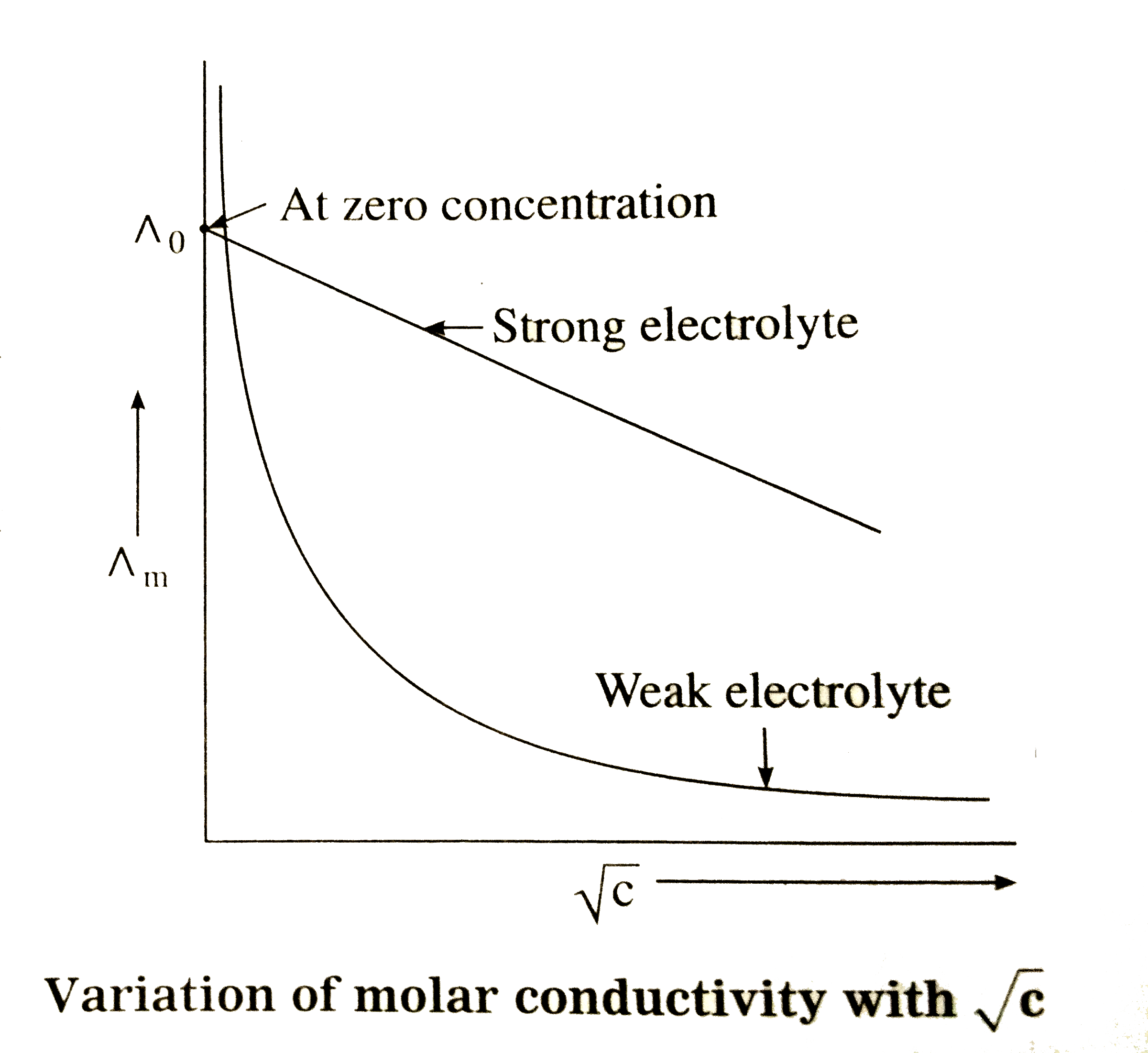Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- How is the molar conductivity of strong electrolytes at zero concentra...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion A: The molar conductance of weak electrolyte is low as compa...
Text Solution
|
- Define molar conductivity of a solution and explain how molar conducti...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the variation of molar conductivity with concentration for str...
Text Solution
|
- How is the molar conductivity of strong electrolytes at zero concentra...
Text Solution
|
- मोलर चालकता सान्द्रता के साथ किस प्रकार बदलती है? (i) दुर्बल विद्युत...
Text Solution
|
- How is molar conductivity related to concentration of the electrolyte ...
Text Solution
|
- (A): The molar conductance of weak electrolytes is low as compared to ...
Text Solution
|
- How does molar conductivity vary with concentration for weak and stron...
Text Solution
|