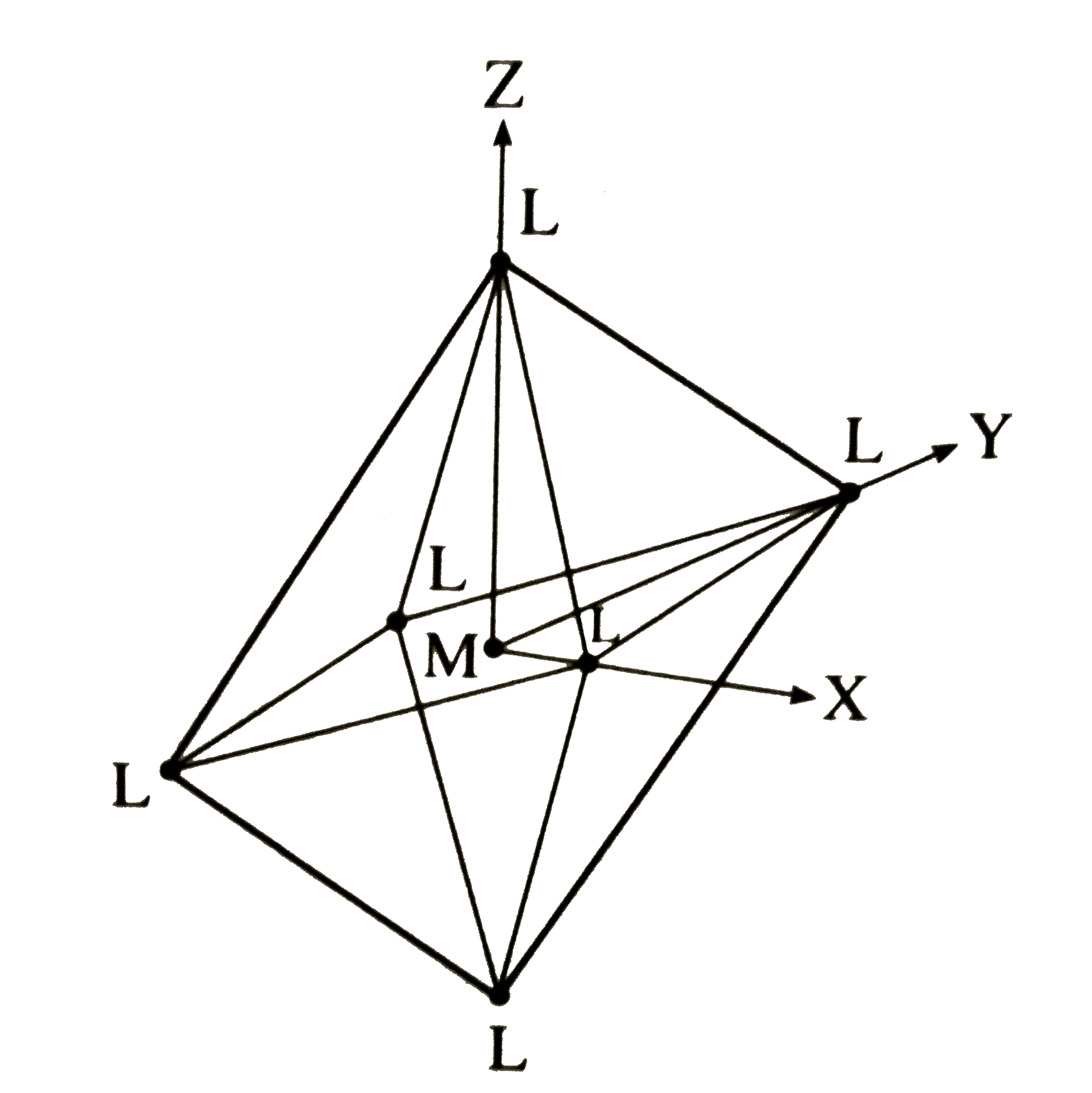
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Explain the octablral geometry of complexes using crystal field ...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the violet colour of the complex [Ti(H(2)O)(6)]^(3+) on the ba...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the octablral geometry of complexes using crystal field theory...
Text Solution
|
- क्रिस्टल क्षेत्र सिद्धान्त को समझाइए |
Text Solution
|
- क्रिस्टल क्षेत्र सिद्धान्त को समझाइए।
Text Solution
|
- Crystal field theory|oxidation state of elements| tetrahedral| octahed...
Text Solution
|
- Using crystal field theory, explain the colour of the coordination com...
Text Solution
|
- Explain about crystal field theory.
Text Solution
|
- According to crystal field theory, the M-L bond in a complex is
Text Solution
|