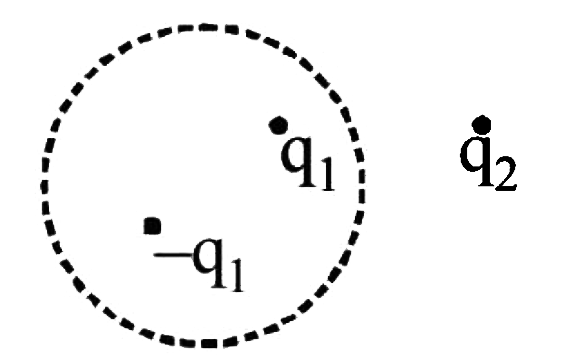
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTROSTATICS
SUNIL BATRA (41 YEARS IITJEE PHYSICS)|Exercise Subjective Problems|2 VideosELECTROSTATICS
SUNIL BATRA (41 YEARS IITJEE PHYSICS)|Exercise Comprehension Based Questions|2 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION AND ALTERNATING CURRENT
SUNIL BATRA (41 YEARS IITJEE PHYSICS)|Exercise JEE Main And Advanced|107 VideosMODERN PHYSICS
SUNIL BATRA (41 YEARS IITJEE PHYSICS)|Exercise MCQ (One Correct Answer|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems