a. Magnetic field at `R` due to both the wires `P` and `Q` will be downwards as shown in figure.
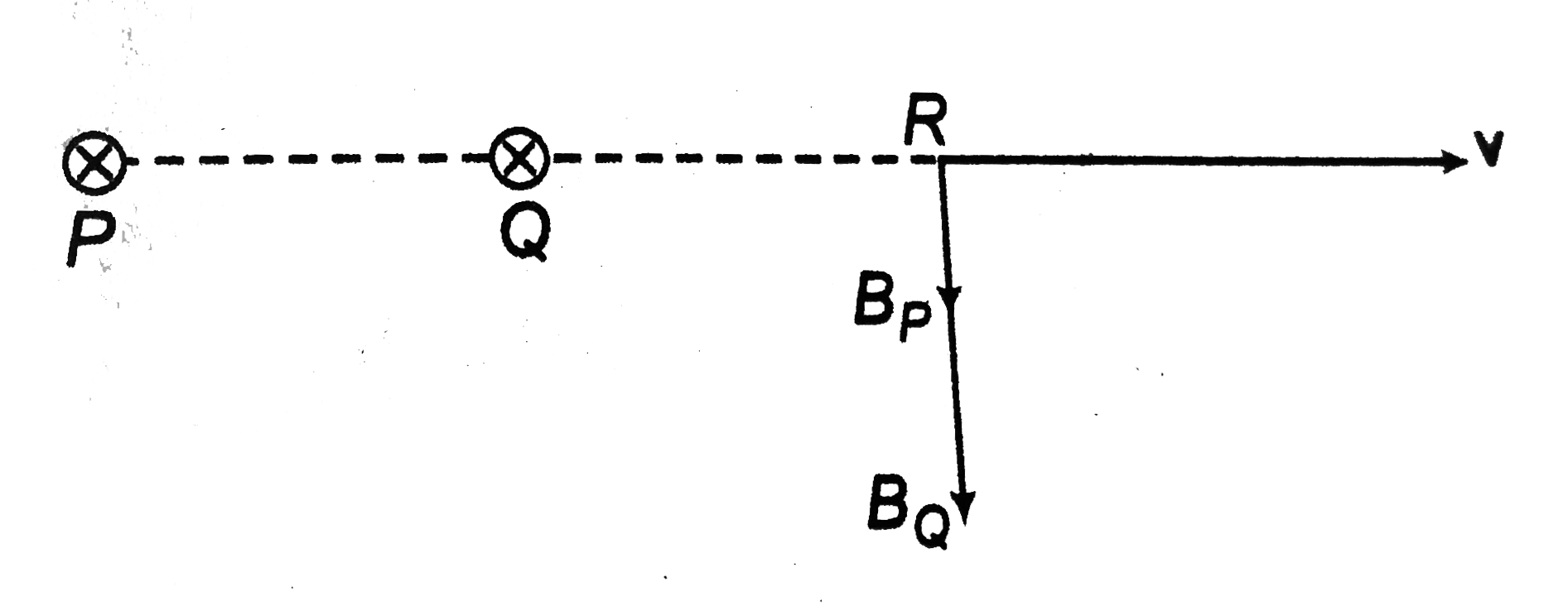
Therefore, net field at `R` will be sum of these two
`B=B_p+B_Q`,
`=mu_0/(2pi) I_P/5+mu_0/(2pi) I_Q/2=mu_0/(2pi)(2.5/5+I/2)`
`=mu_0/(4pi)(I+1)=10^-7(I+1)`
Net force on the electron will be

`F_m=(Bqvsin90^@)`
or `(3.2xx10^-20)=(10^-7)(I+1)(1.6xx10^I-19)(4xx10^5)`
or `I+1=5`
`:. I=4A`
b. Net field at `R` due to wires `P` and `Q` is
`B=10^-7(I+1)T`
`=5xx10^-7T`
Magnetic field due to third wire carrying a current of `2.5 A` should be `5xx10^-7` `T` is upward. direction, so that net field sat `R` becomes zero. Let distance of this wire from `R` be `r`. Then
`mu_0/(2pi)2.5/r=5xx10^-7`
or `((2xx10^-7)(2.5))/r=5xx10^-7m`
`r=1m`
So, the third wire can be put at `M` or `N` as shown in figure.
If it is placed at `M`, then current in it should be outwads and if placed at `N`, then current be inwards.