a. As discussed in type 9 path of the particle is a helix of incresing pitch. The axis of the helix is parallel to y-axis (parrallell to `E`) nd plane of circle of the helix is `xz` (perendicular to `B`). The particle will cross the y-axis after time.
`t=hT-n((2pim)/(Bq))=(2pimn)/(Bq)`
The y-coordinate of particle at this instant is
`y=1/2a_yt^2`
`a_y=F_y/m=(qE)/m`
`:. y=1/2((qE)/m)((2pimn)/(Bq))^2`
`=(2n^2mEpi^2)/(qB^2)`
At this moment y-component of its velocity is
`v_y=a_yt=((qE)/(m))((2pimn)/(Bq))=2pin(E/B)`
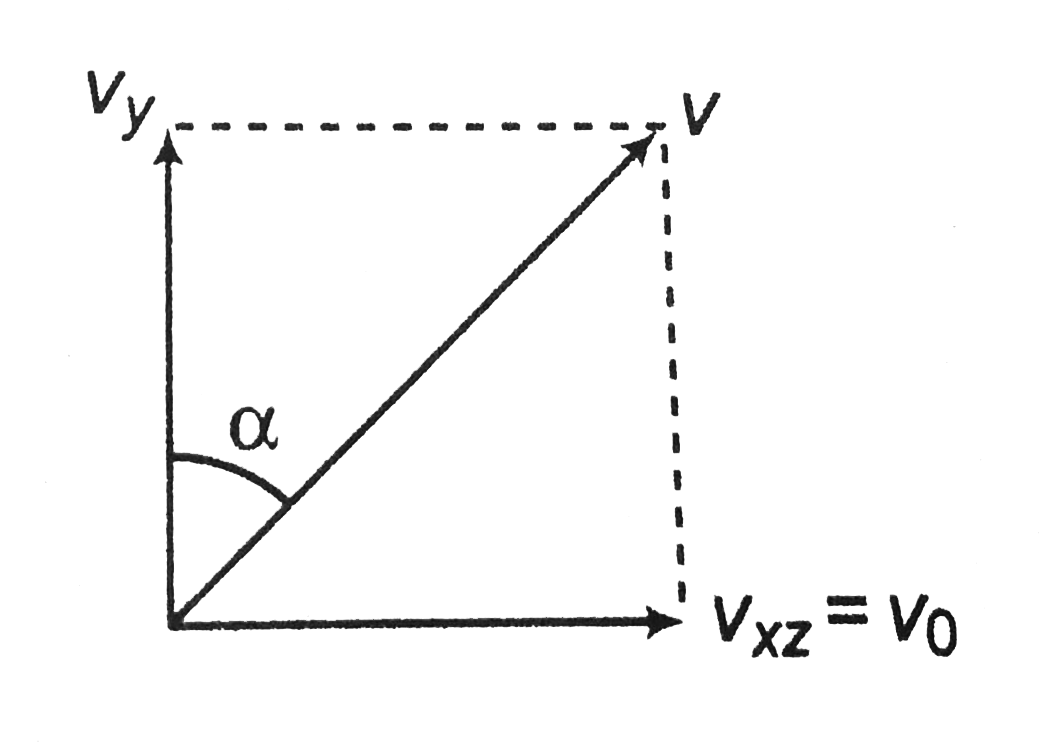
`alpha=tan^-1(v_(xz)/v^-y)`
`Here, v_(xz)=sqrt(v_x^2+v_2^2)=v_0`
`or alpha=tan^-1((Bv_0)/(2pinE))`