Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
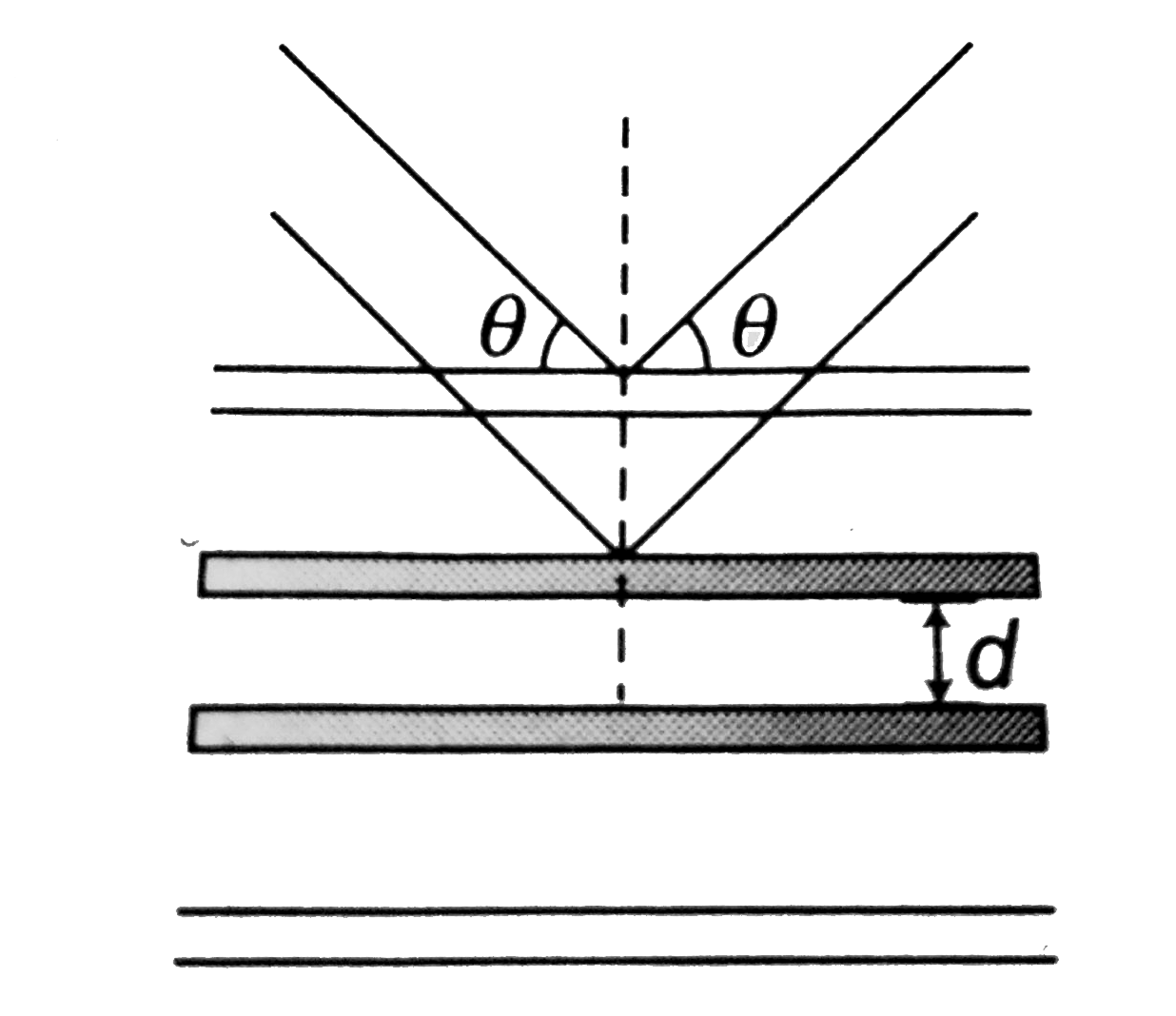
- A beam with wavelength lambda falls on a stack of partially reflecting...
Text Solution
|
- A plane mirror reflects a beam of light to form a real image, The inci...
Text Solution
|
- Demostrate that a light beam reflected from three mutually perpendicul...
Text Solution
|
- A beam of plane-polarized light falls on the surface of water at the B...
Text Solution
|
- A beam with wavelength lambda falls on a stack of partially reflecting...
Text Solution
|
- A plane mirror rotating at an angular velocity of 3 radian/s reflects ...
Text Solution
|
- समतल दर्पण पर लंबवत पड़नेवाली किरण किस प्रकार परावर्तित होती है ?
Text Solution
|
- प्रकाश किरण समतल दर्पण पर अमिलन्बत आपतिट होती है, उसके परावर्तन कोण का...
Text Solution
|
- एक प्रकाश किरण पुंज एक समतल दर्पण पर आपतित होता है और उससे परावर्तित ह...
Text Solution
|