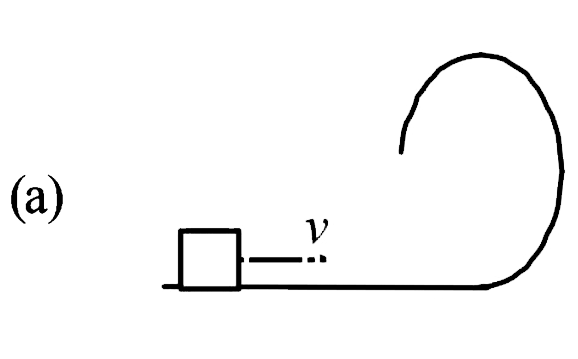
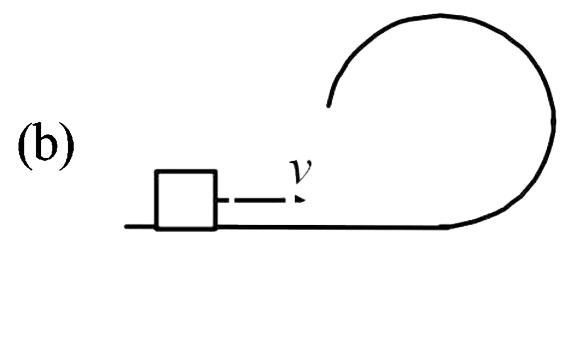
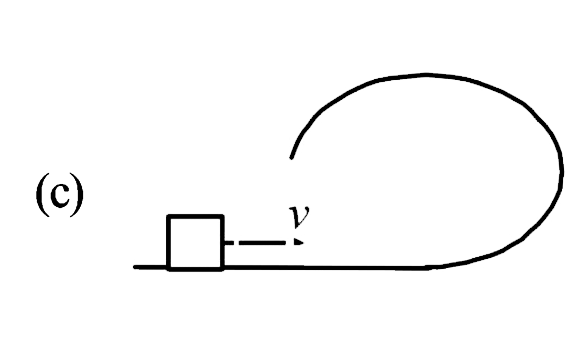
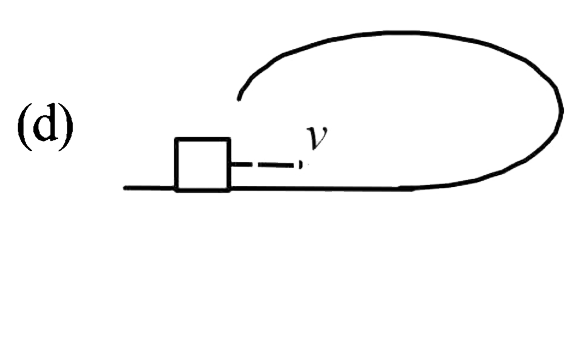
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
SUNIL BATRA (41 YEARS IITJEE PHYSICS)-LAWS OF MOTION-JEE Main And Advanced
- A block of mass 2kg rests on a rough inclined plane making an angle of...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 0.1 is held against a wall applying a horizontal force...
Text Solution
|
- A small block is shot into each of the four tracks as shown below. Eac...
Text Solution
|
- An insect craws up a hemispherical surface very slowly (see fig.). The...
Text Solution
|
- The pulleys and strings shown in the figure are smooth and of negligib...
Text Solution
|
- A string of negligible mass going over a clamped pulley of mass m supp...
Text Solution
|
- What is the maximum value of the force F such that the block shown in ...
Text Solution
|
- A block P of mass m is placed on horizontal frictionless plane. A seco...
Text Solution
|
- The string between blocks of mass m and 2m is massless and inextensibl...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles of mass m each are tied at the ends of a light string of...
Text Solution
|
- A particle moves in the X-Y plane under the influence of a force such ...
Text Solution
|
- A block of base 10 cm xx 10 cm and height 15 cm is kept on an inclined...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is on an inclined plane of angle theta. The coeffici...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass (m) 0.5g is attached to the end of a string having leng...
Text Solution
|
- The image of an object, formed by a plano-convex lens at a distance of...
Text Solution
|
- In the arrangement shown in the Fig, the ends P and Q of an unstretcha...
Text Solution
|
- A reference frame attached to the earth
Text Solution
|
- A simple pendulum of length L and mass (bob) M is oscillating in a pla...
Text Solution
|
- A particle P is sliding down a frictionless hemispherical bowl. It pas...
Text Solution
|
- A small block of mass of 0.1 kg lies on a fixed inclined plane PQ whic...
Text Solution
|