Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTROSTATICS
DC PANDEY|Exercise Exercise 24.1|4 VideosELECTROSTATICS
DC PANDEY|Exercise Exercise 24.2|9 VideosELECTROSTATICS
DC PANDEY|Exercise Example Type 8|3 VideosELECTROSTATIC POTENTIAL AND CAPACITORS
DC PANDEY|Exercise (C) Chapter exercises|50 VideosGRAVITATION
DC PANDEY|Exercise All Questions|120 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY-ELECTROSTATICS-Level 2 Single Correct
- A point charge q is placed on the apex of a cone of semi-vertex angle ...
Text Solution
|
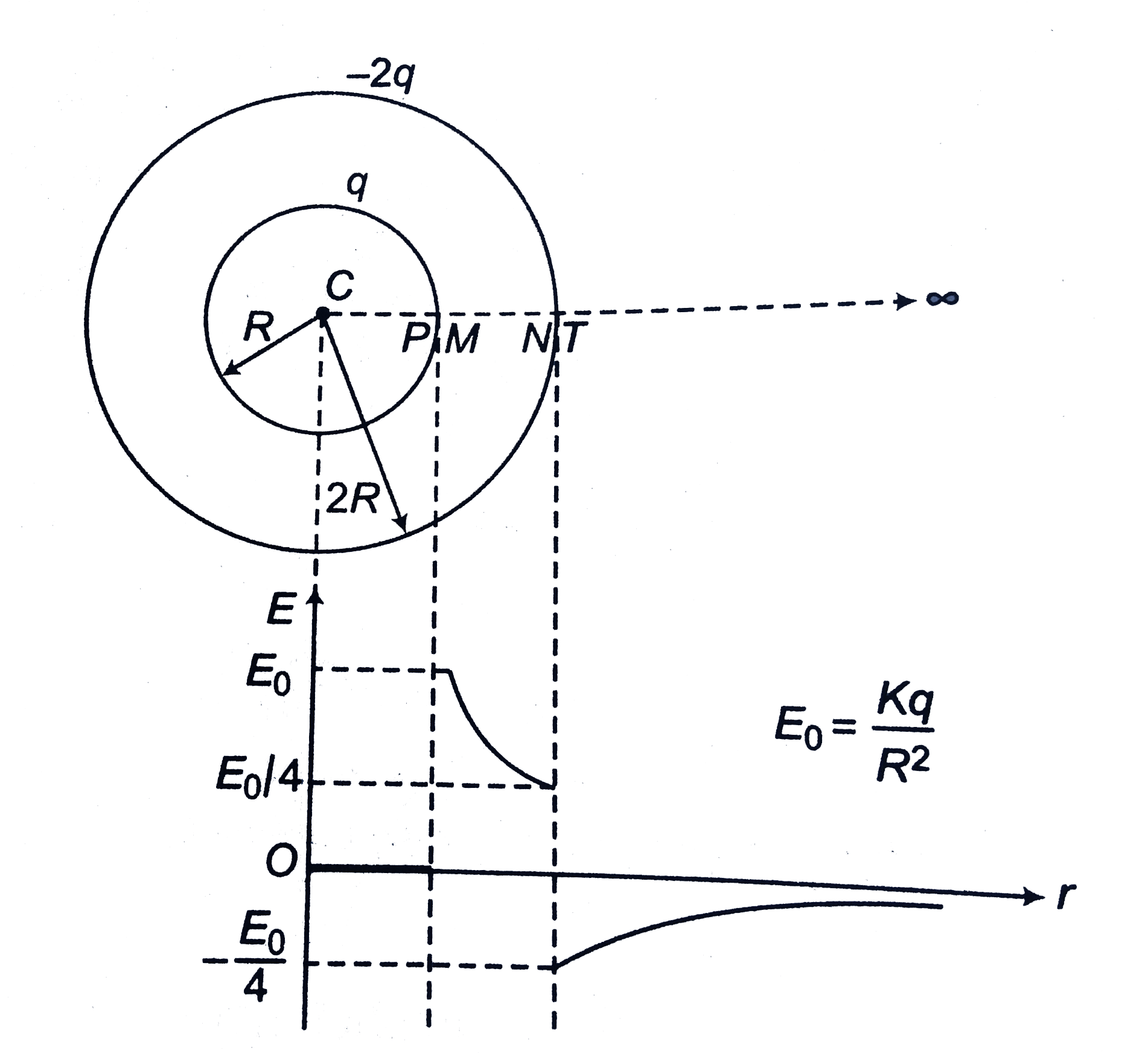
- Draw E-r and V-r graphs due to two point charges + q and -2q kept at s...
Text Solution
|
- Draw E-r and V-r graphs due to two charged spherical shells as shown i...
Text Solution
|
- An electron with a speed 5.00xx10^6 m/s enters an electric field of ma...
Text Solution
|
- A charged particle of mass m=1 kg and charge q=2muC is thrown for a ho...
Text Solution
|
- Find the potential difference V(AB) between A(2m, 1m, 0) and B(0, 2m, ...
Text Solution
|
- Find potential difference V(AB) between A(0,0,0) and B(1m,1m,1m) in an...
Text Solution
|
- An electric dipole of dipole moment p is placed in a uniform electric ...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical thin ring, each of radius R meters, are coaxially placed...
Text Solution
|
- Five point charges, each of value +q coul, are placed on five vertices...
Text Solution
|
- A point charge q1=9.1muC is held fixed at origin. A second point charg...
Text Solution
|
- A point charge q1 =-5.8muC is held stationary at the origin. A second ...
Text Solution
|
- A uniformly charged thin ring has radius 10.0 cm and total charge +12....
Text Solution
|
- Two points A and B are 2 cm apart and a uniform electric field E acts ...
Text Solution
|
- An alpha particle with kinetic energy 10 Me V is heading toward a stat...
Text Solution
|
- Three point charges 1C, 2C and 3C are placed at the corners of an equi...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a spherical surface of radius 4 m cenred at the origin. Point...
Text Solution
|
- The intensity of an electric field depends only on the coordinates x a...
Text Solution
|
- Find the electric field caused by a disc of radius a with a uniform su...
Text Solution
|
- A non-conducting disc of radius a and uniform positive surface charge ...
Text Solution
|