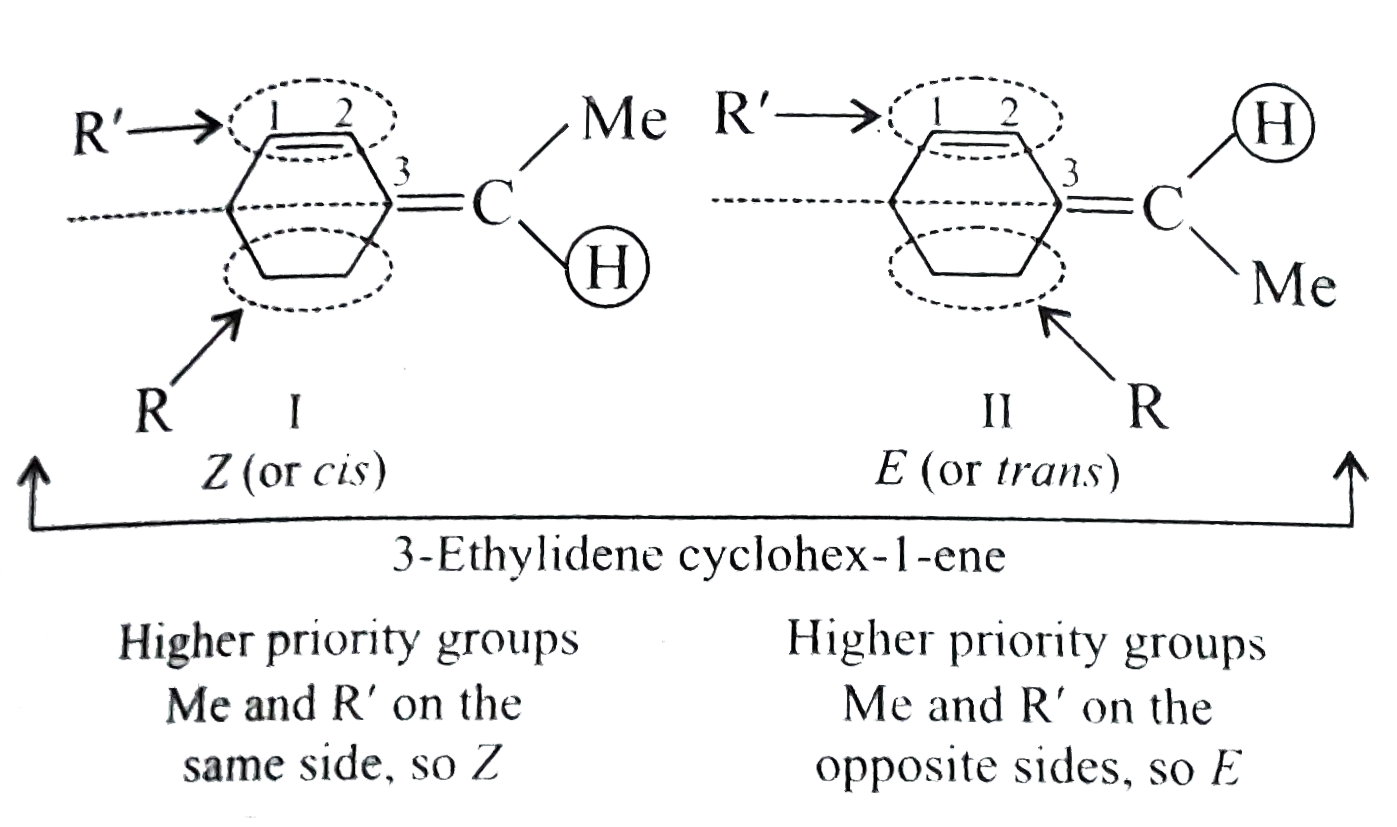
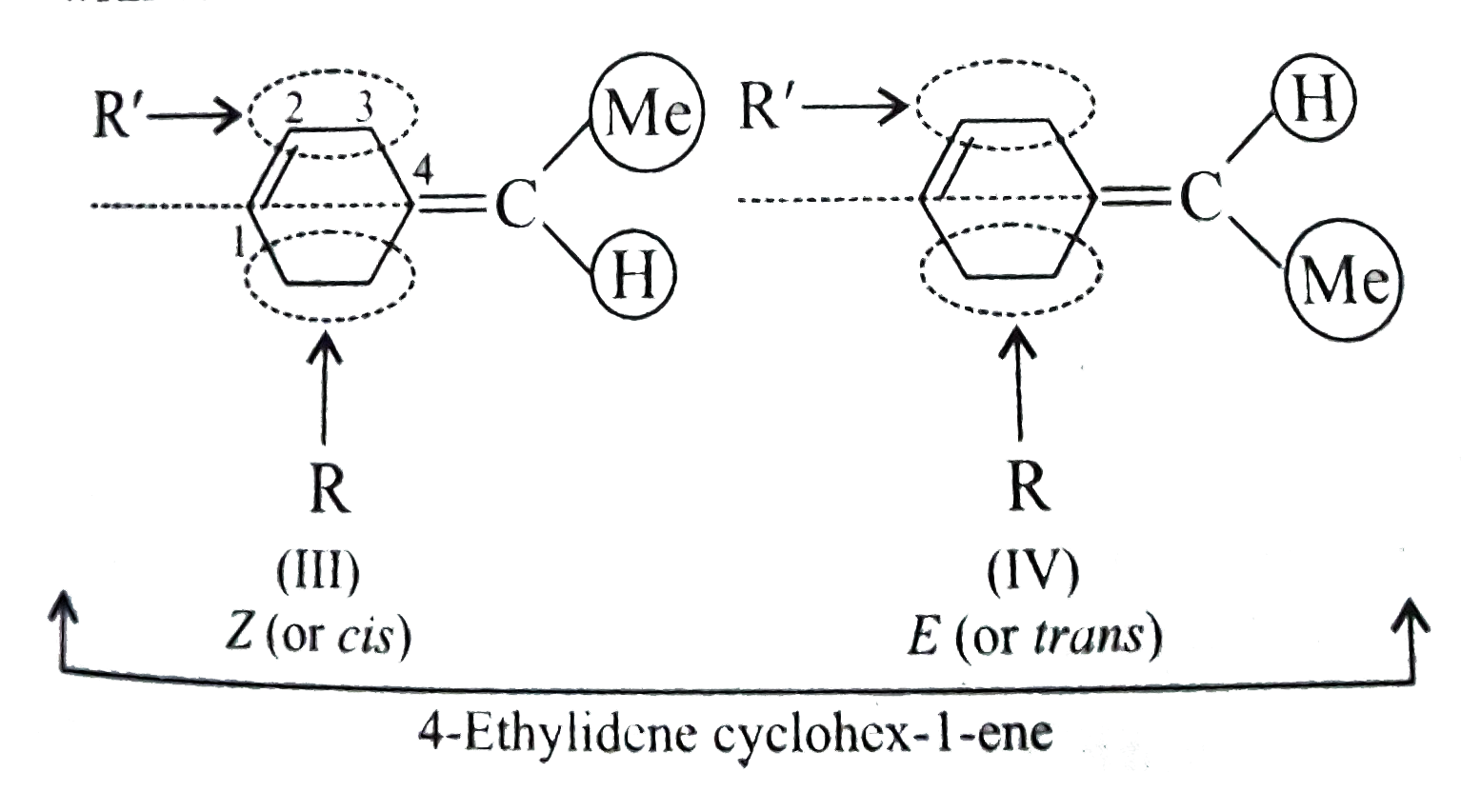
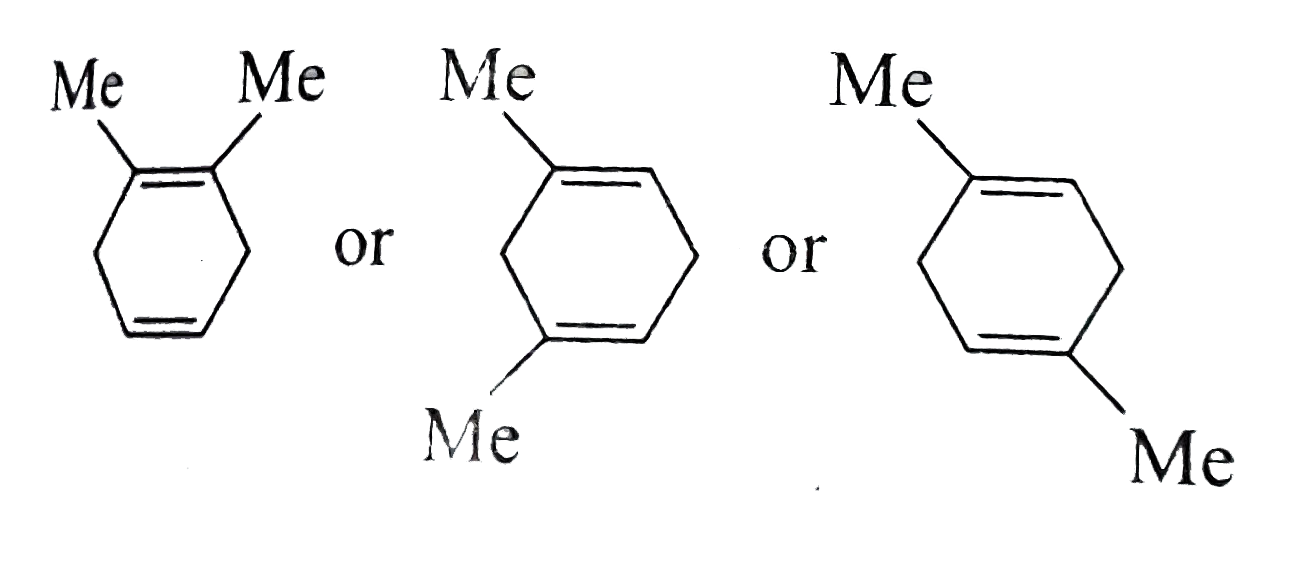
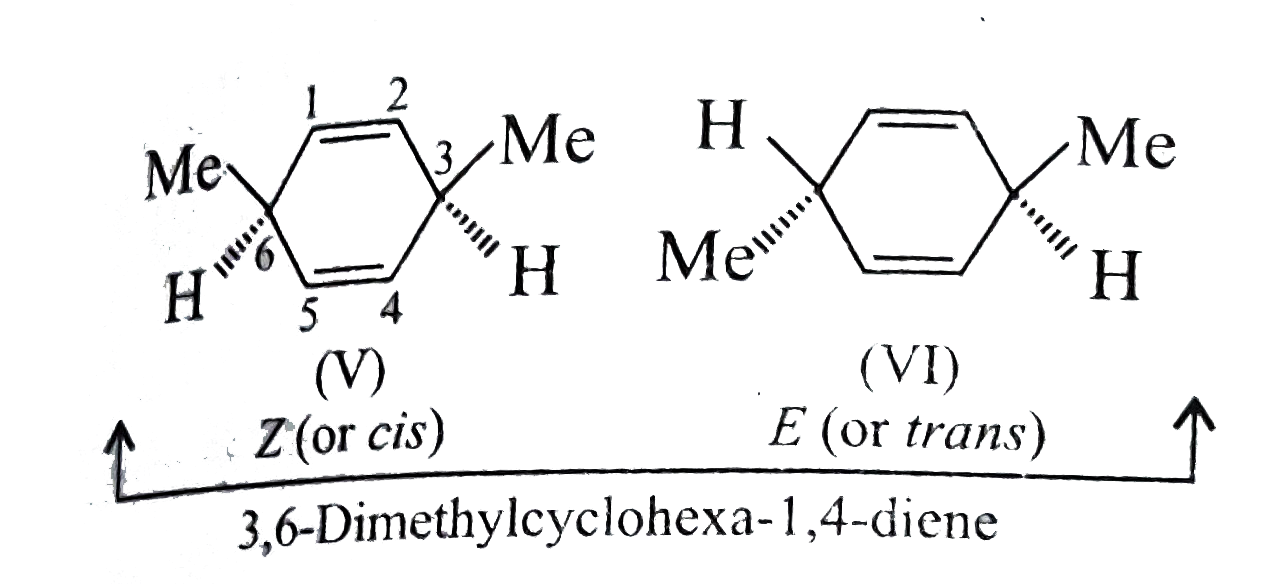Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ISOMERISM
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Exercise|19 VideosISOMERISM
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise (Linked Comprehension Type)Exercise|14 VideosISOMERISM
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Assertion-Reasoning Type|1 VideosIONIC EQUILIBRIUM
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Archives Subjective|28 VideosNCERT BASED EXERCISE
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Chemical Equilibrium|72 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY-ISOMERISM-Example
