Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ARIHANT MATHS-VECTOR ALGEBRA-Exercise (Questions Asked In Previous 13 Years Exam)
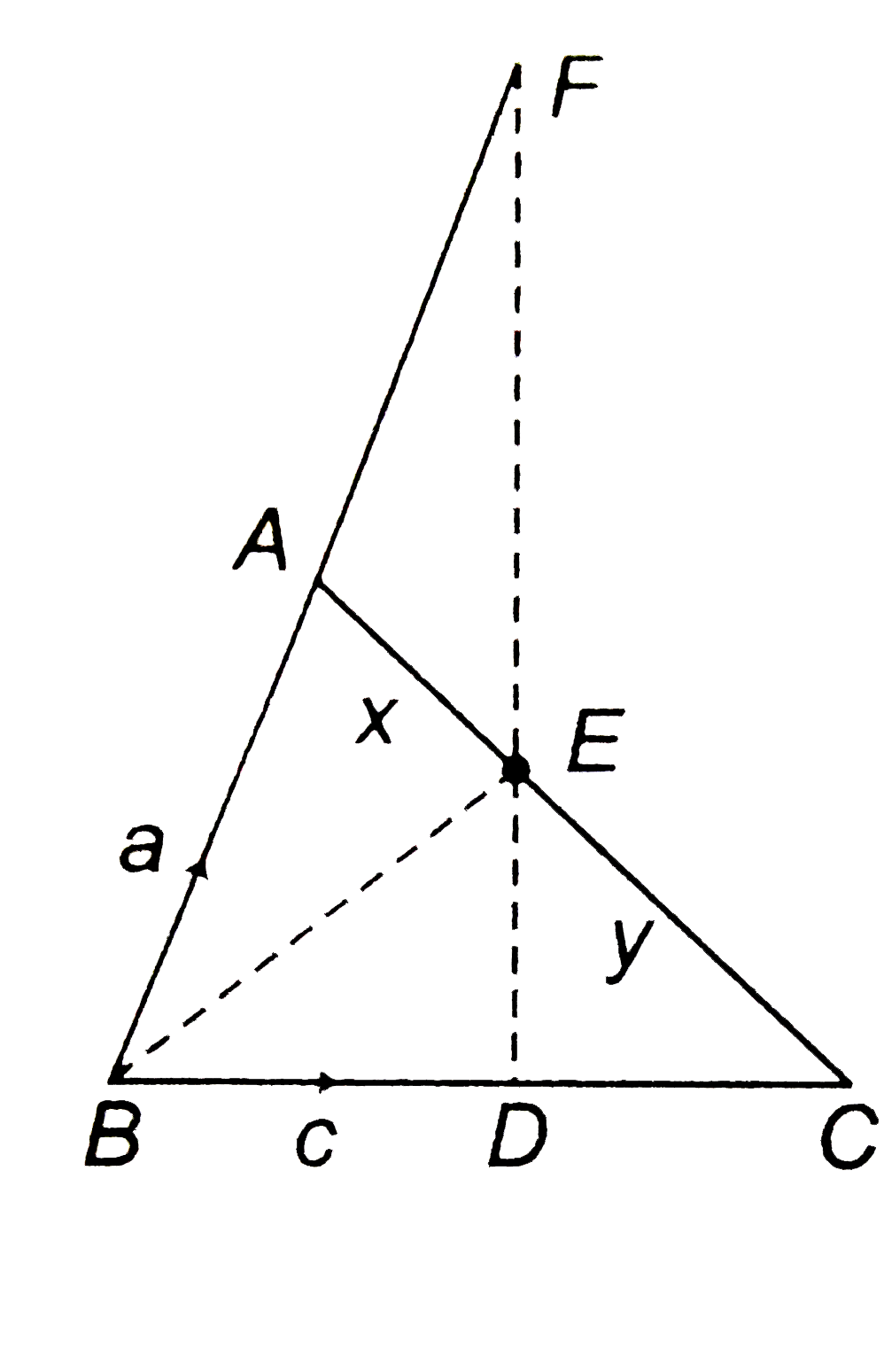
- If D ,Ea n dF are three points on the sides B C ,C Aa n dA B , respect...
Text Solution
|
- The vectors vec(AB)=3hati+4hatk and vec(AC)=5hati-2hatj+4hatk are the ...
Text Solution
|
- Let a,b and c be three non-zero vectors which are pairwise non-colline...
Text Solution
|
- The non-zero vectors are vec a,vec b and vec c are related by vec a= ...
Text Solution
|
- If C is the mid-point of AB and P is any point outside AB, then
Text Solution
|
- If a,b and c are three non-zero vectors such that no two of these are ...
Text Solution
|
- If a,b,c are non-coplanar vectors and lamda is a real number, then the...
Text Solution
|
- Consider points A,B,C annd D with position vectors 7hati-4hatj+7hatk,h...
Text Solution
|
- If |{:(a,,a^(2),,1+a^(3)),(b,,b^(2),,1+b^(3)),(c,,c^(2),,1+c^(3)):}|=0...
Text Solution
|
- The vector hat(i)+xhat(j)+3hat(k) is rotated through an angle theta an...
Text Solution
|