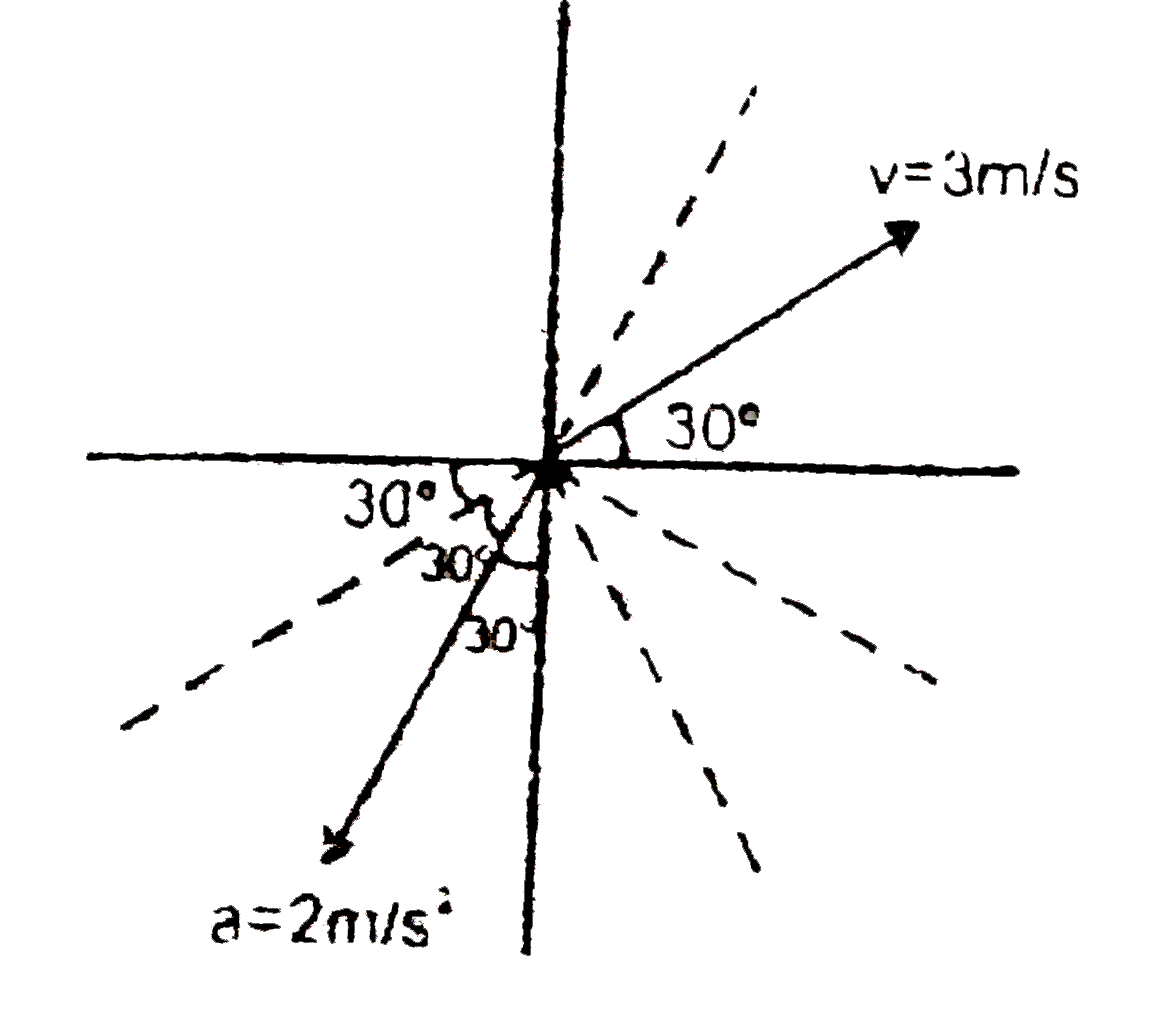
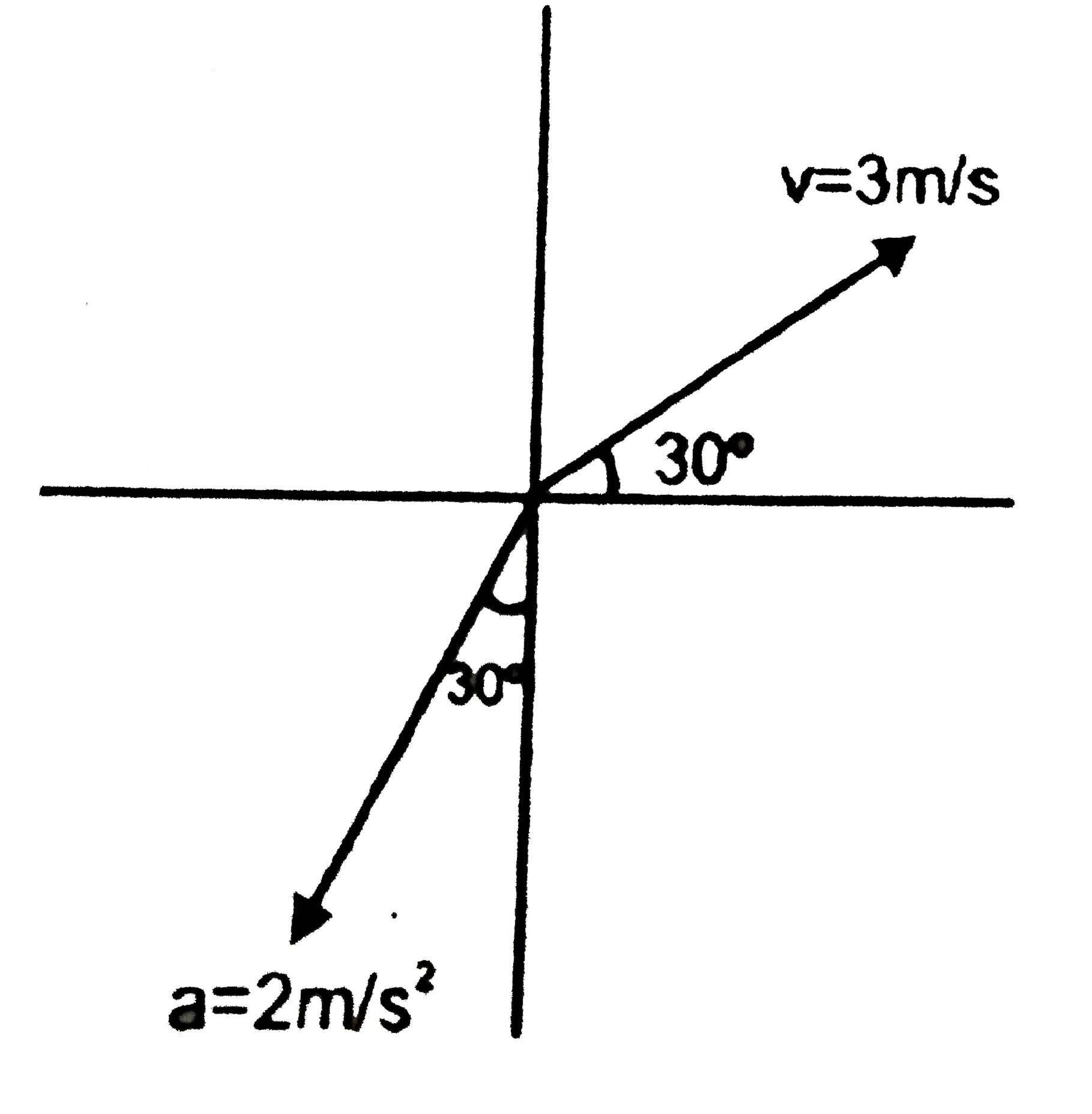A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEM
RESONANCE|Exercise DPP No.35|20 VideosDAILY PRACTICE PROBLEM
RESONANCE|Exercise DPP No.36|20 VideosDAILY PRACTICE PROBLEM
RESONANCE|Exercise DPP No.33|20 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
RESONANCE|Exercise High Level Problems (HIP)|21 VideosELECTRO MAGNETIC WAVES
RESONANCE|Exercise Exercise 3|27 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-DAILY PRACTICE PROBLEM-DPP No.34
- Initial velocity and acceleration of a particles are as shown in the ...
Text Solution
|
- In the arrangement shown, W(1) = 200N, W(2) = 100 N,mu = 0.25 for all ...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 2 kg is hanging over a smooth and light pulley through...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of masses 5 kg and 3 kg are placed in contact over an incli...
Text Solution
|
- In figure , L is half part of an equiconvex glass lens (mu=1.5) whose ...
Text Solution
|
- A wooden cube (density 0.5 gm/c c) of side 10 cm floating in water kep...
Text Solution
|
- Water is filled to height h in a fixed vertical cylinder placed on hor...
Text Solution
|
- Water is filled to height h in a fixed vertical cylinder placed on hor...
Text Solution
|
- Water is filled to height h in a fixed vertical cylinder placed on hor...
Text Solution
|