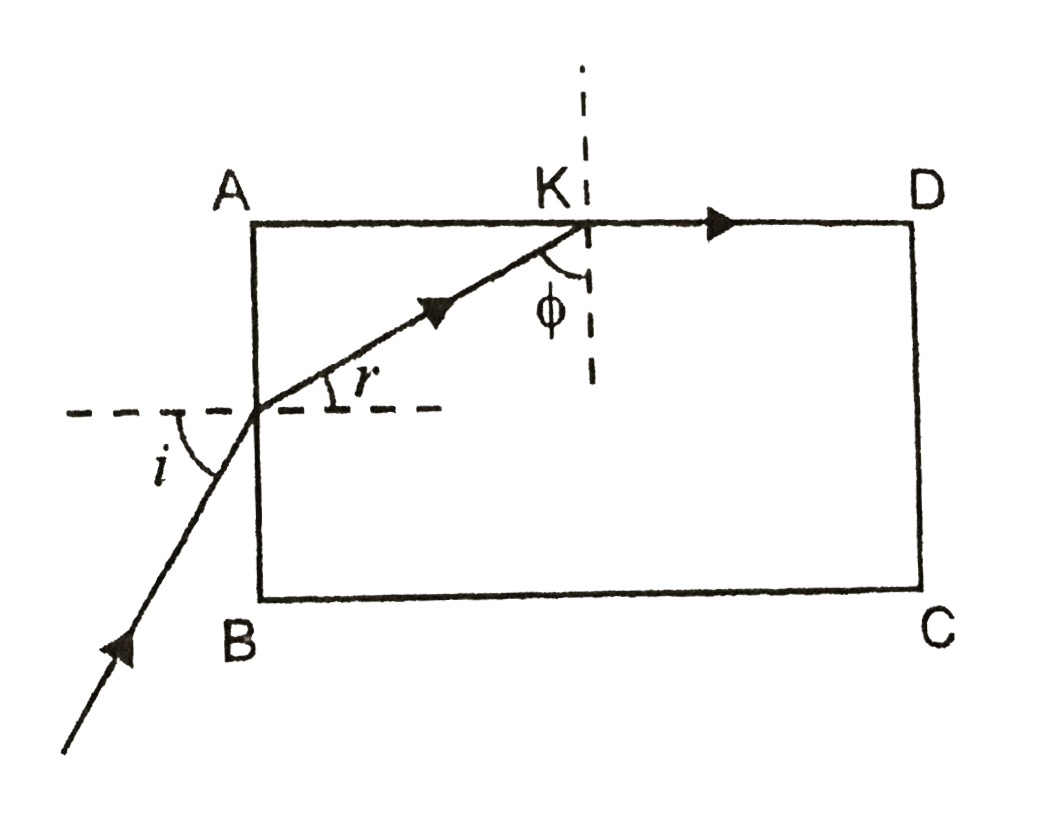
- Show that for a material with refractive index mu ge sqrt(2), light in...
Text Solution
|
- The mixture of a pure liquid and a solution in a along vertical column...
Text Solution
|
- If light passes near a massive object, the gravitational interaction c...
Text Solution
|
- An infinitely long cylinder of radius R is made of an unusal exotic ma...
Text Solution
|
- (i) Consider a thin lens placed between a source (S) and an observer (...
Text Solution
|
 .
.