Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY-SUPERPOSITION OF WAVES-Level 2 Subjective
- Three pieces of string, each of length L, are joined together end-to-e...
Text Solution
|
- In a stationary wave that forms as a result of reflection of waves fro...
Text Solution
|
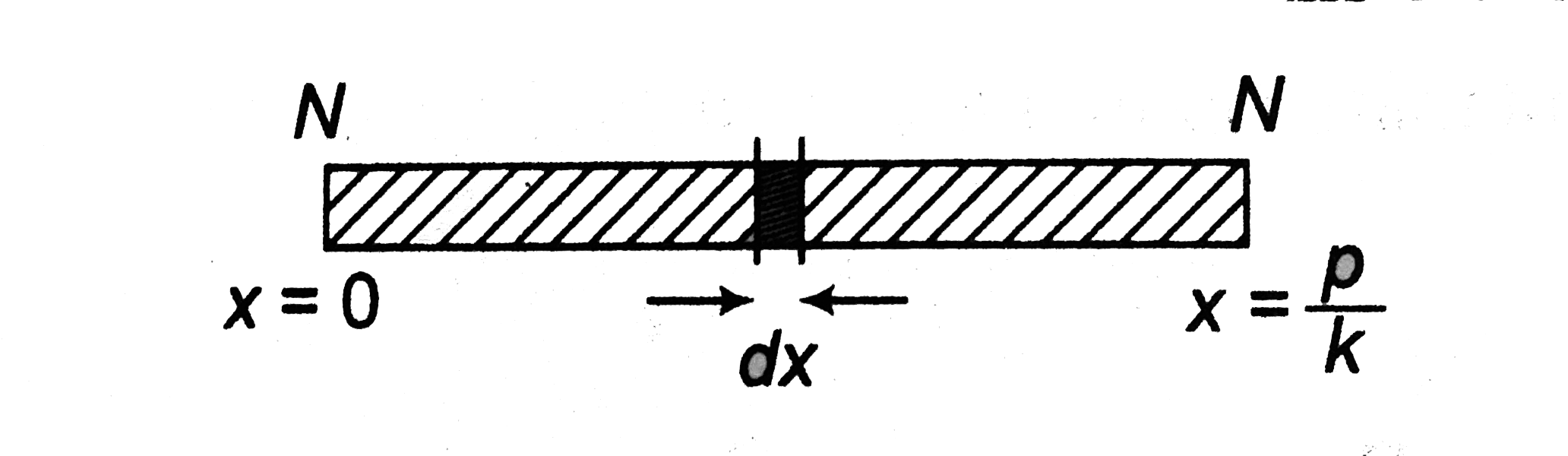
- A standing wave xi= a sin kx. Cos omegat is maintained in a homogeneo...
Text Solution
|
- A string tied between x = 0 and x = l vibrates in fundamental mode. Th...
Text Solution
|
- A long wire PQR is made by joining two wires PQ and QR of equal radii....
Text Solution
|
- A light string is tied at one end to a fixed support and to a heavy st...
Text Solution
|
- A string fixed at both ends is vibrating in the lowest mode of vibrati...
Text Solution
|
- y1 = 8 sin (omegat - kx) and y2 = 6 sin (omegat + kx) are two waves tr...
Text Solution
|