- State whether the following statements are true or false. a. D and L...
Text Solution
|
- a. Write the stable tautomer form the following: b. Explain why a...
Text Solution
|
- Some possible structrues of a compound A (C(10)H(16)) are: Write...
Text Solution
|
- Some possible structrues of a compound A (C(10)H(16)) are: Wri...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the compound (A) given below: a. Give the total number o...
Text Solution
|
- How many geometrical isomers are possible for the following? a. Deca...
Text Solution
|
- How many geometrical isomers are possible for the following ? a. 1,2-...
Text Solution
|
- How many geometrical isomers are possible for the following compounds:...
Text Solution
|
- How many isomaric dienes with a six-membered ring are possible of the ...
Text Solution
|
- Give the name and structrues of six C atom cyclic diene with lowest mo...
Text Solution
|
- Give the structural formula of an unsaturated hydrocarbon with the low...
Text Solution
|
- Give the structural formula of a cyclic alkyne with the lowest number ...
Text Solution
|
- Give the type of isomerism exhibited by each of the following pairs: ...
Text Solution
|
- 2,2'- Dofluoro-6,6'-dimethylbiphenyl is non-resolvable, whereas 2,2'- ...
Text Solution
|
- What is the observed rotation when 0.1 M solutions of (R )-2 butanol i...
Text Solution
|