A particle of mass `m=1.6xx10^-27` kg and charge `q=1.6xx10^-19C` enters a region of uniform magnetic field of stregth `1 T` along the direction shown in figure. The speed of the particle is `10^7 m//s`

a. The magnetic field is directed along the inward normal to the plane of the paper. The particle leaves the region of the fiedl at the point `F`. Find the distasnce `EF` and the angle theta.
b. If the direction of the field is along the outward normal to the plane of the paper find the time spent by the particle in the regin of the magnetic field after entering it at `E`.
A particle of mass `m=1.6xx10^-27` kg and charge `q=1.6xx10^-19C` enters a region of uniform magnetic field of stregth `1 T` along the direction shown in figure. The speed of the particle is `10^7 m//s`

a. The magnetic field is directed along the inward normal to the plane of the paper. The particle leaves the region of the fiedl at the point `F`. Find the distasnce `EF` and the angle theta.
b. If the direction of the field is along the outward normal to the plane of the paper find the time spent by the particle in the regin of the magnetic field after entering it at `E`.

a. The magnetic field is directed along the inward normal to the plane of the paper. The particle leaves the region of the fiedl at the point `F`. Find the distasnce `EF` and the angle theta.
b. If the direction of the field is along the outward normal to the plane of the paper find the time spent by the particle in the regin of the magnetic field after entering it at `E`.
