Text Solution
Verified by Experts
GURUKUL PUBLICATION - MAHARASHTRA PREVIOUS YEAR PAPERS- SEPTEMBER 2014-SECTION-2
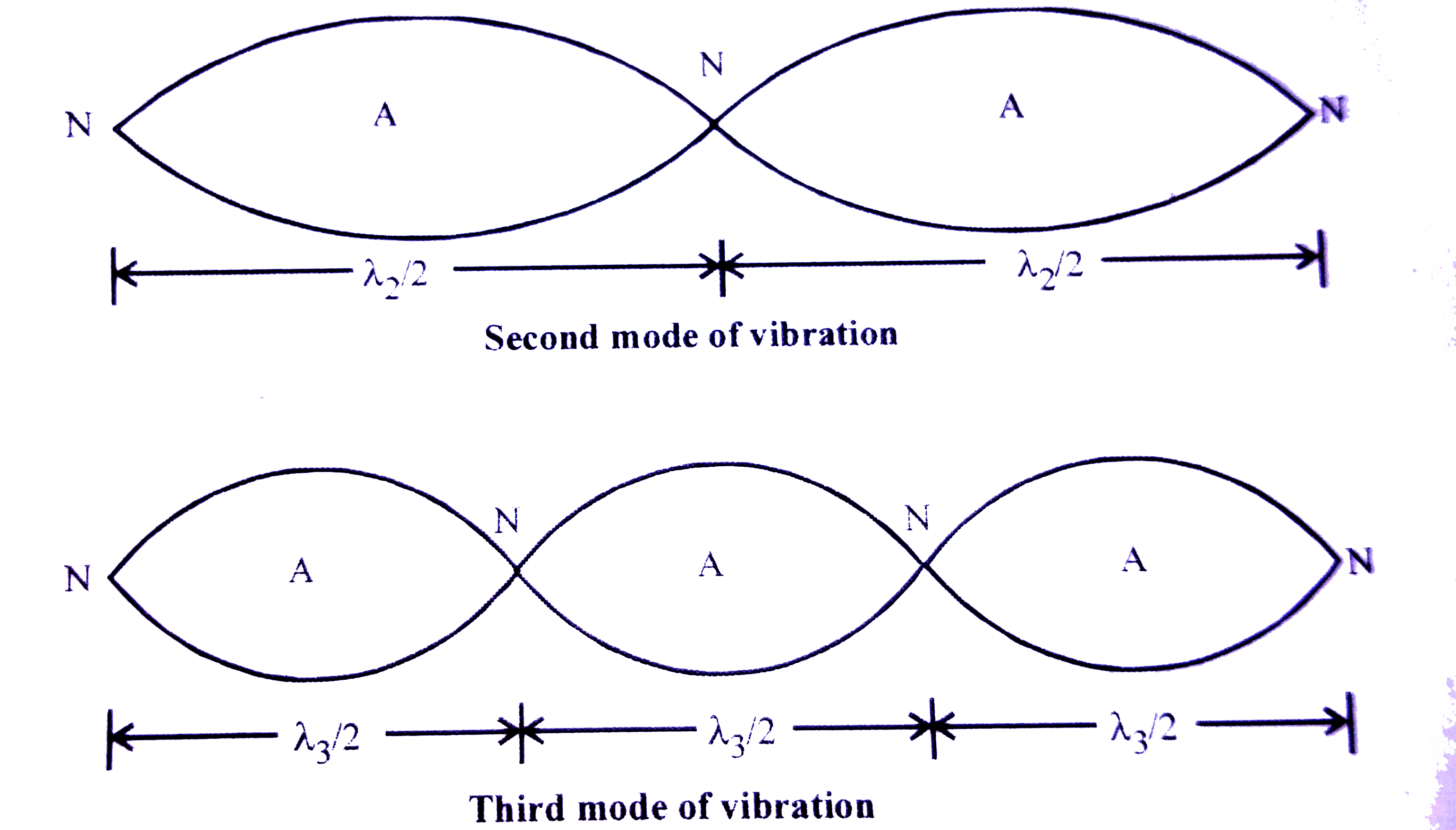
- Distinguish between forced vibrations and resonance. Draw neat, labell...
Text Solution
|
- In a biprism experiment, a slit is illuminated by a light of wavelengt...
Text Solution
|
- Six capacitors of capacities 5muF,5muF,5muF,5muF,10muF and X muF are c...
Text Solution
|
- Show that the current flowing through a moving coil galvanometer is di...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the formation of energy band diagram in case of conductor and ...
Text Solution
|
- Draw a neat labelled diagram showing the plane of vibration and plane ...
Text Solution
|
- State the conditions to get steady interference pattern.
Text Solution
|
- In a hydrogen atom, an electron carrying charge 'e' revolves in an orb...
Text Solution
|
- Sketch a block diagram of a generalised communication system.
Text Solution
|
- Red light of wavelength 6400 Å in air has a wavelength of 4000 Å in ...
Text Solution
|
- The magnetic moment of a magnet of dimensions 4 cm ** 2 cm ** 1.25...
Text Solution
|
- An A.C. circuit consists of inductor of inductance 125mH connected in ...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the de Broglie wavelength of an electron moving with 1//3rd ...
Text Solution
|
- If numerical aperture of a microscope is increased, then its
Text Solution
|
- A solenoid of 2.5 m length and 2.0 cm diameter possesses 10 turns per ...
Text Solution
|
- Kirchhoffs voltage law and current law are respectively in accordance ...
Text Solution
|
- When radiations of wavelength lamda(1) and lamda(2) are incident on ce...
Text Solution
|
- Colour of light emitted by LED depends upon
Text Solution
|
- Line of sight propagation is also called propagation
Text Solution
|
- Two parallel plates separated by distance d are kept at potential diff...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the phenomenon of self induction and mutual induction. Define ...
Text Solution
|