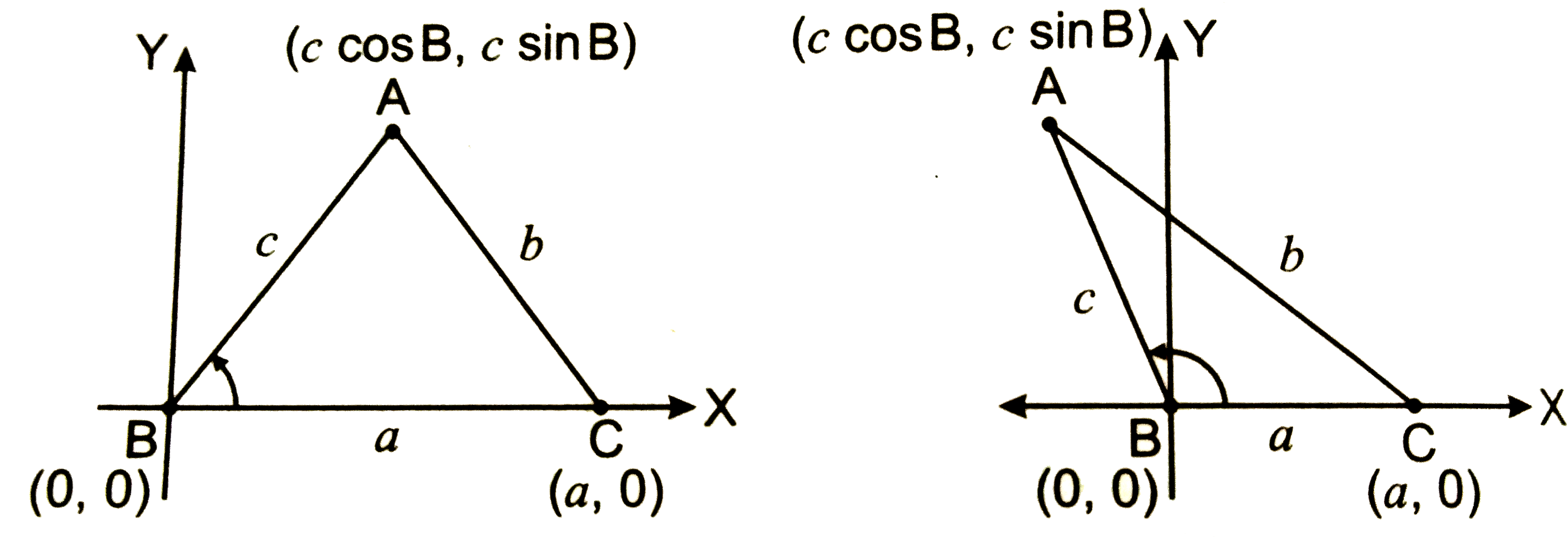Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
GURUKUL PUBLICATION - MAHARASHTRA PREVIOUS YEAR PAPERS- MARCH 2019-SECTION-D
- Find the symbolic form of the given switching circuit . Construct i...
Text Solution
|
- If three numbers are added , their sum is 2 . If two times the seco...
Text Solution
|
- In Delta ABC , with usual notations prove that : b^(2) = c^(2)...
Text Solution
|
- In Delta ABC, prove that (a - b)^(2) cos^(2).(C)/(2) + (a + b)^(2) sin...
Text Solution
|
- Find P and k if the equation px^(2)-8xy+3y^(2)+14x+2y+k=0 repres...
Text Solution
|
- {:("Maximize" ,z = 3x + 5y , "subject to "),( ,x + 4y le 24 , 3x + y...
Text Solution
|
- If x=f(t), y=g(t) are differentiable functions of parameter 't' then p...
Text Solution
|
- f(x) = (x - 1) (x - 2) (x - 3) , x in [ 0, 4 ] " find "'c' if LMVT...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of 108 meters long is bent to from a rectangle . Find its dime...
Text Solution
|
- int 1/ sqrt (a^2 + x^2) dx = log ( x + sqrt(x^2 + a^2) + c
Text Solution
|
- Evaluate int0^(pi/4) log(1+tanx)dx
Text Solution
|
- The integrating factor of linear differential equation (dy)/(dx) + y s...
Text Solution
|
- Solve the differential equation : (x + y) (dy)/(dx) = 1 .
Text Solution
|