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Inside a magnetic field, speed of charged particle does not change. Futher, velocity is perpendicular to magnetic field in both the cses hene path of the particle in the magnetic field will be circular. Centre of circle can be obtained by drawing perpendiculars to velocity (or tantent to the circular path) at `E` and `F`. Radius and angular speed of circular path would be
`r=(mv)/(Bq)` and `omega=(Bq)/m`
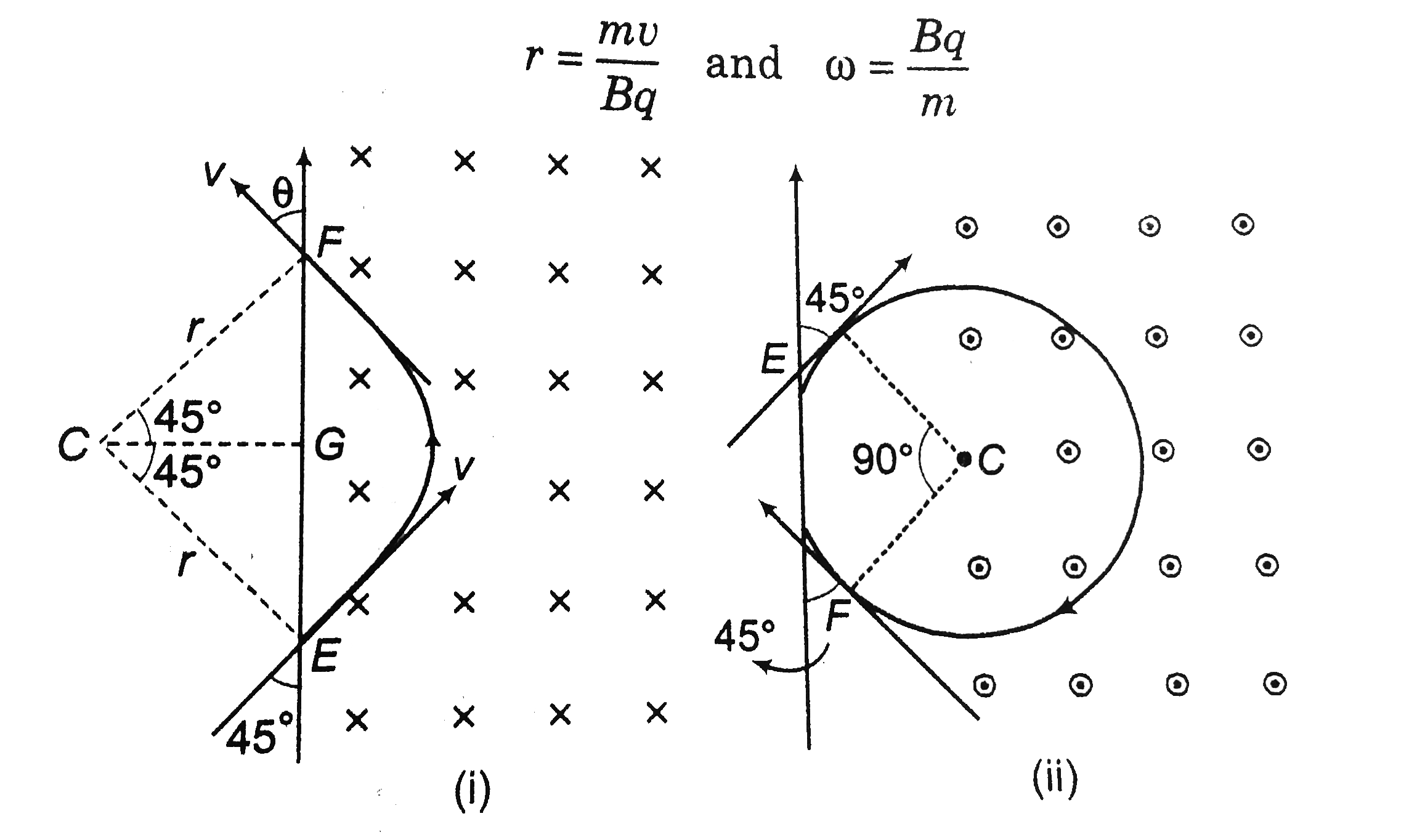
a. Refer figure i
`/_CFG=90^@-theta` and `/_CEG=90^@-45^@=45^@`
since `CF=CE`
`:. /_CFG=/_CEG`
or `90^@-theta=45^@` or `theta=45^@`
Further `FG=GE=rcos45^@`
`:. EF=2FG=2rcos45^0=(2mvcos45^@)/(Bq)`
`=(2(1.6xx10^-27)(10^7)(1/sqrt2))/((1)(1.6xx10^-19))=0.14m`
b. refer figure ii In this casse particle will complete `3/4` th of circle in the magnetic field.
Hence, the time spend in the magnetic field
`t=3/4` (time period of circular motion)
`=3/4((2pim)/(Bq)=(3pim)/(2Bq))`
`((3pi)(1.6xx10^I-27))/((2)(1)(1.6xx10^-19))`
`=4.712xx10^-8s`
In figure a Centre of circulr path is lying on the boundary line of magnetic field. Deviation of the particle is `180^@` and time spend in magnetic field `t=T/2`
In figure b. Centre of circular path lies outside the magnetic fiedl. Deviation of the particle is less than `180^0` and time spend in magnetic field `ltT/2`
In figure c. Centre of circular path lies inside the magnetic field. Deviation of the particle is more than `180^@` and time spent in magnetic field `tgtT/2`
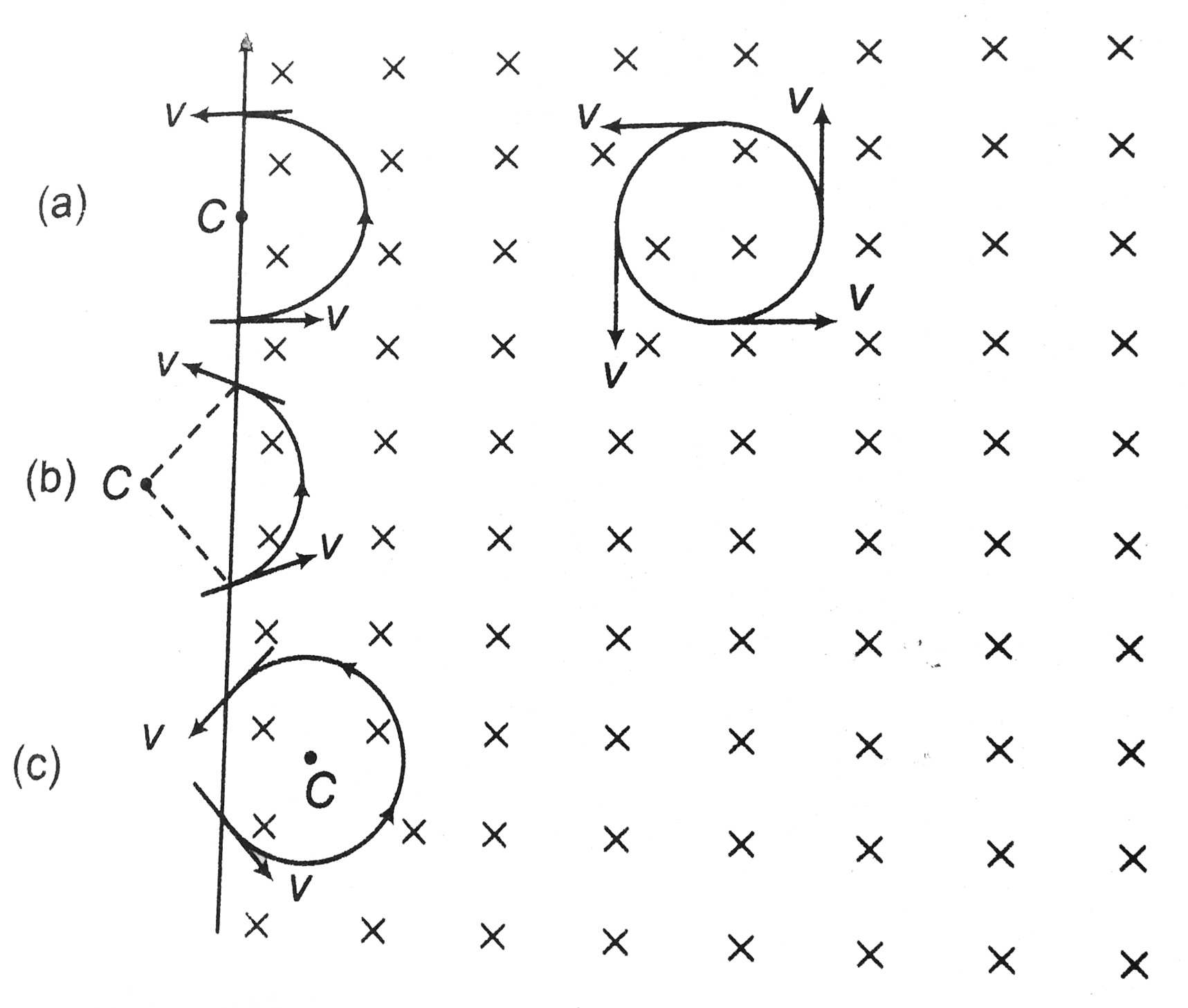
`r=(mv)/(Bq)` and `omega=(Bq)/m`

a. Refer figure i
`/_CFG=90^@-theta` and `/_CEG=90^@-45^@=45^@`
