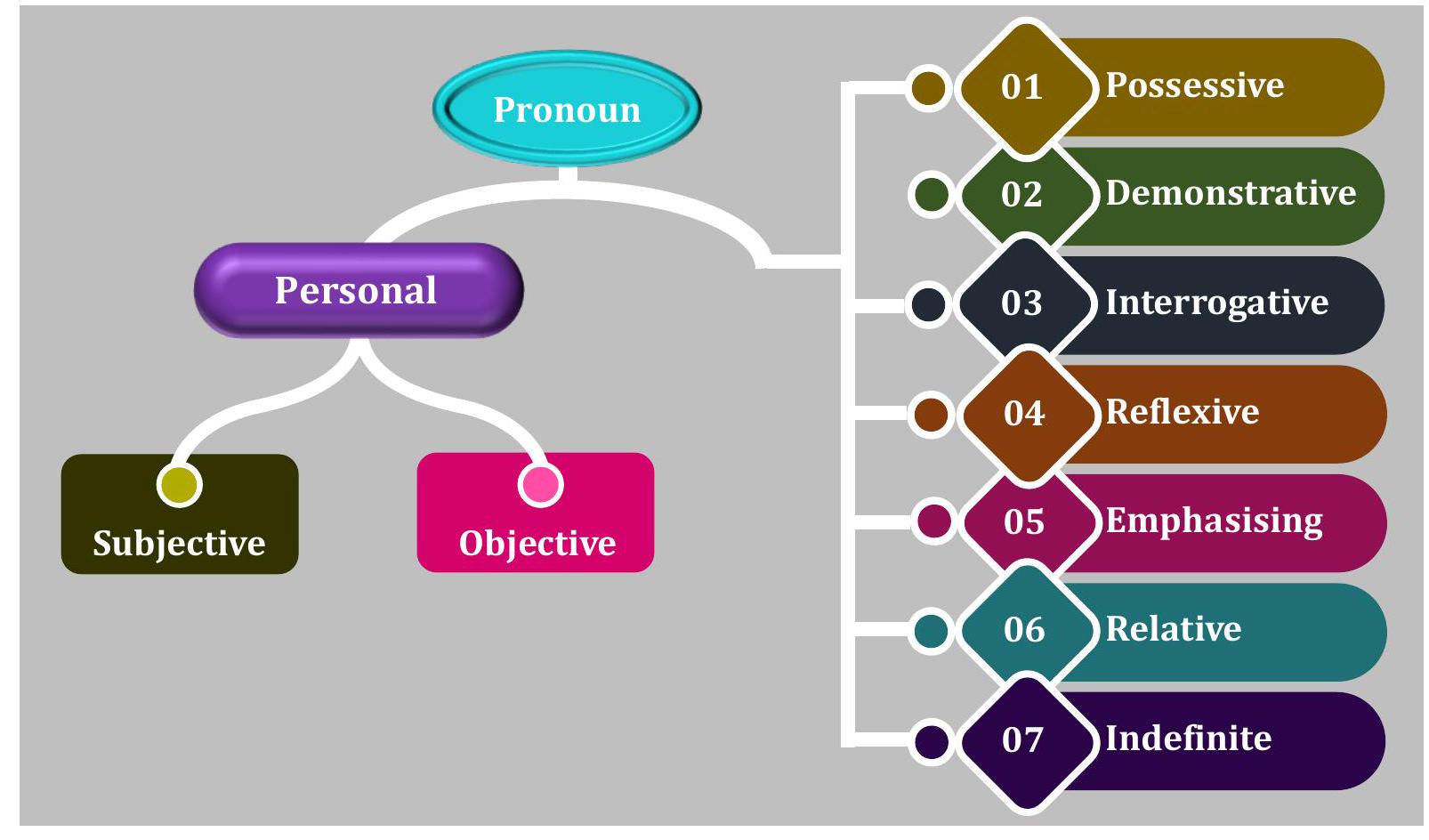
Pronouns
Definition
A pronoun is a word which is used in place of a noun. Examples: Ram and Ravi are best friends. They are best friends. Here, 'Ram' and 'Ravi' are replaced by 'They'. Types of Pronouns Pronouns are of different types.
1.0- Personal Pronouns
Personal pronouns stand for persons and things. The personal pronouns are called 'personal' as they stand for three persons- first person, second person and third person. The first person is the person speaking, the second person is the person spoken to and the third person is the person spoken about.
Forms of the personal pronouns
- The First Person
- I and we
- The Second Person
- you
- The Third Person
- he, she, it, and they
Personal Pronouns are of two types.
- Subjective - Pronouns that act as the subject of a sentence such as I, you, he, etc.
- Objective - Pronouns that act as the object of a verb or preposition in a sentence such as me, him, her, etc.
Quick Tips
- The personal pronoun 'it' is used to refer to an animal, a thing, or a child.
Example: The child is crying. It must be hungry.
- We use 'it' as a dummy subject also.
Examples: It is a fine day. It is easy to advise others.
Position of Personal Pronouns
Pronouns such as I, we, you, he, she, it and they are used at the place of a subject in a sentence. Pronouns such as me, us, you, him, her, it and them are used at the place of an object in a sentence. Examples: She will certainly help me. I am really thankful to her. They scolded him.
The use of objective form of Pronouns
- We use the objective form of pronouns after prepositions. a. Give this book to her. b. Should we buy sweets for them? c. There had been a quarrel between him and me. d. Take the money from them.
- We use the objective form of pronouns after the verb 'let'. a. Let him continue the study. b. Let me know the results. c. Let us finish the work. d. Let them decide the case.
