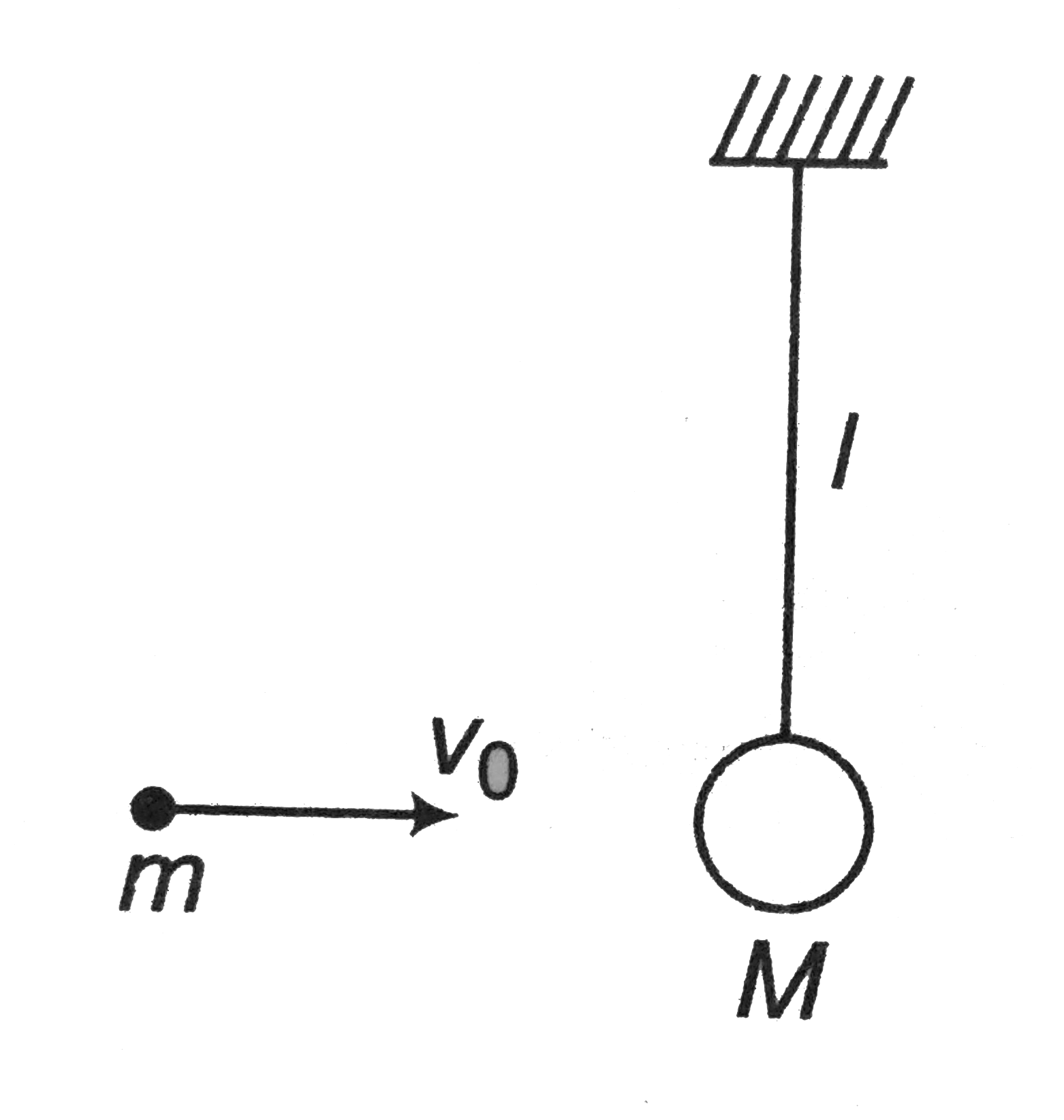
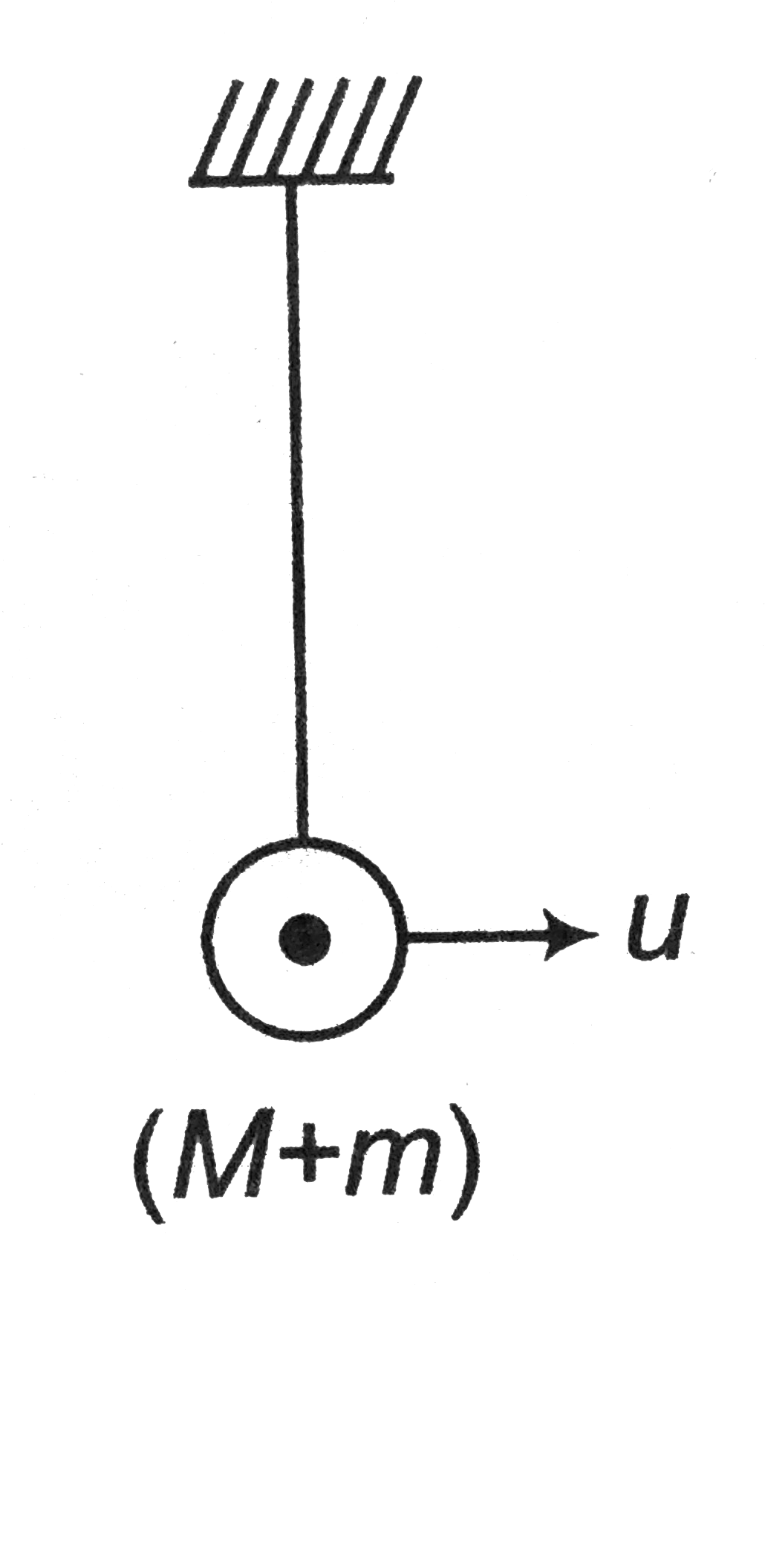
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CENTRE OF MASS, LINEAR MOMENTUM AND COLLISION
DC PANDEY|Exercise Type 1|1 VideosCENTRE OF MASS, LINEAR MOMENTUM AND COLLISION
DC PANDEY|Exercise MiscellaneousExamples|9 VideosCENTRE OF MASS, LINEAR MOMENTUM AND COLLISION
DC PANDEY|Exercise Level 2 Subjective|21 VideosCENTRE OF MASS, IMPULSE AND MOMENTUM
DC PANDEY|Exercise Comprehension type questions|15 VideosCIRCULAR MOTION
DC PANDEY|Exercise Medical entrances s gallery|19 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY-CENTRE OF MASS, LINEAR MOMENTUM AND COLLISION-Solved Examples
- A trolley of mass M is at rest over a smooth horizontal surface as sho...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is placed on a triangular block of mass M(M = 2m) , ...
Text Solution
|
- All surfaces shown in figure are smooth. Wedges of mass 'M' is free to...
Text Solution
|
- A wooden plank of mass 20kg is resting on a smooth horizontal floor. A...
Text Solution
|
- A man of mass m1 is standing on a platform of mass m2 kept on a smooth...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is released from the top of a wedge of mass M as sho...
Text Solution
|
- A bomb of mass '5m' at rest explodes into three parts of masses 2m, 2m...
Text Solution
|
- A projectile of mass 3kg is projected with velocity 50m//s at 37^@ fro...
Text Solution
|
- A constant force F is applied on a trolley of initial mass m0 kept ove...
Text Solution
|
- A trolley of initial mass m0 is kept over a smooth surface as shown in...
Text Solution
|
- Two balls of masses m and 2m and momenta 4p and 2p (in the directions ...
Text Solution
|
- In the situation discussed above, find (a) velocity of combined mass...
Text Solution
|
- A pendulum bob of mass 10^-2kg is raised to a height 5xx10^-2m and the...
Text Solution
|