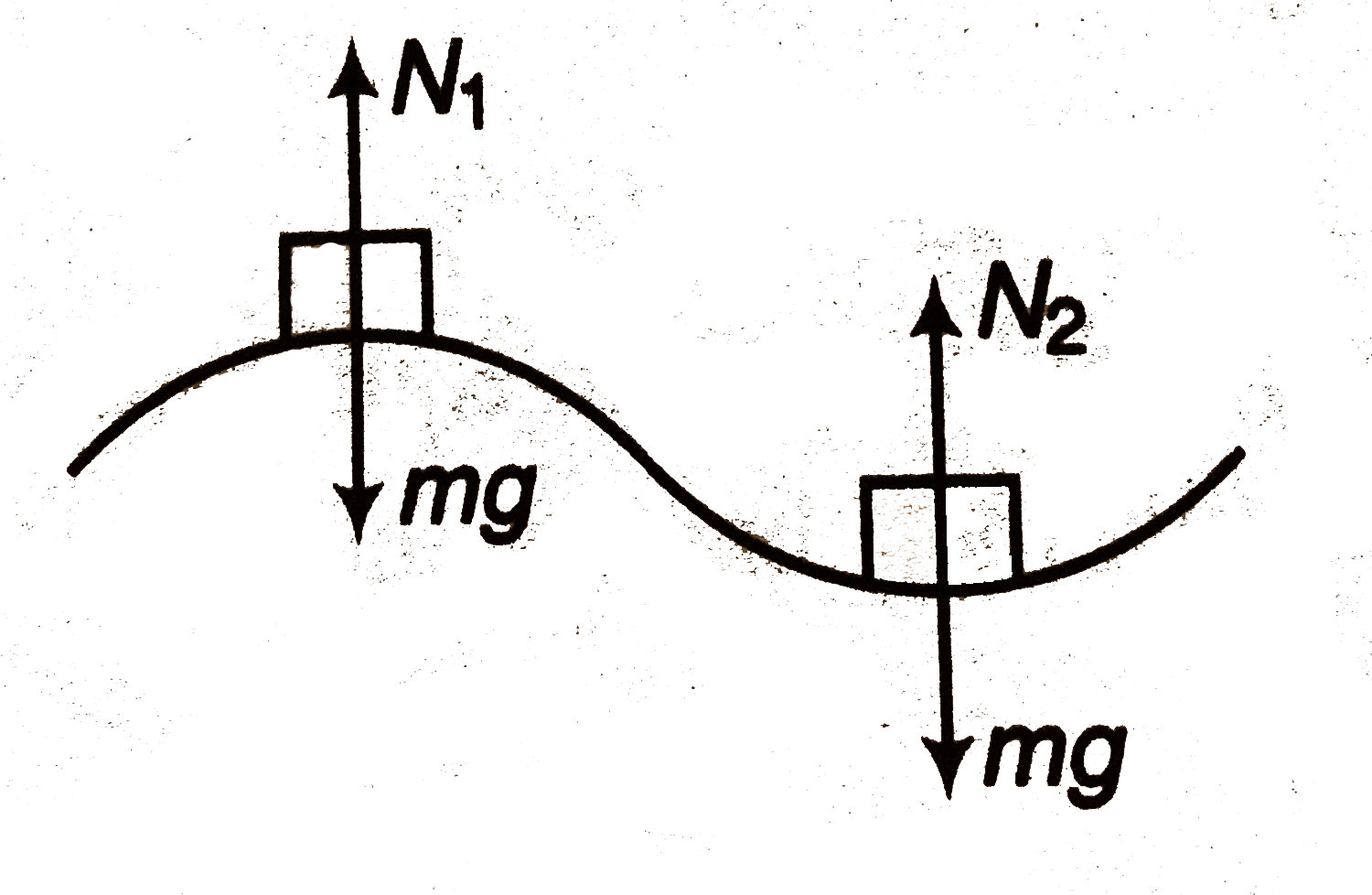
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CIRCULAR MOTION
DC PANDEY|Exercise Exercise 10.3|4 VideosCIRCULAR MOTION
DC PANDEY|Exercise Assertion And Reason|28 VideosCIRCULAR MOTION
DC PANDEY|Exercise Exercise 10.1|7 VideosCENTRE OF MASS, LINEAR MOMENTUM AND COLLISION
DC PANDEY|Exercise Level 2 Subjective|21 VideosCOMMUNICATION SYSTEM
DC PANDEY|Exercise Only One Option is Correct|27 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY-CIRCULAR MOTION-Exercise 10.2
- A turn has a radius of 10m if a vehicle goes round it at an average sp...
Text Solution
|
- If the road of the previous problem is horizontal (no banking), what s...
Text Solution
|
- A circular road of radius 50m has the angle of banking equal to 30^(@)...
Text Solution
|
- Is a body in uniform circular motion in equilibrium ?
Text Solution
|
- A car driver going at speed v suddenly finds a wide wall at a distance...
Text Solution
|
- A 4kg block is attached to a vertical rod by means of two strings of e...
Text Solution
|
- A car moves at a constant speed on a straigh but hilly road. One secti...
Text Solution
|