Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY-LAWS OF MOTION-Miscellaneous Examples
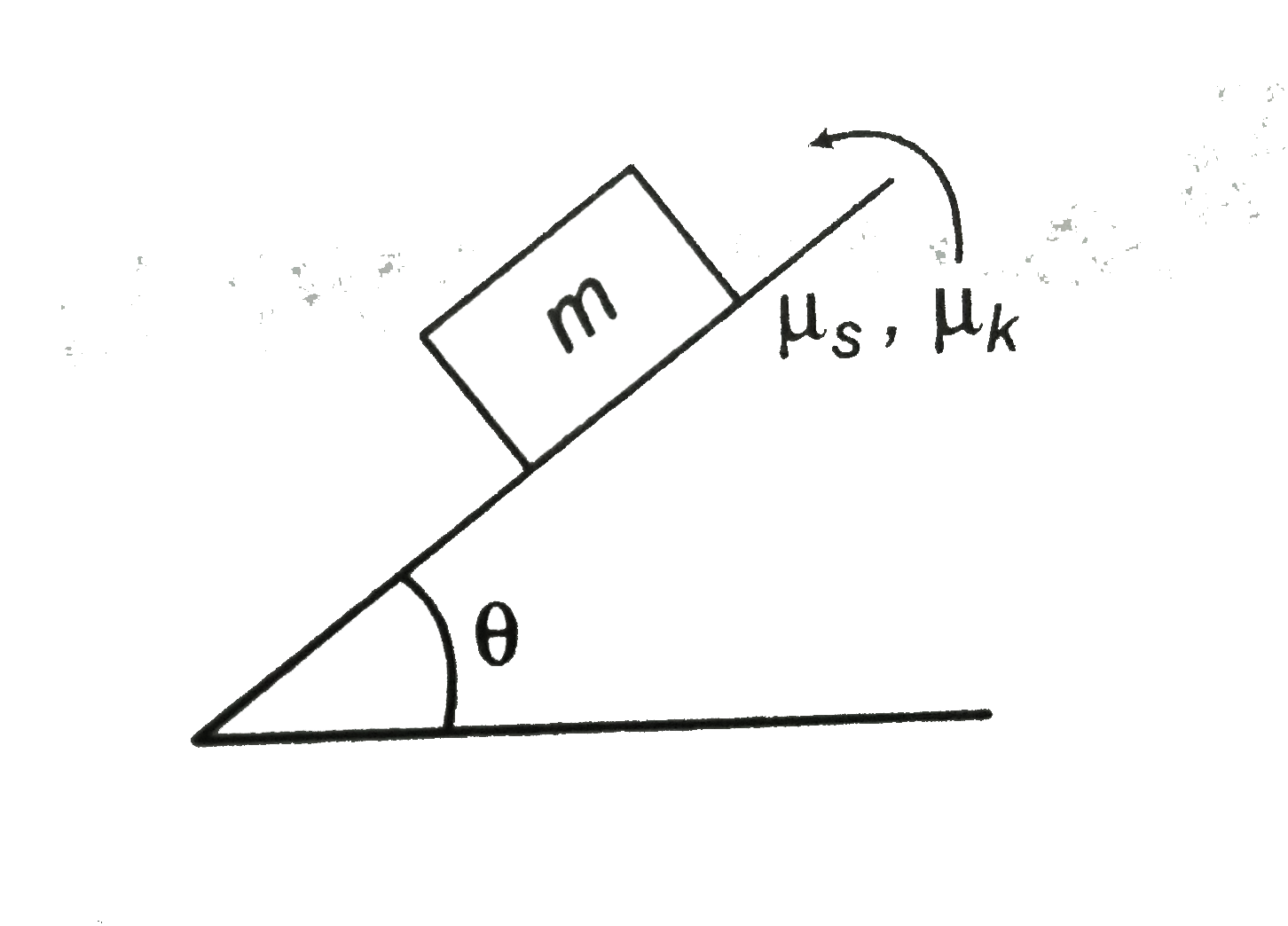
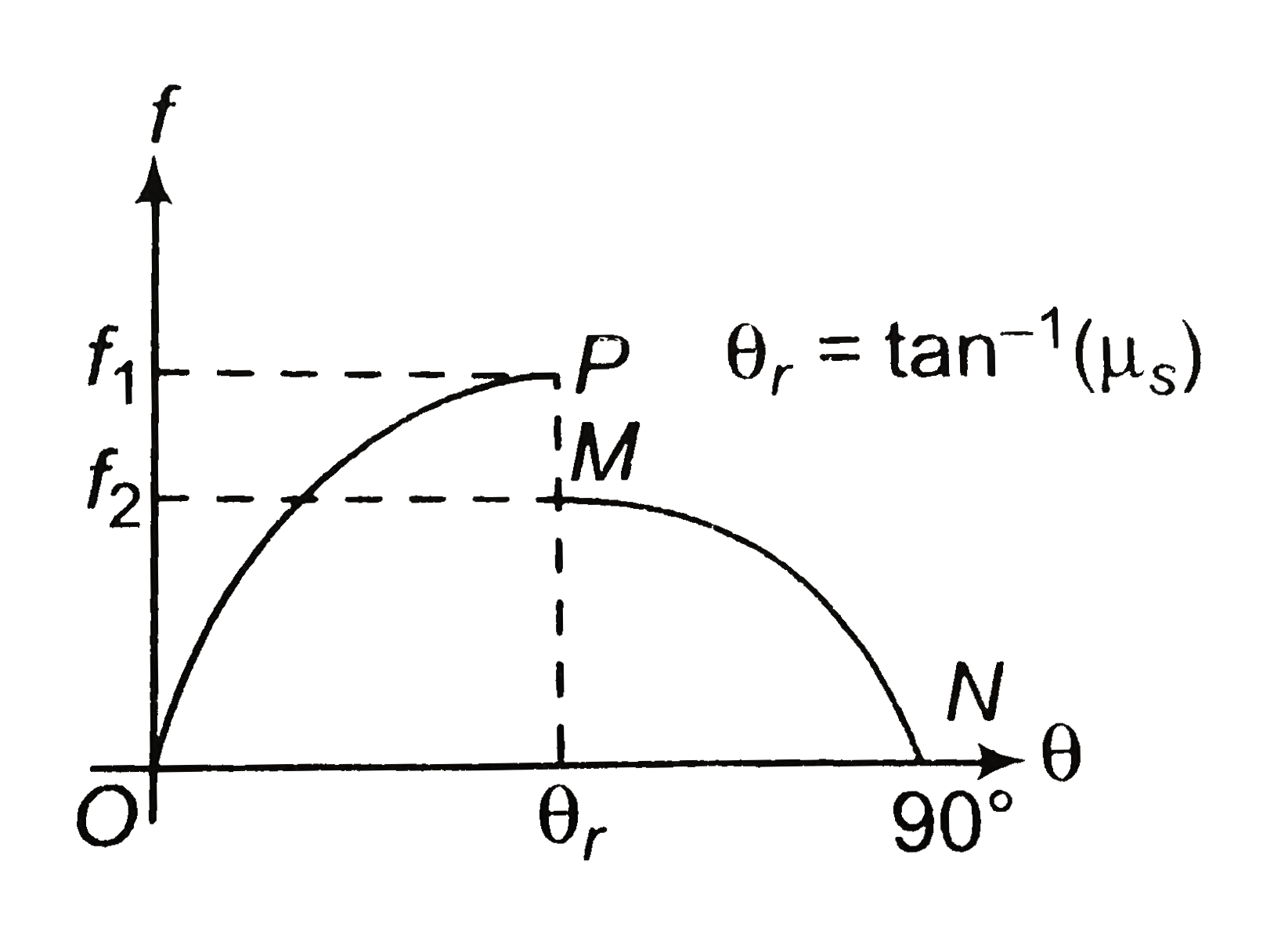
- In the odjoining figure, angle of plane theta is increased from 0^(@)t...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shown two blocks in contact sliding down an inclined surfase of...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shown a man standing stationary with respect to a horizontal co...
Text Solution
|
- Two block of masses m =5kg and M =10kg are connected by a string passi...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the situation shown in figure. The block B moves on a frictio...
Text Solution
|
- Two block A and B of masses 1kg and2kg respectively are connected by ...
Text Solution
|
- Find the acceleration of the body of mass m(2) in the arrangement show...
Text Solution
|
- In the arrangement shown in figure the mass of the ball is eta times a...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shown a small block A of mass m kept at the left end of a plank...
Text Solution
|