Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY-VECTORS-Medical enrances gallery
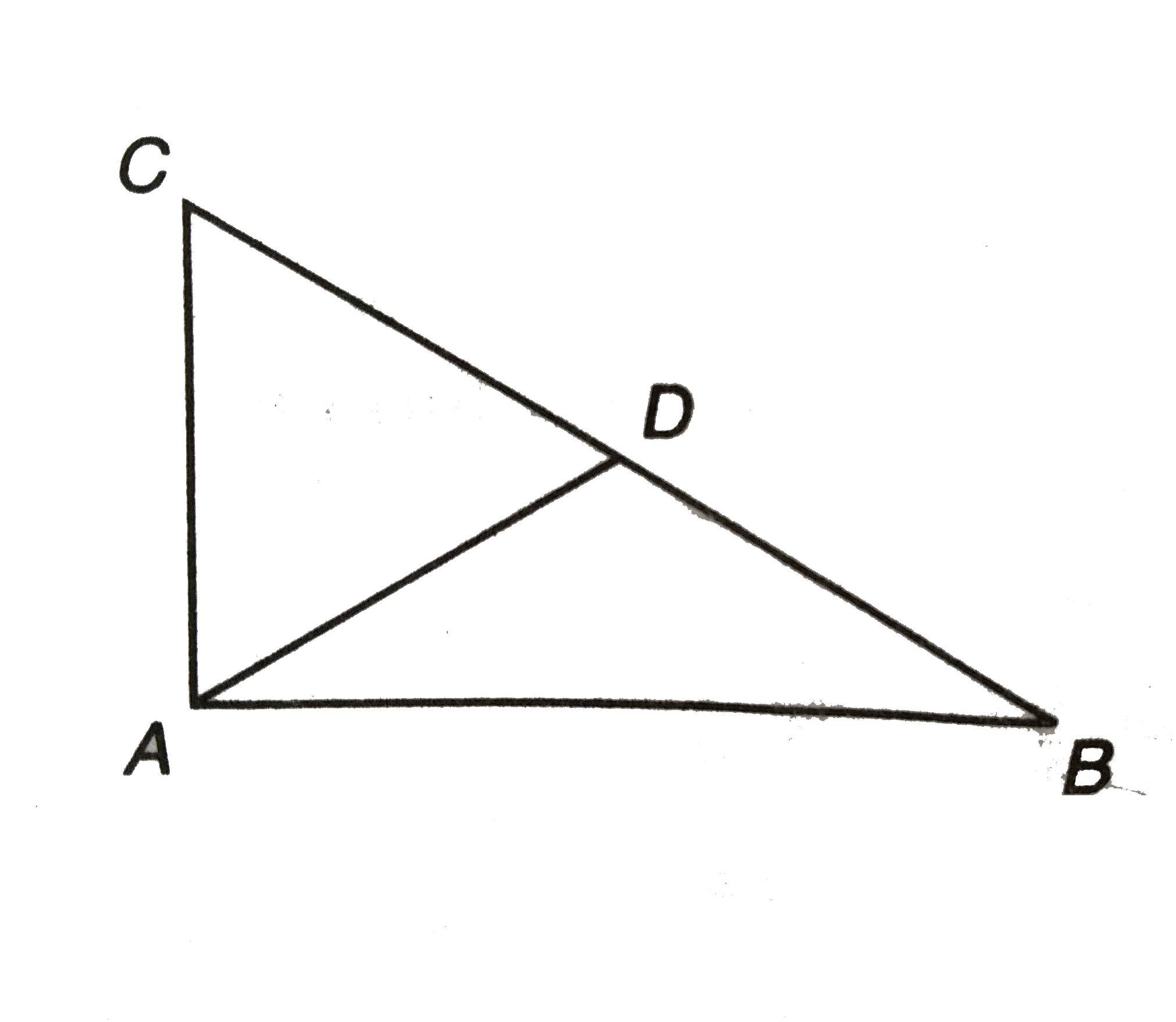
- Prove that the mid-point of the hypotenuse of right angled triangle i...
Text Solution
|
- If the magnitude of sum of two vectors is equal to the magnitude of di...
Text Solution
|
- If a vector 2hati +3hatj +8hatk is perpendicular to the vector 4hati -...
Text Solution
|
- The angle theta between the vector p=hati+hatj +hatk and unit vector a...
Text Solution
|
- Consider three vectors A=hati +hatj-2hatk, B=hati +hatj+2hatk and 2h...
Text Solution
|
- Two equal vector have a resultant equal to either of them, then the an...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is not a cloning vector ?
Text Solution
|
- The scalar product of two vectors A=2hati +2hatj -hatk and B=-hatj +ha...
Text Solution
|
- If A.B=AxxB, then angle between A and B is
Text Solution
|
- A vector vec(B) which has a magnitude 8.0 is added to a vector vec(A) ...
Text Solution
|