Transformer is an electrical device which conversts low a.c. voltage at high current into high a.c. voltage at low current and vice varas. It works on the principle of mutual induction i.e., ''whenever the magnetic flux linked with a coil changes, an e.m.f. is induced in the neighbouring coil''
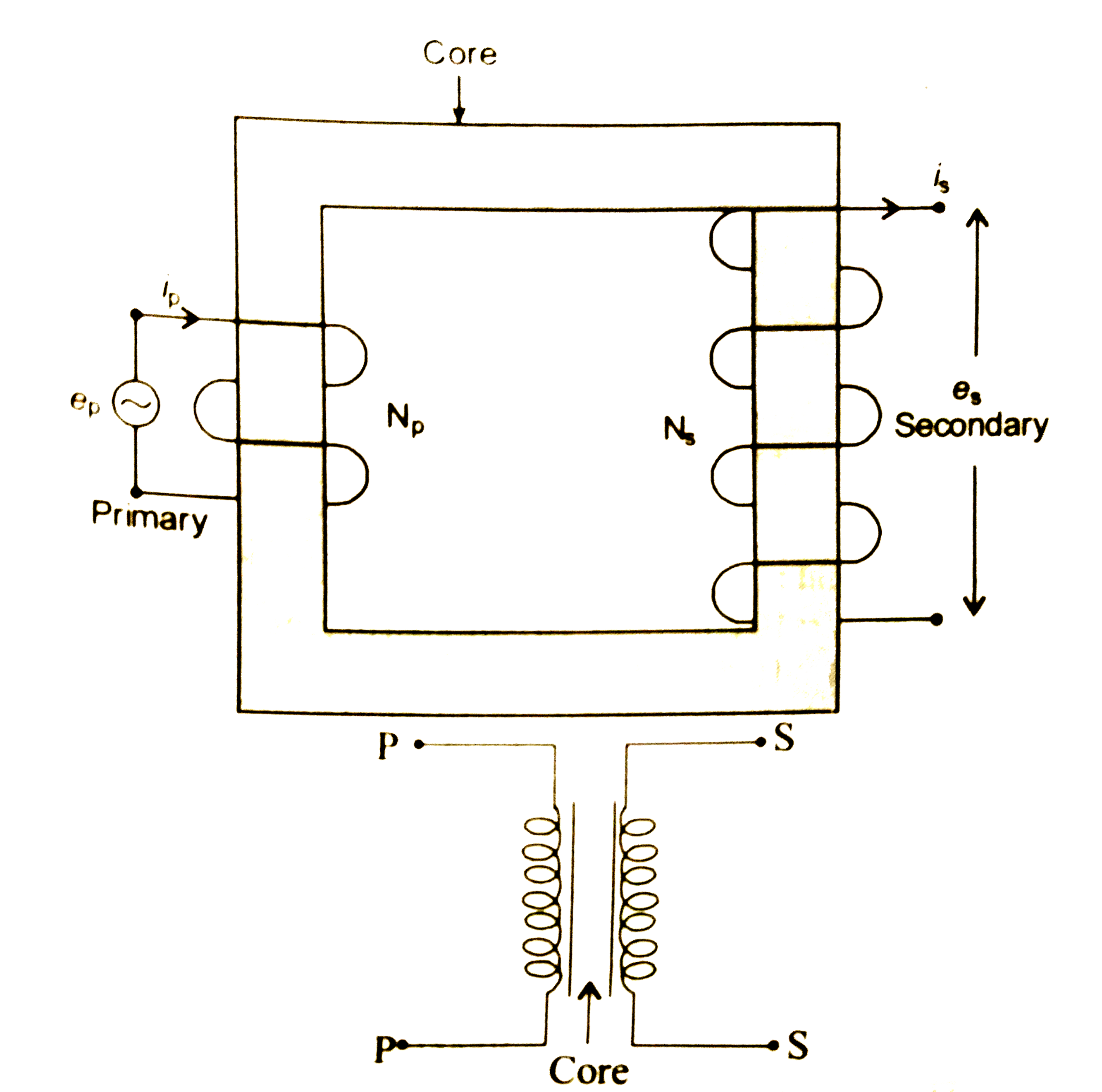
Construction of transformer : It consists of two coils, primary (P) and secondary (S) which are insulated from each other and wound on a soft iron core. The primary and secondary coils are called as input and output coil respectively.
Working of transformer : When an alternating voltage is applied to the input coil (primary coil), the current through the coil goes on changing. This also changes the magnetic flux through the core. As this changing magnetic flux is linked with both the coils, an emf, is induced in each coil. The amount of the magnetic flux linked with the coil depend upon the number of turns of the coil.
Expreisson for e.m.f. and current : Let `phi` be the maganetic flux linked per turn with both the coils at certain instant 't'. Also suppose `'N'_(p) and 'N'_(s)` as the number of turns of primary and secondary coil respectively.
Now, `N_(2)phi`= Magnetic flux linked with the primary coil at certain instant 't'. And
`N_(x)phi`= Magnetic flux linked with the secondary coil at certain instant 't'
Then, induced e.m.f. produced in both the coils is given by
`e_(p)=(-dphi_(p))/(dt)=-N_(p)(dphi)/(dt)" "......(i)`
`e_(s)=(-dphi_(s))/(dt)=-N_(s)(dphi)/(dt)" "......(ii)`
Dividing equation (ii) by equation (i) we get
`(e_(s))/(e_(p))=(N_(s))/(N_(p))`
which represents the equation of transformer ration.
For an ideal transformer,
Input power= Output power
i.e., `e_(p)i_(p)=e_(s)i_(s)`
`:.(e_(s))/(e_(p))=(i_(p))/(i_(s))" "......(iii)`
But `(e_(s))/(e_(p))=(N_(s))/(N_(p))`
`:.(N_(s))/(N_(p))=(i_(p))/(i_(s))" "......(iv)`
From equations (iii) and (iv)
`(e_(s))/(e_(p))=(N_(s))/(N_(p))=(i_(p))/(i_(s))`
Numerical :
Given `l=10cm=10xx10^(-2)` m, area of cross-section, `A=4cm^(2)=4xx10^(-4)m^(2),M_("net")=2Am^(2)`
`V=lxxA`
`=10xx10^(-2)xx4xx10^(-4)`
`=4xx10^(-5)m^(3)`
As we know,
Magnetization `(M_(z))=(M_("net"))/(V)=(2)/(4xx10^(-5))`
`=50000Am^(-1)`
Therefore, the magnetisation of a bar magnet is 50000A/m.