since `CF=CE`
`:. /_CFG=/_CEG`
or `90^@-theta=45^@` or `theta=45^@`
Further `FG=GE=rcos45^@`
`:. EF=2FG=2rcos45^0=(2mvcos45^@)/(Bq)`
`=(2(1.6xx10^-27)(10^7)(1/sqrt2))/((1)(1.6xx10^-19))=0.14m`
b. refer figure ii In this casse particle will complete `3/4` th of circle in the magnetic field.
Hence, the time spend in the magnetic field
`t=3/4` (time period of circular motion)
`=3/4((2pim)/(Bq)=(3pim)/(2Bq))`
`((3pi)(1.6xx10^I-27))/((2)(1)(1.6xx10^-19))`
`=4.712xx10^-8s`
In figure a Centre of circulr path is lying on the boundary line of magnetic field. Deviation of the particle is `180^@` and time spend in magnetic field `t=T/2`
In figure b. Centre of circular path lies outside the magnetic fiedl. Deviation of the particle is less than `180^0` and time spend in magnetic field `ltT/2`
In figure c. Centre of circular path lies inside the magnetic field. Deviation of the particle is more than `180^@` and time spent in magnetic field `tgtT/2`
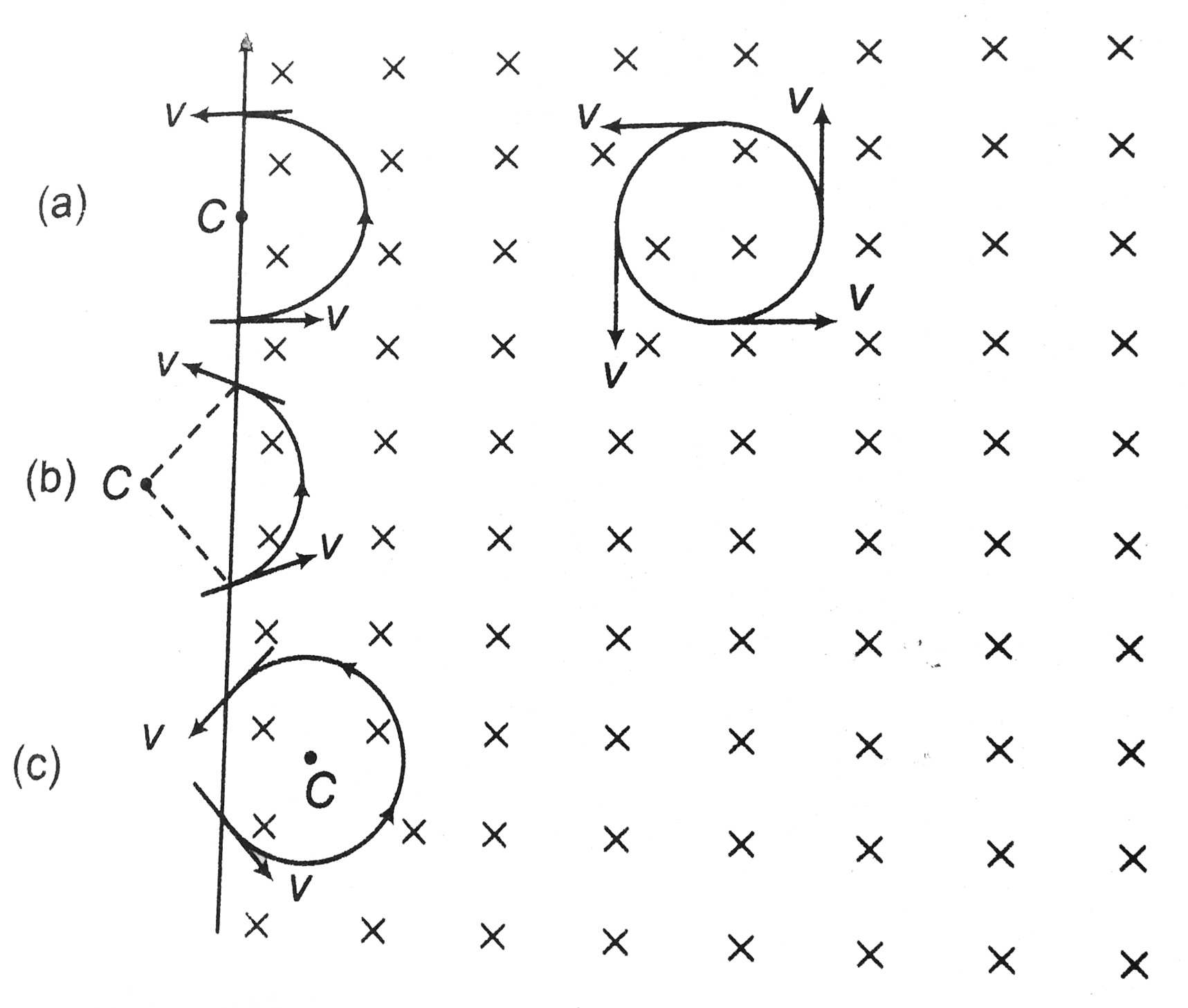
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
A particle of mass m = 1.6 X 10^(27) kg and charge q = 1.6 X 10^(-19) C moves at a speed of 1.0 X10^7 ms^(-7) . It enters a region of uniform magnetic field at a point E, as shown in The field has a strength of 1.0 T. (a) The magnetic field is directed into the plane of the paper. The particle leaves the region of the filed at the point F. Find the distance EF and the angle theta. (b) If the field is coming out of the paper, find the time spent by the particle in the regio the magnetic feld after entering it at E .
