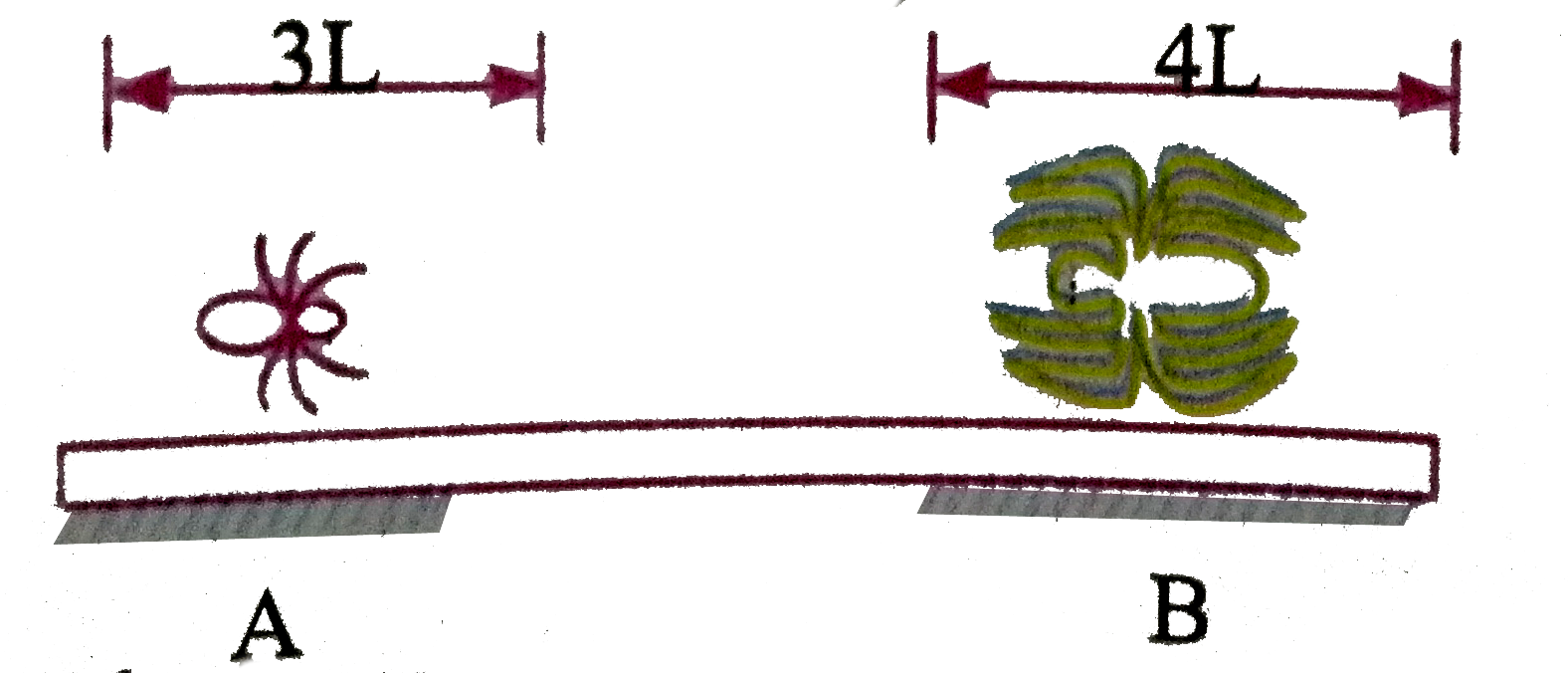
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CENTRE OF MASS, LINEAR MOMENTUM AND COLLISION
DC PANDEY|Exercise Level 2 Comprehension Based Questions|3 VideosCENTRE OF MASS, LINEAR MOMENTUM AND COLLISION
DC PANDEY|Exercise Level 2 Subjective|21 VideosCENTRE OF MASS, LINEAR MOMENTUM AND COLLISION
DC PANDEY|Exercise Level 2 More Than One Correct|8 VideosCENTRE OF MASS, IMPULSE AND MOMENTUM
DC PANDEY|Exercise Comprehension type questions|15 VideosCIRCULAR MOTION
DC PANDEY|Exercise Medical entrances s gallery|19 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY-CENTRE OF MASS, LINEAR MOMENTUM AND COLLISION-Level 2 Comprehension Based
- A block of mass 2kg is attached with a spring of spring constant 4000N...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 2kg is attached with a spring of spring constant 4000N...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform bar of length 12 L and mass 48 m is supported horizontally o...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform bar of length 12 L and mass 48 m is supported horizontally o...
Text Solution
|