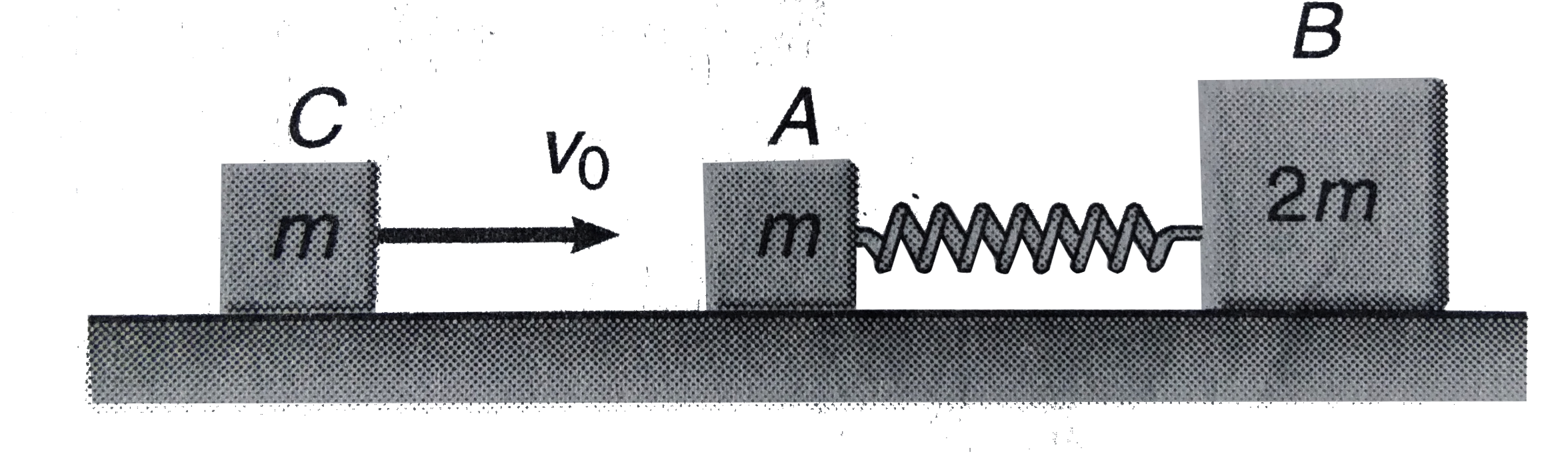Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CENTRE OF MASS, LINEAR MOMENTUM AND COLLISION
DC PANDEY|Exercise Exercise 11.1|13 VideosCENTRE OF MASS, LINEAR MOMENTUM AND COLLISION
DC PANDEY|Exercise Exercise 11.2|6 VideosCENTRE OF MASS, LINEAR MOMENTUM AND COLLISION
DC PANDEY|Exercise Type 1|1 VideosCENTRE OF MASS, IMPULSE AND MOMENTUM
DC PANDEY|Exercise Comprehension type questions|15 VideosCIRCULAR MOTION
DC PANDEY|Exercise Medical entrances s gallery|19 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY-CENTRE OF MASS, LINEAR MOMENTUM AND COLLISION-MiscellaneousExamples
- The friction coefficient between the horizontal surface and each of th...
Text Solution
|
- Three identical balls, ball I, ball II and ball III are placed on a sm...
Text Solution
|
- A planck of mass 5kg is placed on a frictionless horizontal plane. Fur...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is projected from the ground with speed u at an angle alpha wit...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass m=1kg falling vertically with a velocity v0=2m//s strik...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of equal mass m are connected by an unstretched spring and ...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is connect to another block of mass M by a massless ...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks A and B of masses m and 2m respectively are placed on a smo...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform chain of mass m and length l hangs on a thread and touches t...
Text Solution
|