Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
GURUKUL PUBLICATION - MAHARASHTRA PREVIOUS YEAR PAPERS- MARCH 2015-SECTION-II
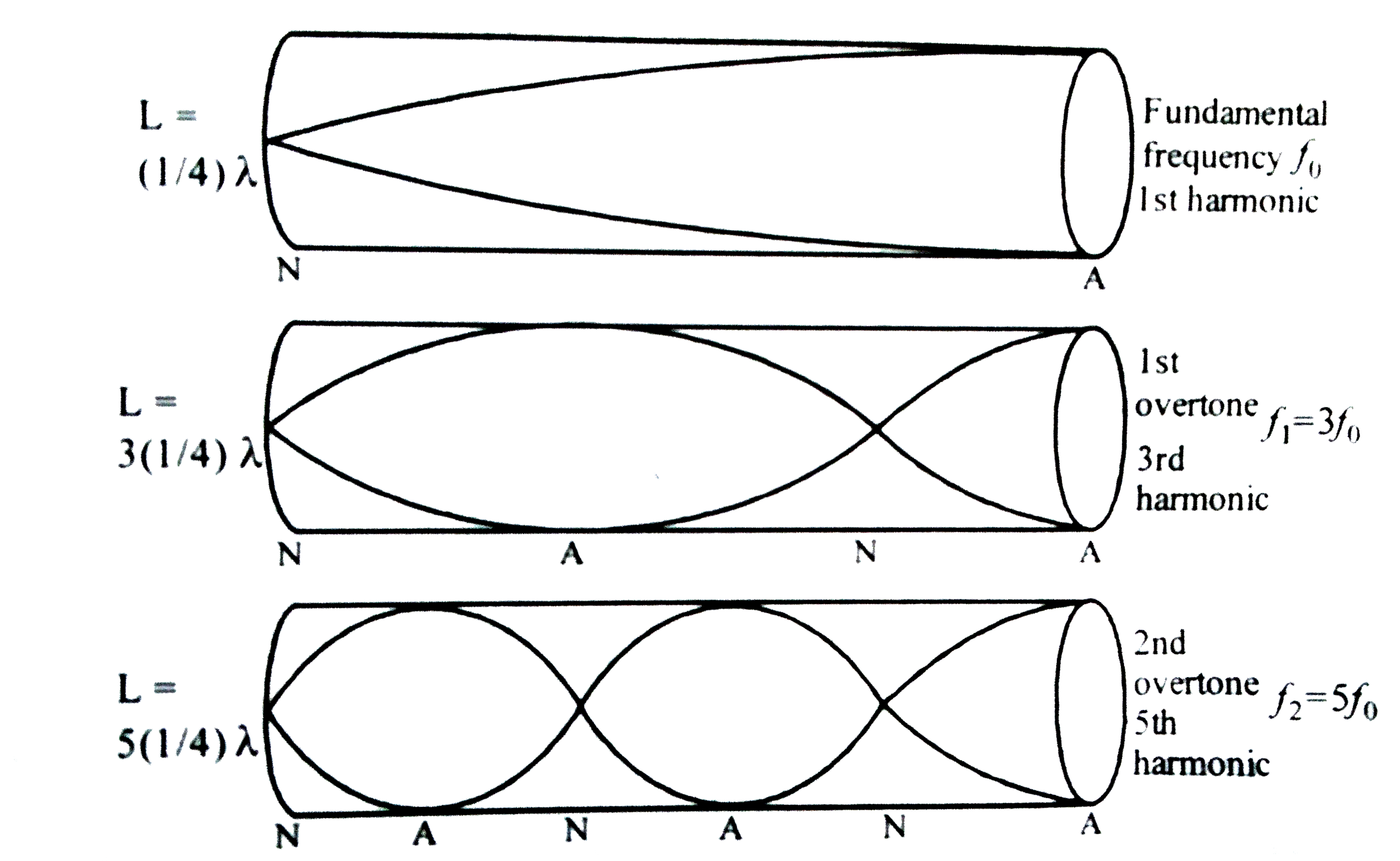
- What are forced vibrations and resonance ? Show that only odd harmonic...
Text Solution
|
- The electric field intensity in free space at a distance 'r' outside a...
Text Solution
|
- Instrument which can measure terminal potential difference as well as ...
Text Solution
|
- The frequency of incident light falling on a photosensitive metal plat...
Text Solution
|
- Linear momentum of an electron in Bohr obrit of H-atom (principal quan...
Text Solution
|
- In a semiconductor , acceptor impurity is
Text Solution
|
- The power radiated by linear antenna of length 'l' is proportional to ...
Text Solution
|
- The numerical aperture of objective of a microscope is 1*12. The limit...
Text Solution
|
- What is a Polaroid ? State its two uses.
Text Solution
|
- Draw a neat and labelled diagram of suspended coid type moving coil g...
Text Solution
|
- Define : (a) Moganetization and (b) Magnetic intensity.
Text Solution
|
- Draw a block diagram of generalized communications system.
Text Solution
|
- A solenoid 3*142 m long and 5*0 cm in diameter has two layers of windi...
Text Solution
|
- A circular coil of 300 turns and average area 5xx10^(-3)m^(2) carries ...
Text Solution
|
- The magnetic flux thropugh a loop varies according to the relation phi...
Text Solution
|
- An electron is orbiting is 5th Bohr orbit. Calculate ionisation energy...
Text Solution
|
- Obtain an expression for the radius of Bohr orbit for H atom.
Text Solution
|
- Define alpha and beta parameters of a transistor. What is the relatio...
Text Solution
|
- Two metal spher4s having charge densities 5 muC//m^2 and -2muC//m^2 wi...
Text Solution
|
- The threshold wavelenght of silver is 3800 Å . Calculate the maximum k...
Text Solution
|
- Obtain an expression for e.m.f. induced in a coil rotating with unifor...
Text Solution
|