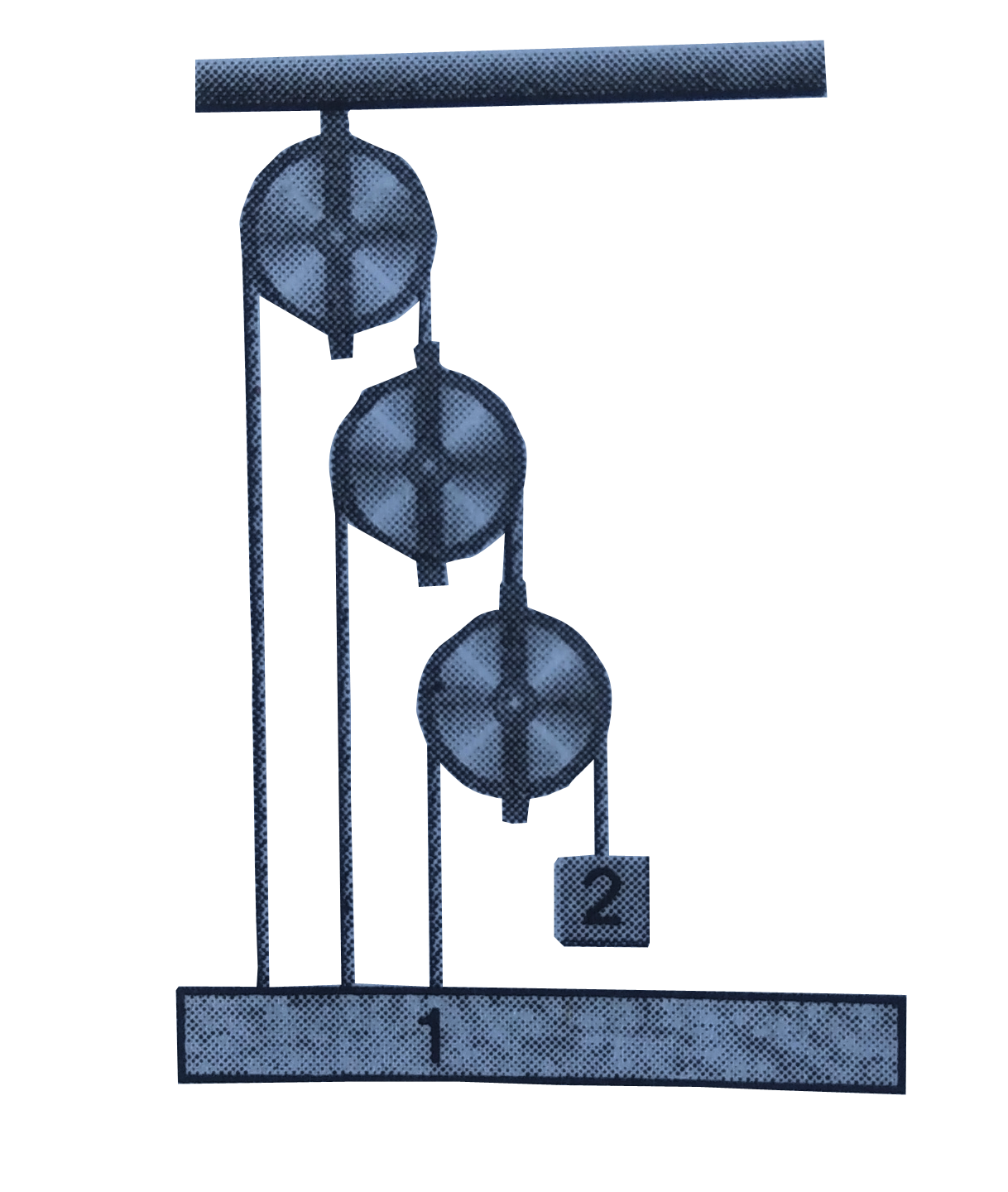
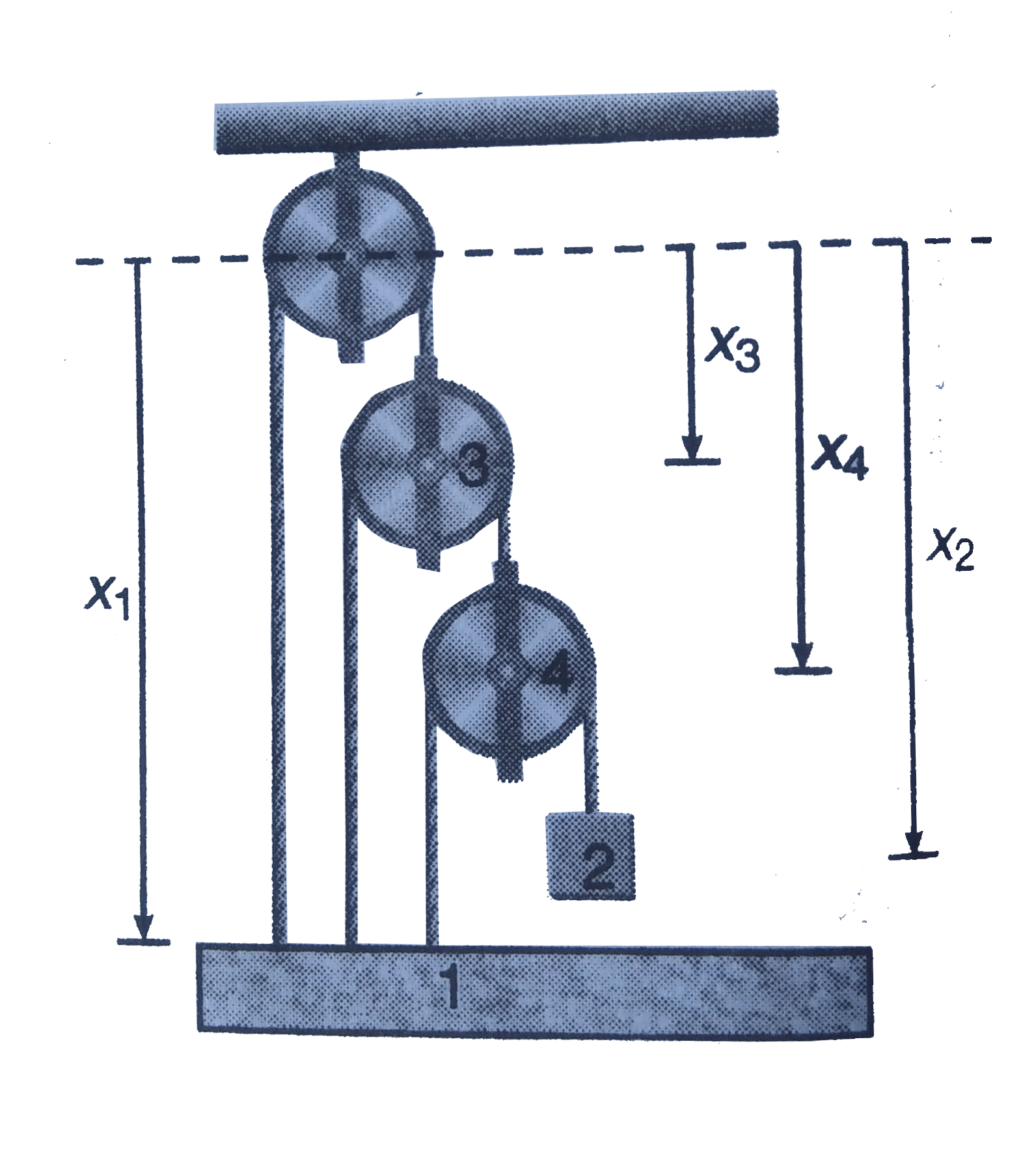
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Using constraint method find the relation between of a(1) and a (2).
Text Solution
|
- Using constraint method find the relation between accelerations of 1 a...
Text Solution
|
- Using constraint method find the relation between of a(1) and a (2).
Text Solution
|
- Make the constraint relation between a(1),a(2) and a(3)
Text Solution
|
- Find the relation between a(1) and a(2) .
Text Solution
|
- Find the relation between acceleration of blocks a(1), a(2) and a(3).
Text Solution
|
- Using contraint equation. Find the relation between a(1) and a(2).
Text Solution
|
- Find the relation between acceleration a(1) and a(2)
Text Solution
|
- In given system a(1) and a(2) are the accelerations of blocks 1 and 2....
Text Solution
|