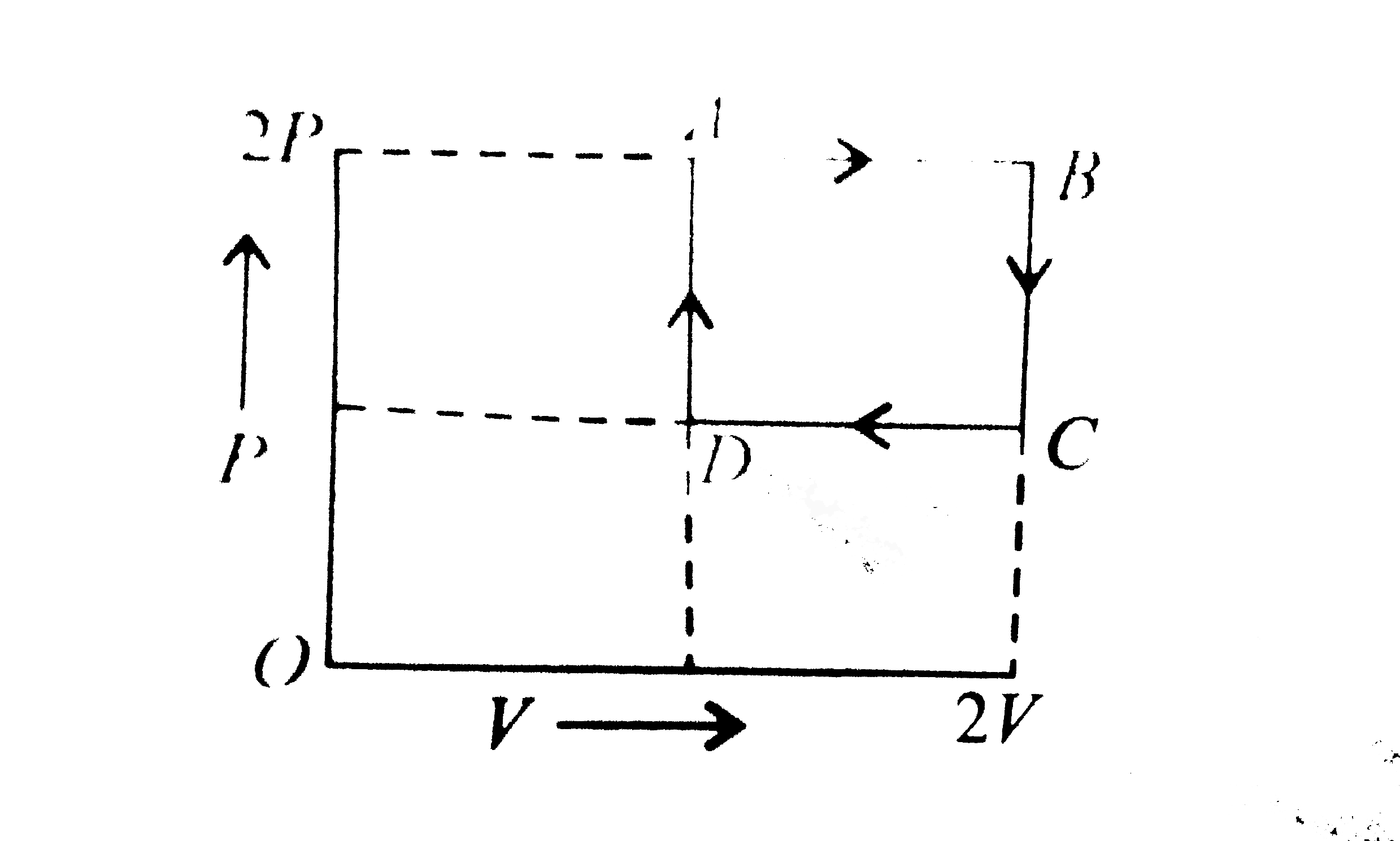
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY-THERMODYNAMICS-Exercises (Linked Comprehension)
- The state of a mole of an ideal gas changed from state A at pressure 2...
Text Solution
|
- The state of a mole of an ideal gas changed from state A at pressure 2...
Text Solution
|
- The state of a mole of an ideal gas changed from state A at pressure 2...
Text Solution
|
- The state of a mole of an ideal gas changed from state A at pressure 2...
Text Solution
|
- The second law of thermodynamics is a fundamental law of science. In t...
Text Solution
|
- The second law of thermodynamics is a fundamental law of science. In t...
Text Solution
|
- The second law of thermodynamics is a fundamental law of science. In t...
Text Solution
|
- A sample consisting of 1mol of a mono-atomic perfect gas (C(V) = (3)/(...
Text Solution
|
- A sample consisting of 1mol of a mono-atomic perfect gas (C(V) = (3)/(...
Text Solution
|
- A sample consisting of 1mol of a mono-atomic perfect gas (C(V) = (3)/(...
Text Solution
|
- A sample consisting of 1mol of a mono-atomic perfect gas (C(V) = (3)/(...
Text Solution
|
- Chemical reactions are invariably associated with the transfter of ene...
Text Solution
|
- Chemical reactions are invariably associated with the transfter of ene...
Text Solution
|
- Chemical reactions are invariably associated with the transfter of ene...
Text Solution
|
- Chemical reactions are invariably associated with the transfter of ene...
Text Solution
|
- Bond energies can be obtained by using the following relation: DeltaH ...
Text Solution
|
- Bond energies can be obtained by using the following relation: DeltaH ...
Text Solution
|
- Bond energies can be obtained by using the following relation: DeltaH ...
Text Solution
|
- Bond energies can be obtained by using the following relation: DeltaH ...
Text Solution
|
- Bond energies can be obtained by using the following relation: DeltaH ...
Text Solution
|