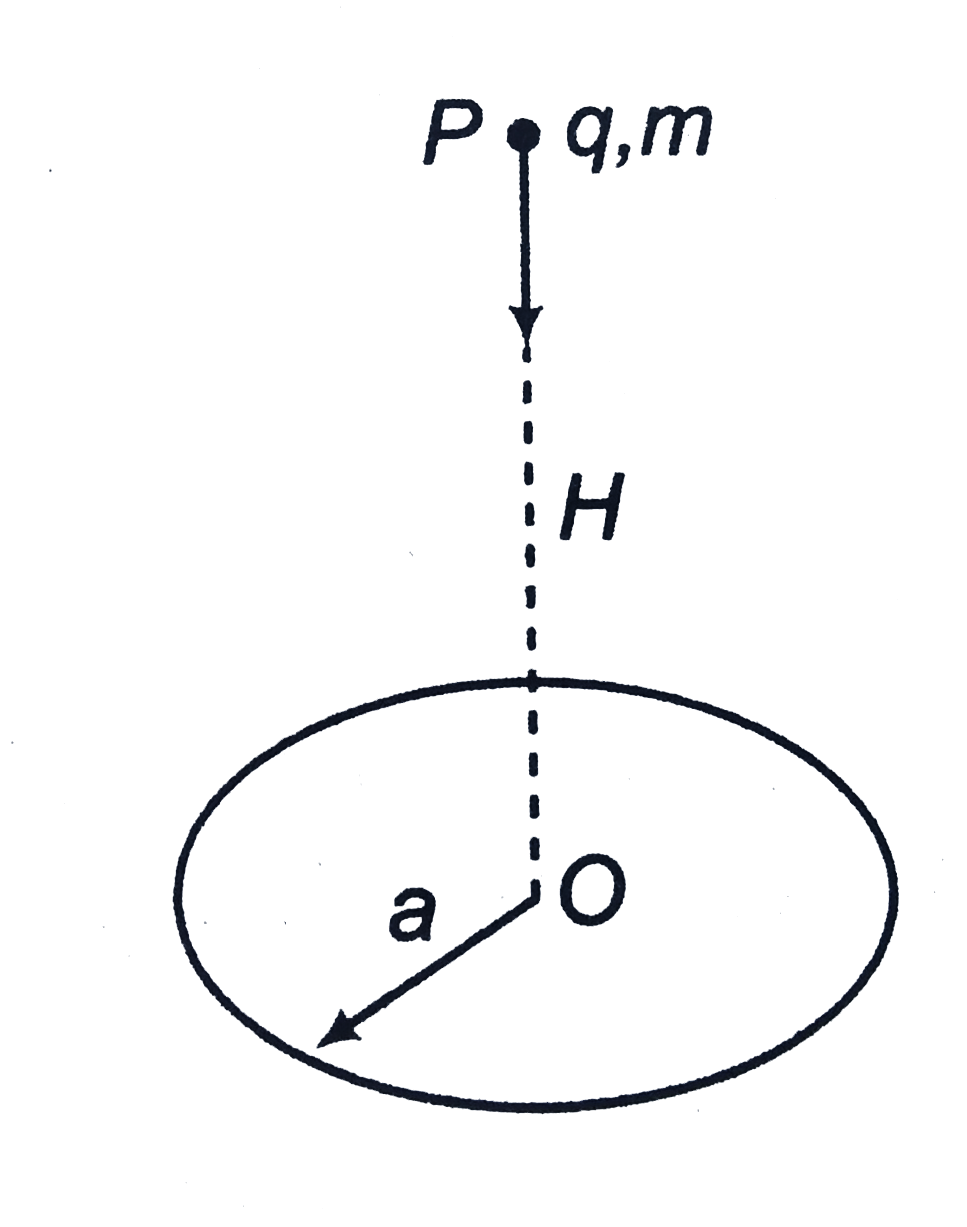
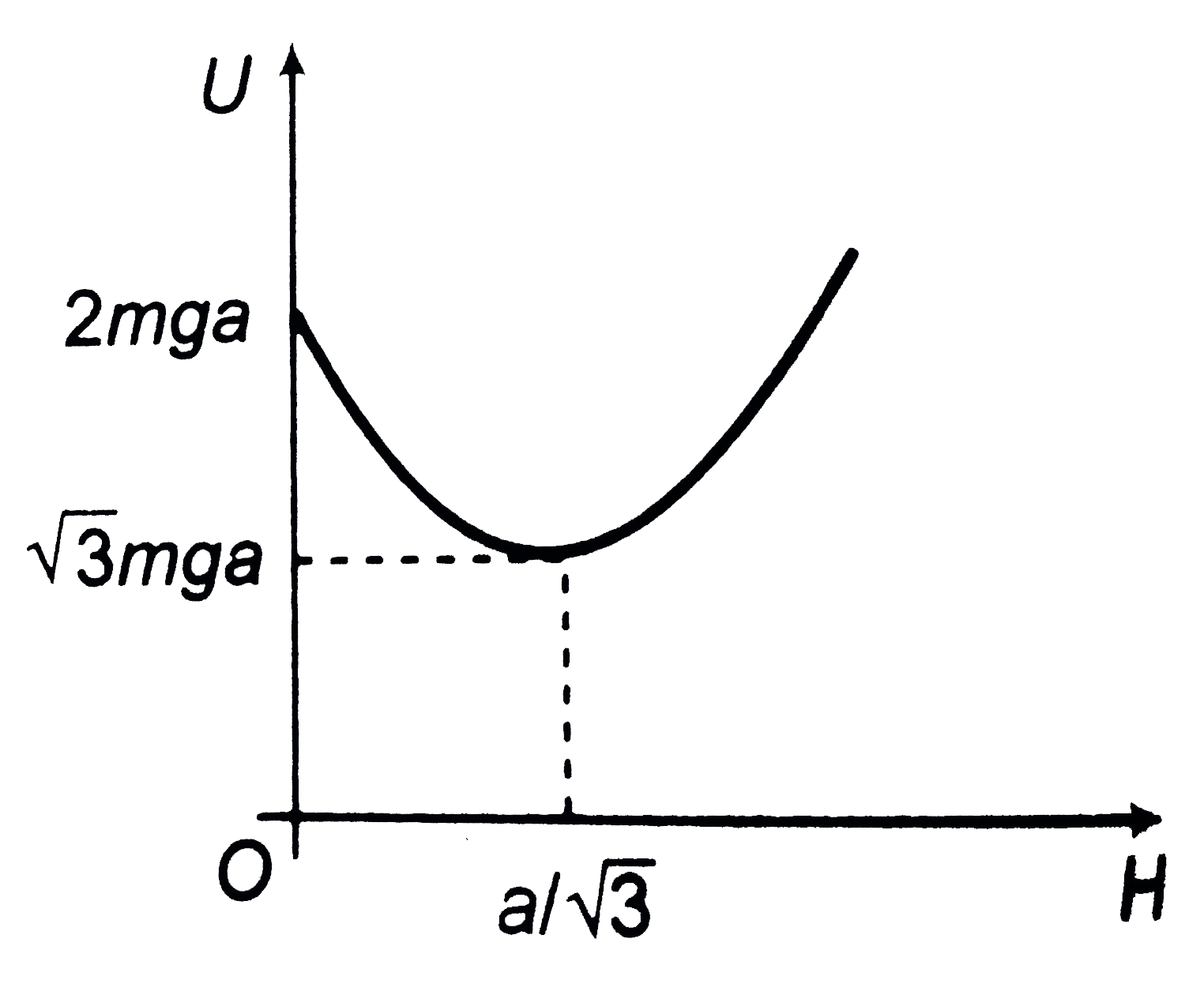
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTROSTATICS
DC PANDEY|Exercise Exercise 24.1|4 VideosELECTROSTATICS
DC PANDEY|Exercise Exercise 24.2|9 VideosELECTROSTATICS
DC PANDEY|Exercise Example Type 8|3 VideosELECTROSTATIC POTENTIAL AND CAPACITORS
DC PANDEY|Exercise (C) Chapter exercises|50 VideosGRAVITATION
DC PANDEY|Exercise All Questions|120 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY-ELECTROSTATICS-Level 2 Single Correct
- The intensity of an electric field depends only on the coordinates x a...
Text Solution
|
- Find the electric field caused by a disc of radius a with a uniform su...
Text Solution
|
- A non-conducting disc of radius a and uniform positive surface charge ...
Text Solution
|
- Four point charges +8muC,-1muC,-1muC and , +8muC are fixed at the poin...
Text Solution
|
- Potential difference beween centre and surface of the sphere of radius...
Text Solution
|
- A positively charged disc is placed on a horizontal plane. A charged ...
Text Solution
|
- The curve represents the distribution of potential along the staight l...
Text Solution
|
- A point charge q1=q is placed at point P. Another point charge q2=-q i...
Text Solution
|
- The variation of electric field between two charge q1 and q2 along the...
Text Solution
|
- A charge q is placed at O in the cavity in a spherical uncharged condu...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform electric field of 400 V/m is directed at 45^@ above the x-ax...
Text Solution
|
- Initially the spheres A and B are at potentials VA and VB. Find the po...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m and charge q is fastened to one end of a string o...
Text Solution
|
- A charged particle of mass m and charge q is released from rest the po...
Text Solution
|
- A charge +Q is uniformly distributed in a spherical volume of radius R...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical coaxial rings each of radius R are separated by a distan...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform electric field exists in x-y plane. The potential of points ...
Text Solution
|
- Two fixed charges -2Q and +Q are located at points (-3a,0) and (+3a,0)...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m and charge -q is projected from the origin with a...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of charge -q and mass m moves in a circle of radius r aroun...
Text Solution
|