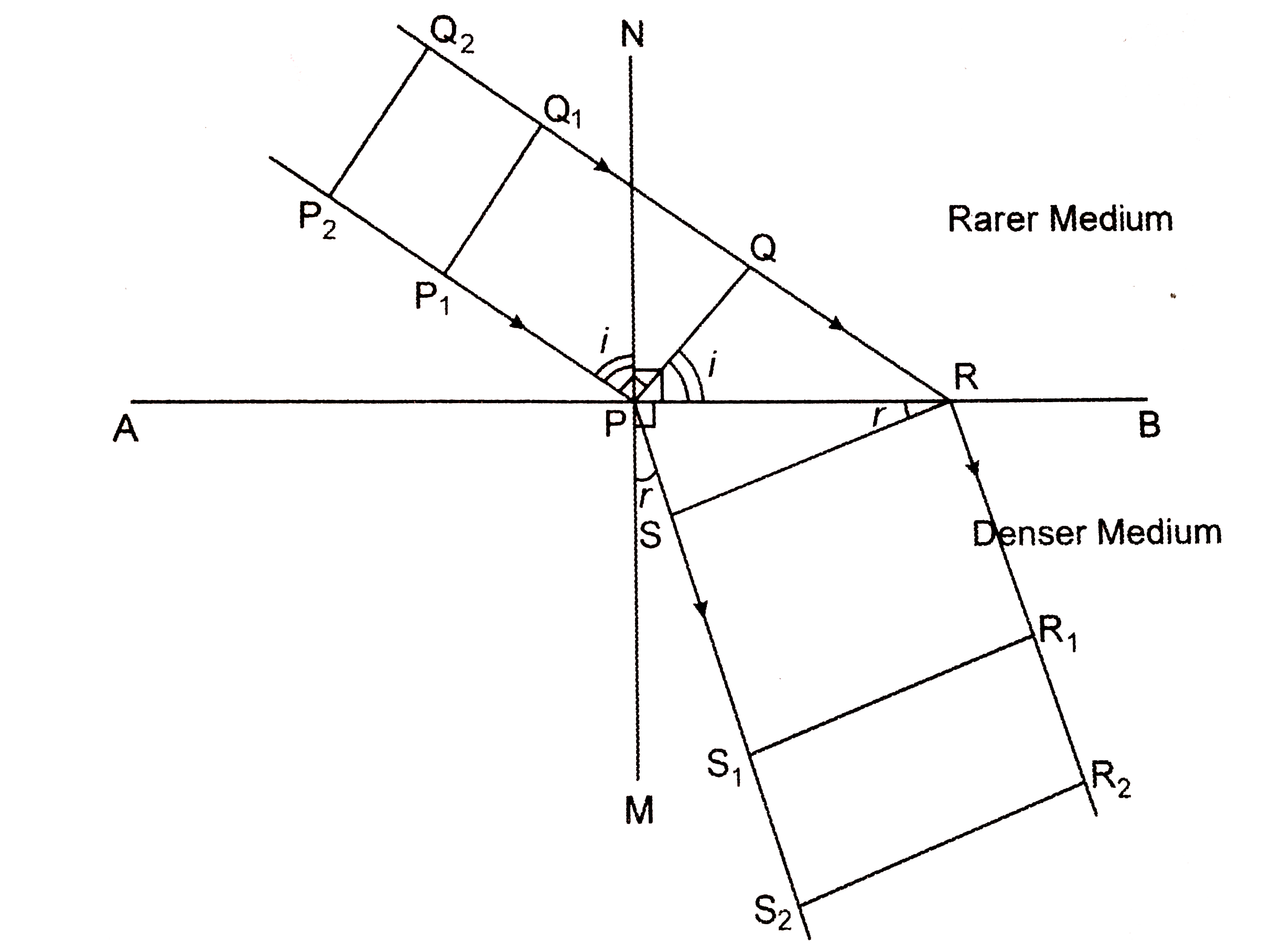
Consider a polane wavefront of monochromatic light obliquely incident at a plane refracting surface AB sperating two me mediums. Let `P_(2)Q_(2),P_(1)Q_(1) and PQ` be the successive positions of the incident wavefront. As soon as the wavefront reaches the point P, accroding to Huyge's principle's, it becomes th secondary source and emites secondary waves in the denser medium.
Let `v_(1) and v_(2)` be the speed of light in rarer medium and the denser medium respectively. If t is the time taken by the incident ray to coer the distance QR, then Qr `v_(1)t`. During this time the secondary wave originating from P will cover a distance `v_(2)t` in the denser medium. Hence. the secondary spherical wavefront has a radiys `v_(2)t`.
With P as centre, draw, a hemisphere or radius `v_(2)t` in the denser mediy. Draw a tangent Rs to the secondary wavefron. RS represents a refracted wavefront.
`R_(1)S_(1) and R_(2)S_(2)` are the successive positions of the refracted wavefronts . Draw NPM normal to AB at point P.
Now, `angleP_(2)PN`=i= angle of incidence
`angle MPS_(2)` =r= angle of refraction
From teh figure,
`angleP_(2)PN+angle NPQ=90^(@)`
`angleNPQ+angle QPR= 90^(@)`
`:. angleP_(2)PN=angle QPR=i`
Alos, `angle MPS_(2)+angleS_(2)RP= 90^(@)`
`angle S_(2)PR+angle PRS=90^(@)`
`:. MPS_(2)= angle PRS=r`
From `Delta PQR = sin i= (QR)/(PR)`
From `Delta RSP, sind r=(PS)/(PR)`
`:. (sin i)/(sin r) =(QR//PR)/(PS//PR)=(QR)/(PS)`
`(sin i)/(sin r)=(v_(1)t)/(v_(2)t)`
`:. (sin i)/(sin r)=(v_(i))/(v_(2))`
But by definition,
`""_(1)mu_(2)=("Speed of light in medium1")/("speed of light in medium 2")`
`""_(1)mu_(2)=(v_(1))/(v_(2))`= constant
`(sin i)/(sin r)= ""_(1)mu_(2)`
This is Snell's law of refraction.
Also, it can be seen from the figure that the incident ray and the normal and all three of them lie in the sample plane.
Thus, the laws of refractioin of light can be explained on the basis of Huyge's wave theory.
Numerical
Given `(I_(1))/(I_(2))=(81)/(1)`
`I prop a^(2)`
`:. (I_(1))/(I_(2))=(a_(1)^(2))/(a_(2)^(2))=(81)/(1)`
`(a_(1))/(a_(2))=(9)/(1)`
`(I_("max"))/(I_("min"))=((a_(1)+a_(2))^(2))/((a_(1)-a_(2))^(2)`
`(I_("max"))/(I_("min))=((9+1)^(2))/((9-1)^(2))`
`(I_("max"))/(I_("min))=(100)/(64)=(25)/(16)`
`(I_("max"))/(I_("min))=(25)/(16)`
