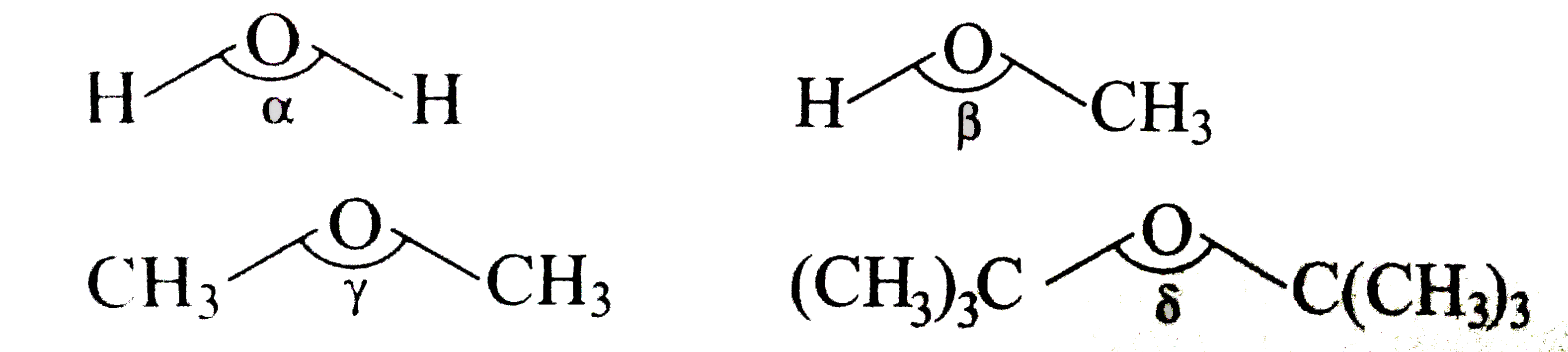A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
INTRODUCTION TO ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
OP TANDON|Exercise Passage-3|4 VideosINTRODUCTION TO ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
OP TANDON|Exercise Passage-4|5 VideosINTRODUCTION TO ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
OP TANDON|Exercise Passage-1|7 VideosCHEMISTRY IN EVERYDAY LIFE
OP TANDON|Exercise SINGLE INTEGER ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS|5 VideosMISCELLANEOUS (TOPICS OF GENERAL INTEREST)
OP TANDON|Exercise SET-VI: Problems on graphical aptitude|53 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
OP TANDON-INTRODUCTION TO ORGANIC CHEMISTRY -Passage-2
- Geometry of organic compound is often described in terms of the valenc...
Text Solution
|
- Geometry of organic compound is often described in terms of the valenc...
Text Solution
|
- Geometry of organic compound is often described in terms of the valenc...
Text Solution
|
- Geometry of organic compound is often described in terms of the valenc...
Text Solution
|
- Geometry of organic compound is often described in terms of the valenc...
Text Solution
|