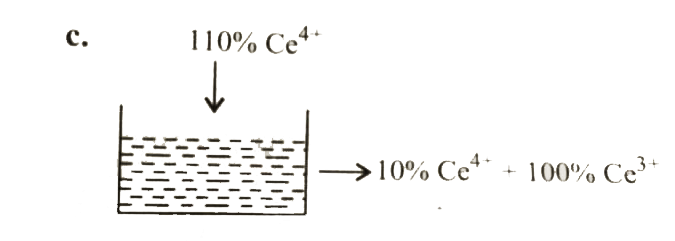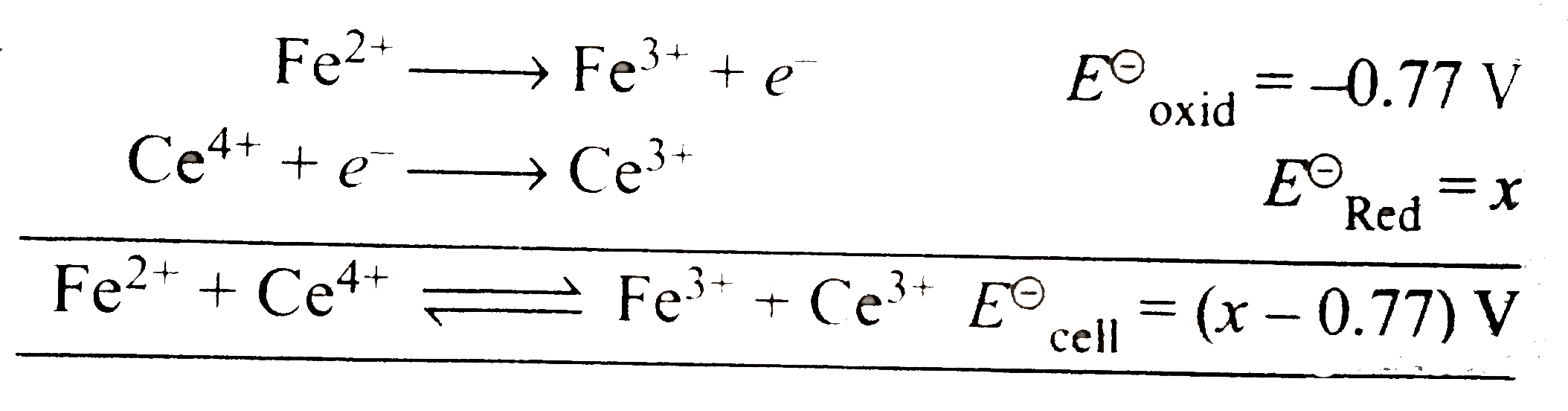Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTROCHEMISTRY
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Solved Examples(Electrolysis And Electrolytic Cells)|12 VideosELECTROCHEMISTRY
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Ex 3.1 (Objective)|28 VideosELECTROCHEMISTRY
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Archieves Subjective|35 VideosD AND F BLOCK ELEMENTS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Archives Subjective|29 VideosGENERAL PRINCIPLES AND PROCESS OF ISOLATION OF ELEMENTS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Archives (Subjective)|14 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY-ELECTROCHEMISTRY-Solved Examples (Electrochemical Cell)
- The EMF of the cell : Ag|Ag(2)CrO(4)(s),K(2)CrO(4)(0.1 M)||AgNO(3)(0...
Text Solution
|
- The EMF of a galvanic cell Pt|H(2)(1 atm)|HCl(1M)|Cl(2)(g)|Pt is 1.29V...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the potential of silver electrode in a saturated solution of...
Text Solution
|
- A solution of Fe^(2+) is titrated potentiaometrically using Ce^(4+) so...
Text Solution
|
- Find the EMF of the cell at 25^(@)C. E^(c-).(red("quinhydrone elec...
Text Solution
|
- The EMF of the following cell is found to be -0.46V: If the stan...
Text Solution
|
- The EMF of the following cell is observed to be 0.118V at 25^(@)C: ...
Text Solution
|
- Find the standard electrode potential of I(2)|2I^(c-) if the equilibri...
Text Solution
|
- A silver electrode dipping in AgNO(3) solution (0.1M) is combined salt...
Text Solution
|
- The EMF of a galvanic cell composed of two hydrogen electrodes is 177 ...
Text Solution
|
- The EMF of the cell : Pt|Ce^(4+)(90%),Ce^(3+)(10%)| Normal calomel...
Text Solution
|
- A hydrogen electrode placed in a buffer solution of sodium cyanide and...
Text Solution
|
- Two electrochemical cells are assembled in which the following reactio...
Text Solution
|
- Predict whether or not Cl(2) would disproportionate in cold alkaline m...
Text Solution
|
- What would be the electrode potential of a silver electrode dipped in ...
Text Solution
|
- E^(c-) of some elements are given as : {:(I(2)+2e^(-)rarr 2I^(c-),,,...
Text Solution
|
- Select the spontaneous rreactions from the changes given below a. Sn...
Text Solution
|
- Two metals M(1) and M(2) have E^(c-).(red)=-0.76 V and 0.80V, respecti...
Text Solution
|
- Determine whether O(2)(g) can oxidize sulphate (SO(4)^(2-)) ion to pe...
Text Solution
|
- Quinones are good electron acceptors, party because reduction restores...
Text Solution
|