2.0- Interrogative Pronouns
Interrogative pronouns are used to ask questions. who, whose, whom, which and what are interrogative pronouns. Examples: What was that noise? Who will be introducing the speaker? With whom are you conversing? Which is your house?
Interrogative Pronouns and Interrogative Adjectives
Look at these two sentences: (1) Which is your house? (2) Which house is yours?
In sentence (1), 'which' has been used as an interrogative pronoun. In sentence (2), since 'which' qualifies the noun 'house', so it has been used as an 'interrogative adjective'. Now look at these two sentences: (1) What do you think? (2) What plan have you made?
In sentence (1), 'what' is an interrogative pronoun. In sentence (2), 'what' is an 'interrogative adjective'.
3.0- Demonstrative Pronouns
Demonstrative Pronouns are used to point out the object or objects they refer to. Examples: This is a big river. These are pretty dresses imported from Japan. That is a terrific idea. Those are the best ones. Demonstrative pronouns such as 'this' and 'that' sometimes refer to what is said in a whole sentence or clause. Examples: A. I had to do my English homework, but this went out of my mind. 'This' refers to 'I had to do my English homework.' B. I went to see the movie, but 'that' was not possible.
Demonstrative Pronoun and Demonstrative Adjective This, that, these and those can act as both demonstrative pronouns and demonstrative adjectives.
Demonstrative Pronouns This That These Those Examples:
- This is very yummy!
- I would like to have those.
- That is not mine.
Look at these two sentences: (1) This is a book. (2) This book is a novel.
In sentence (1), 'this' stands for the noun 'book'; so 'this' is a demonstrative pronoun. In sentence (2), this qualifies the noun 'book'; so this is a demonstrative adjective. Now look at these two sentences: (1) These are geese. (2) These geese are yours.
In sentence (1), 'these' is a 'demonstrative pronoun'. In sentence (2), 'these' is a 'demonstrative adjective'.
Do You Remember ?
- Like demonstrative pronouns, interrogative pronouns can also act both as interrogative adjectives and interrogative pronouns.
- When these words qualify nouns they act as interrogative adjectives.
- When they stand for the persons or things about which the questions are asked, they act as interrogative pronouns. Examples: Which is your favorite colour? (Interrogative pronoun) Examples: Which colour is your favorite? (Interrogative adjective)
4.0- Possessive Pronouns
Possessive pronouns are used to show possession.
That suit is 'yours'. This coat is 'mine'.
Possessive Pronouns mine yours his hers its ours theirs
Possessive Adjectives my your his her its our their
Examples:
- This car is 'mine'.
- This is 'my' car.
- These gloves are 'hers'.
- These are 'her' gloves.
5.0- Reflexive Pronouns
Pronouns like myself, himself, yourself when used as the receiver of an action are called 'reflexive pronouns'.
- She blamed herself for the failure.
- Shashwat hurt himself.
Words such as itself, myself, yourself and ourselves are the objects of the verb in the sentence. But they refer to the same person as the subject does. The 'self' forms of personal pronouns are called reflexive pronouns. A reflexive pronoun cannot be used as the subject of a sentence. We cannot say Myself want to join the army. A reflexive pronoun can only be used as the object of a verb.
6.0- Emphasising Pronouns
Emphasising pronouns are used with a noun and pronoun to convey emphasis. (i) They themselves damaged their car. (ii) She herself hurt her pet.
Remember
- Indefinite Pronouns do not name the words they replace. They refer to persons or things in a general way. They do not refer to any particular person or thing. They are, therefore, called 'Indefinite Pronouns.' everyone other everything anybody none nothing somebody something no one
- Relative Pronouns
The pronouns who, whom, whose, which and that, which join two sentences and refer back to nouns going before them are called 'relative pronouns'. The Noun to which a Relative Pronoun refers or relates is called its antecedent.
Examples: (i) This is the horse. It won the race. This is the horse which won the race.
(ii) I have found the pen. It was lost. I have found the pen which was lost.
(iii) Here is the book. You lent me the book. Here is the book that you lent me.
Uses of Relative Pronouns
- As a general rule, who is used for persons only. It may refer to singular or plural nouns: (i) People who work hard always succeed.
- Whose is used in speaking of persons, animals and also things in possessive case: (i) Where is the cat whose kittens disappeared? (ii) This is the man whose son is an IAS officer.
- Whom is used for objective case: (i) This is the boy whom everybody loves. (ii) She is the girl whom everybody avoids.
- Which is used for things, animals: (i) The time which is lost is lost forever. (ii) The dog which bit her, has died.
- That is used for persons and things: (i) Uneasy lies the head that wears the crown. (ii) I have lost the book that you gifted me.
- What is used for things or ideas: (i) What cannot be cured must be endured. (ii) She has found what she was seeking.
7.0Let's Recall
- Pronouns are closely associated with nouns, replacing them wherever required and agreeing with them in number and gender.
- The position of a pronoun is the same as that of a noun in a sentence. Like a noun, a pronoun also plays the role of a subject, direct object and indirect object in a sentence.
- Personal pronouns are used in place of a person or a thing.
- Pronouns such as, who, which, whose and whom that introduce questions, are called interrogative pronouns.
- Demonstrative pronouns are used to point out the object or objects they refer to.
- Mine, ours, yours, his, hers and theirs are 'Possessive pronouns.' They do not come before nouns.
- Reflexive Pronouns are words that refer back to the person or animal that is the subject in a sentence.
- A reflexive pronoun can only be used as the object of a verb.
- Emphasising pronouns are used to convey emphasis.
- Indefinite pronouns refer to persons or things in a general way. They do not refer to any particular person or thing.
- Relative pronouns are used to join two sentences and refer back to the nouns before them.
Related Articles:-
Join ALLEN!
(Session 2026 - 27)