Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
RAY OPTICS
PRADEEP|Exercise Sample Problem(a)|5 VideosRAY OPTICS
PRADEEP|Exercise Solved Example(a)|14 VideosRAY OPTICS
PRADEEP|Exercise (NCERT)Exercise With Solution|38 VideosPROPERTIES OF BULK MATTER
PRADEEP|Exercise Multiple choice questions|7 VideosSYSTEMS OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION
PRADEEP|Exercise Assertion- Reason Type questions|20 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PRADEEP-RAY OPTICS-Higher Thinking Order
- Figure shows an irregular block of material of refractive indec sqrt(2...
Text Solution
|
- An equiconvex lens with radii of curvature of magnitude R each is put ...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light incident on the horizontal surface of a glass slab at 7...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light the face AB of a glass prism of refractive index mu at ...
Text Solution
|
- The diameter of a plano convex lens is 6 cm and thickness at the centr...
Text Solution
|
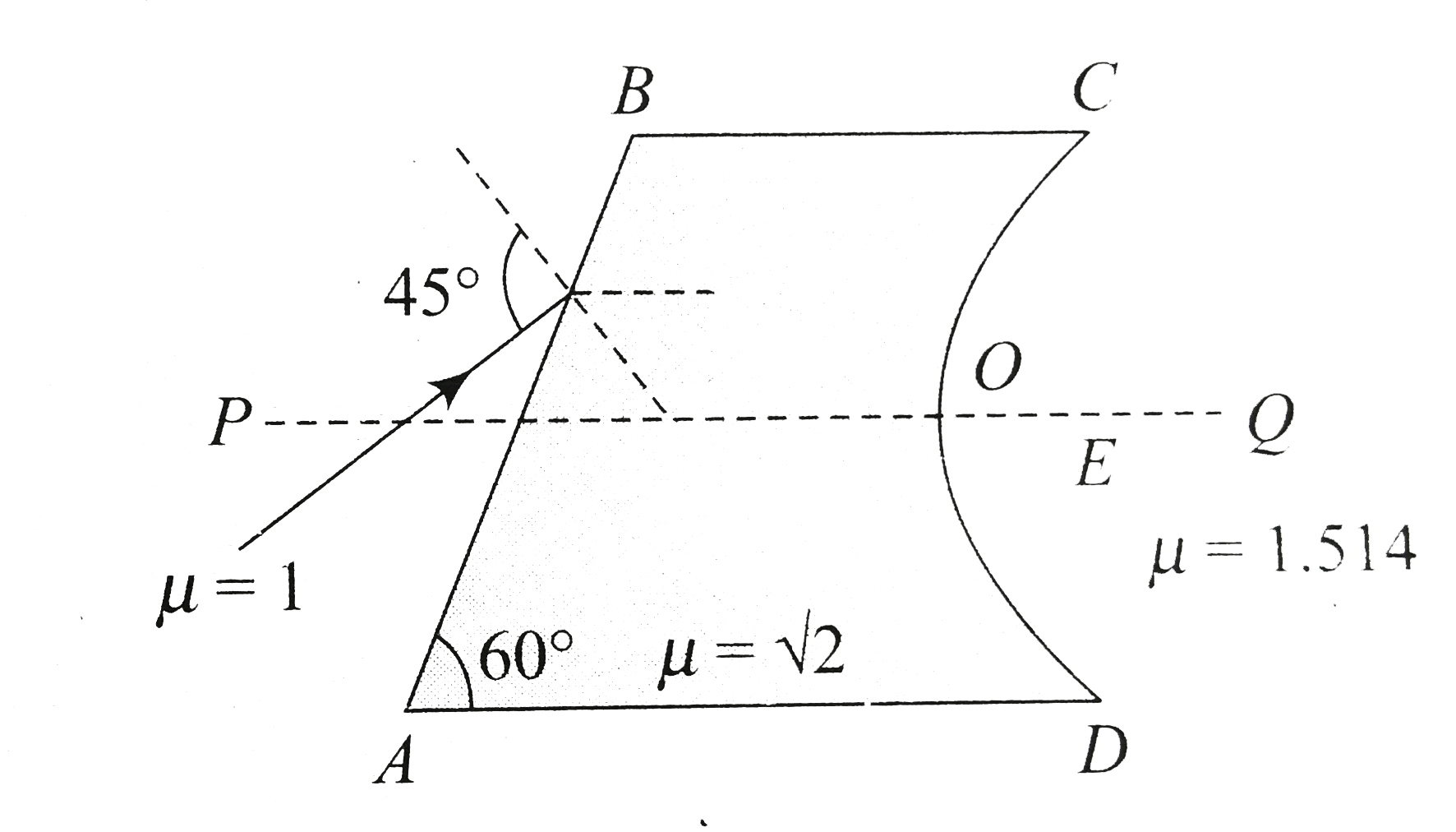
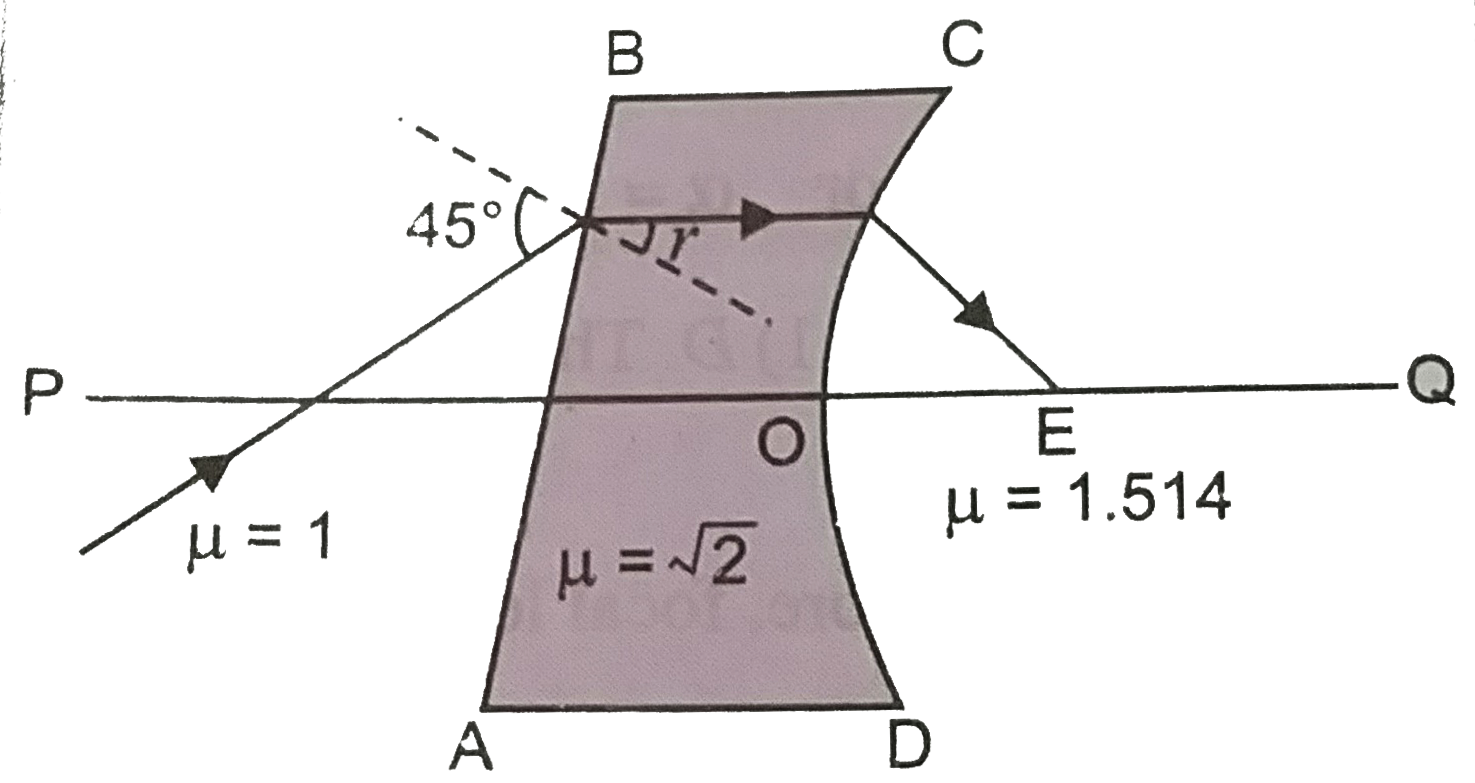 .
.