A particle enters the region of a uniform magnetic field as shown in figure. The path of the particle inside the field is shown by dark line. The particle is :
Four particles enter a region of uniform magnetic field. Their trajectories are shown in figure. What are the signs of the charge of all four particles ?
A proton of mass 1.67 xx 10^(-27) kg and charge 1.6 xx 10^(-19) C is shot a uniform magnetic field, and perpendicular to the field with a velocity 5 xx 10^(6) m//s . If the magnetic induction of the field is 1 tesla, find (i) The radius of the circular path
A small particle of mass m = 1 kg and charge of 1C enters perpendicularly in a triangular region of uniform magnetic field of strength 2T as shown in figure : Calculate maximum velocity of the particle with which it should enter so that it complete a half-circle in magnetic region :
A particle of mass 6.4xx10^(-27) kg and charge 3.2xx10^(-19)C is situated in a uniform electric field of 1.6xx10^5 Vm^(-1) . The velocity of the particle at the end of 2xx10^(-2) m path when it starts from rest is :
A neutron, a proton, an electron and an a-particle enters a uniform magnetic field with equal velocities. The field is directed along the inward normal to the plane of the paper. Which of these tracks followed are by a - particle.
A particle of mass m and charge +q enters a region of magnetic field with a velocity v, as shown in Fig. 1.93. a. Find the angle subtended by the circular arc described by it in the magnetic field. b. How long does the particle stay inside the magnetic field? c. If the particle enters at E, what is the intercept EF?