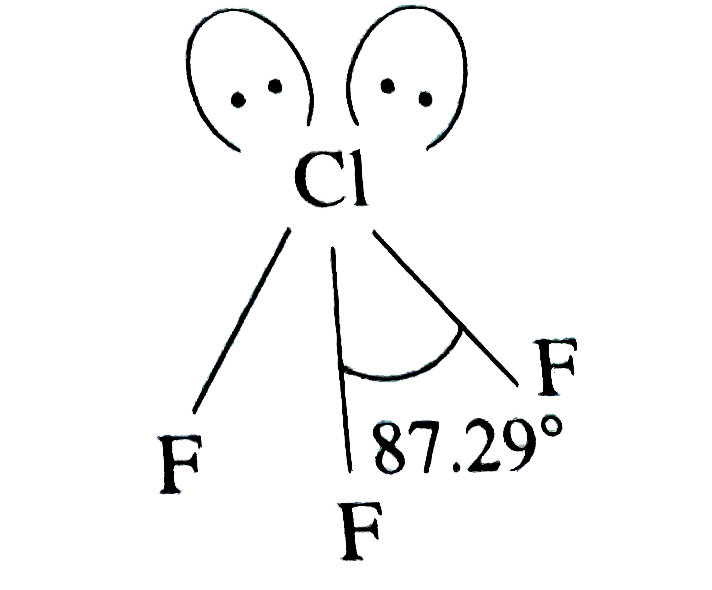Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
GURUKUL PUBLICATION - MAHARASHTRA PREVIOUS YEAR PAPERS- FEBRUARY 2016-SECTION-I
- Calculate C - Cl bond enthalpy from following reaction : CH(3) Cl(g)...
Text Solution
|
- Define cell constant. Draw a neat and well labelled diagram of primary...
Text Solution
|
- Write four points of difference between properties of nitrogen and oth...
Text Solution
|
- What are neutral oxides? Explain the nature of zinc oxide with the hel...
Text Solution
|
- The molecular formula of H(2)S(2)O(2) represents which oxoacid among t...
Text Solution
|
- Iodine exists of……..
Text Solution
|
- Absolute entropies of solids, liquid and gases can be determined by ……...
Text Solution
|
- The determination of molar mass from elevation in boiling point is cal...
Text Solution
|
- The Process of leaching, alumina using the sodium carbonate is called…...
Text Solution
|
- On calculating the strength of current in amperes if a charge of 840 C...
Text Solution
|
- A to B is a first order reaction with rate 6.6 xx 10^(-5) m-s^(-1). Wh...
Text Solution
|
- Sc^(3+) is colourless is aqueous solution whereas Ti^(3+) is coloured.
Text Solution
|
- Double Salt and Coordination Compound
Text Solution
|
- How is chlorobenzene prepared from aniline? How is chlorobenzene conve...
Text Solution
|
- What is metamerism? Explain metamerism with suitable examples of ether...
Text Solution
|
- What are ketones? How are ketones classified?
Text Solution
|
- How are (a) I-nitropropane and (b) 2-nitropropane prepared from suitab...
Text Solution
|
- Define antioxidants. Draw structure of BHT
Text Solution
|
- What are carbohydrates? Write the reaction for the preparation of Nylo...
Text Solution
|
- What are f-block elements? Distinguish between lanthanoid and actinoid...
Text Solution
|