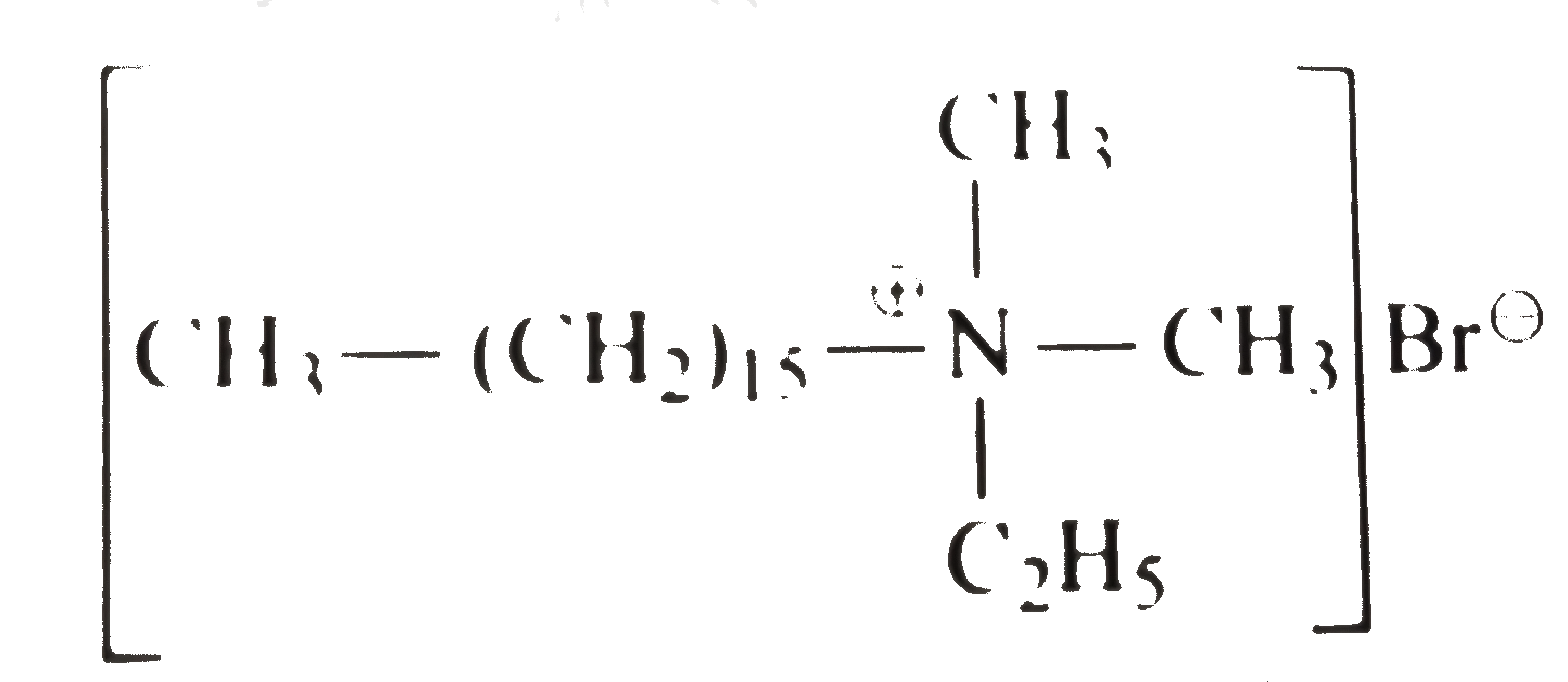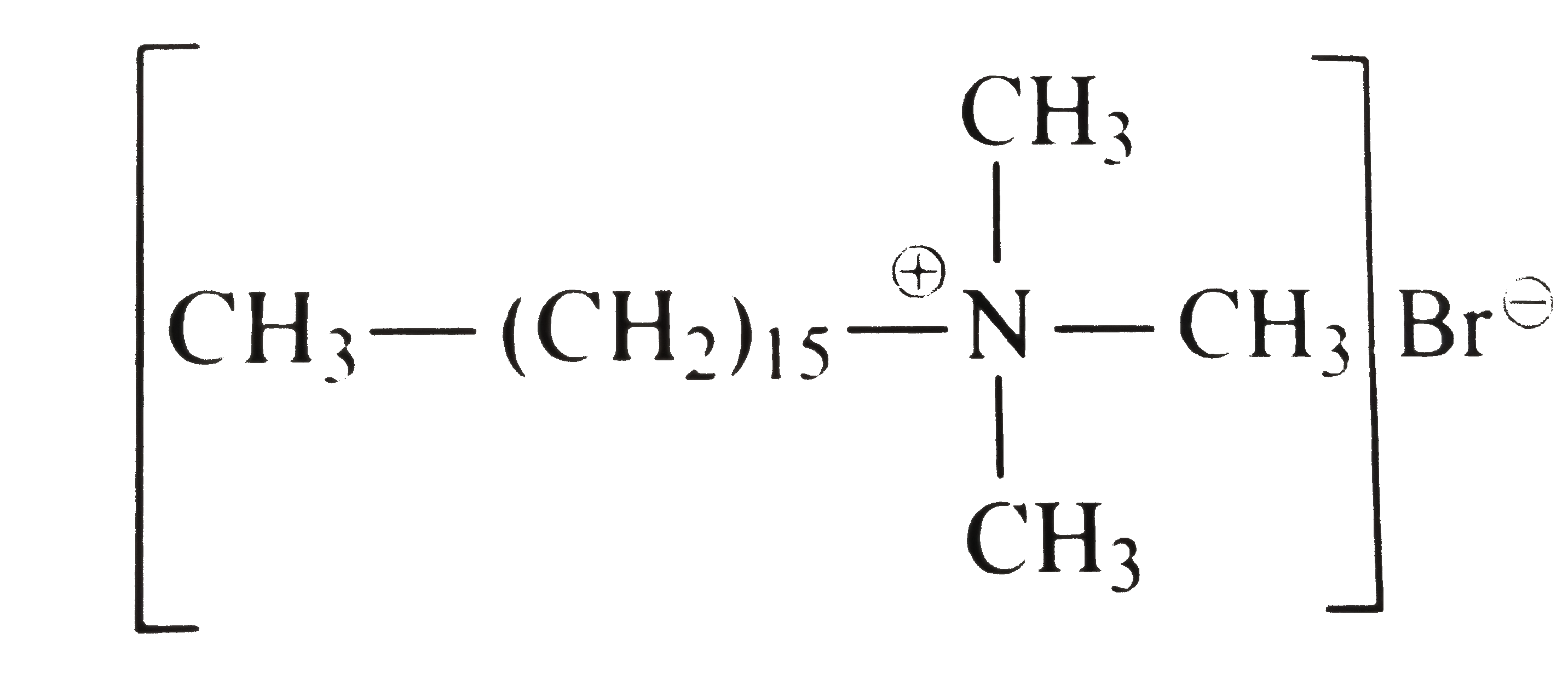Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
CLASSIFICATION AND NOMENCLATURE OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Exercises|10 VideosCLASSIFICATION AND NOMENCLATURE OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Concept Application Type|7 VideosCLASSIFICATION AND NOMENCLATURE OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Analytical and Descriptive Type|3 VideosCHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Archives (Subjective)|11 VideosGENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Analytical and Descriptive|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY-CLASSIFICATION AND NOMENCLATURE OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS-Solved Example
Text Solution
|
- 1.6-Diethy1 cyclohexene 2. 4-Hydrocy-5-isopropy1 hept-6-yn-2-one 3...
Text Solution
|
- Write the correct name of the following : 1. Pent-1-yn-5-ol 2. 2-E...
Text Solution
|
- Write the structure of cety ethy1 dimethy1 ammonium bromide, a compoun...
Text Solution
|
- Write the structure (s) of the simplest alkane (s), with fewest number...
Text Solution
|