A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
DC PANDEY|Exercise Level 1 Objective|36 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
DC PANDEY|Exercise Objective Questions|3 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
DC PANDEY|Exercise Exercise 27.7|2 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
DC PANDEY|Exercise Medical entrances gallery|97 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES
DC PANDEY|Exercise Sec C|22 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY-ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION-Level 1 Assertion And Reason
- Assertion : A square loop is placed in x-y plane as shown in figure. M...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: Magnetic field B (shown inwards) varies with time t as show...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : Electric field produced by a variable magnetic field can't...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion: Current flowing in the circuit is i=2t-8. At t=1s, Va-...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : Angular frequency of LC oscillations is 2 rad//s and maxim...
Text Solution
|
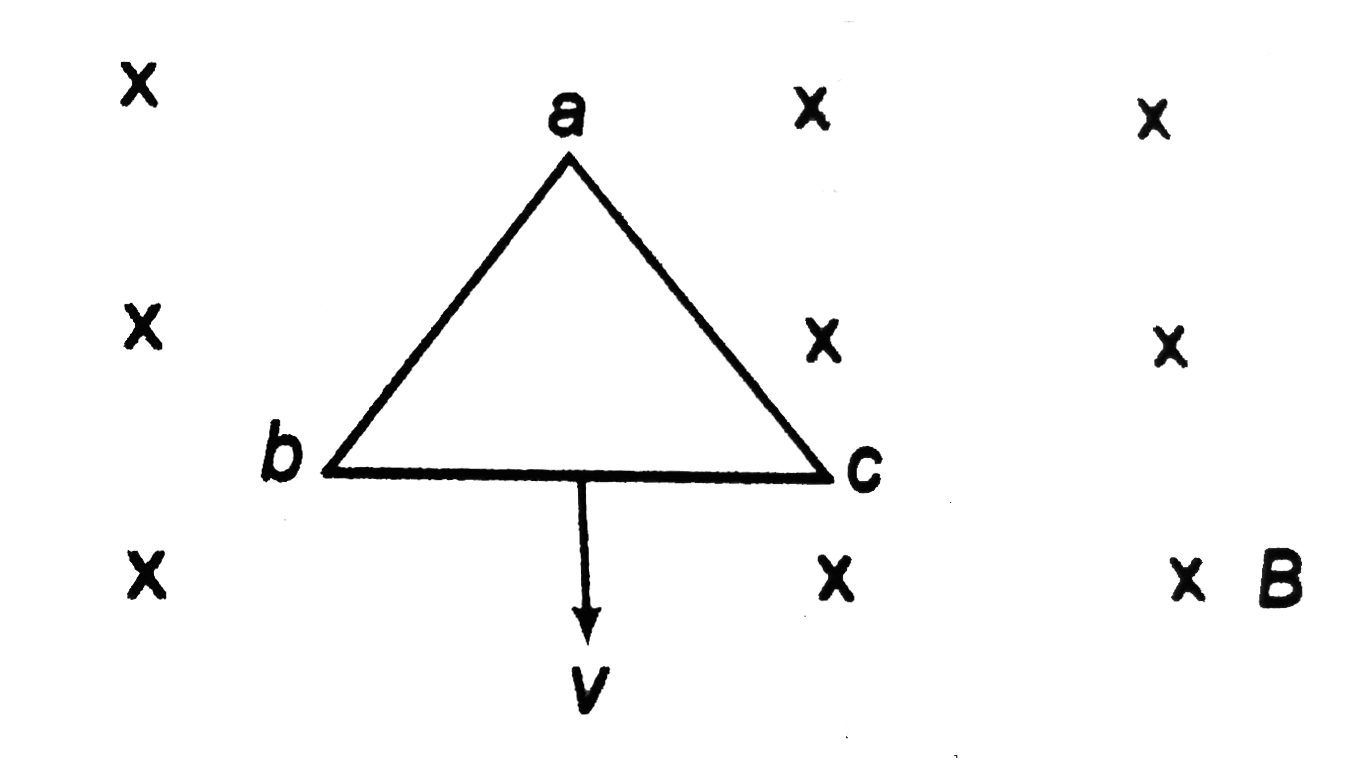
- Assertion : A conducting equilateral loop abc is moved translationally...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : Motional induced emf e = Bvl can be derived from the relat...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : If some ferromagnetic substance is filled inside a solenoi...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : In the circuit shown in figure, current in wire ab will be...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion : In parallel, current distributes in inverse ratio of induc...
Text Solution
|