Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
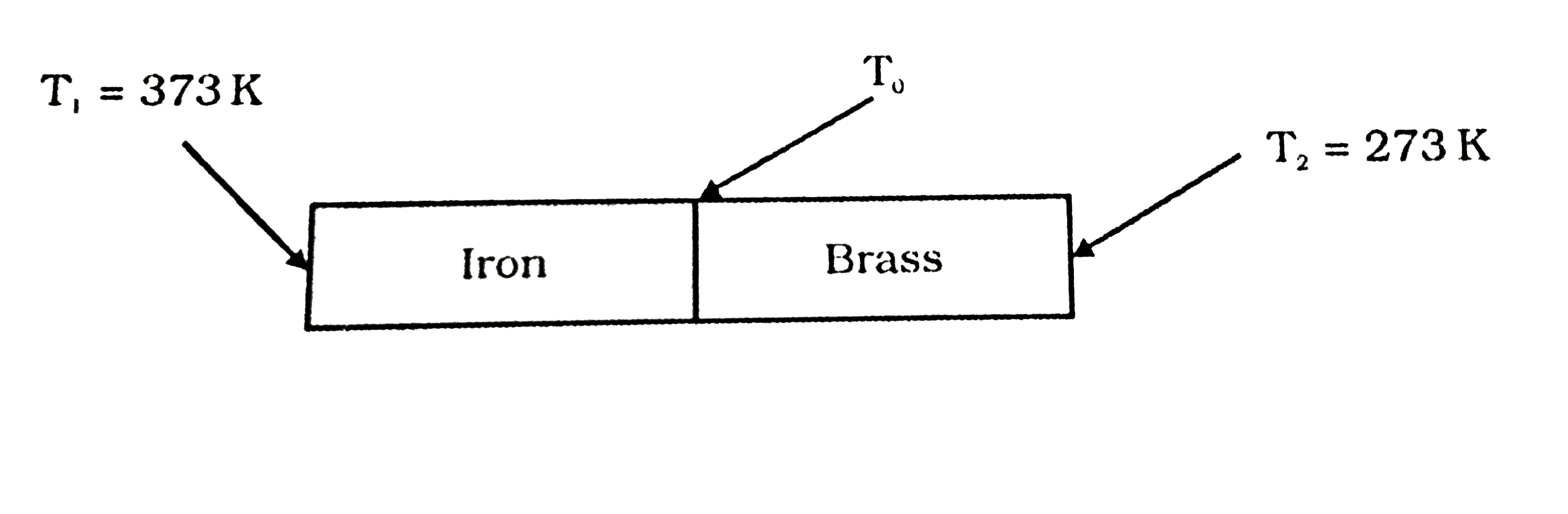
- An iron bar (L(1) = 0.1 m, A(1) = 0.02 m^(2), K(1) = 79 W m^(–1) K^(–1...
Text Solution
|
- An iron bar ( L(1) = 0.1 m, A(1) = 0.02 m^(2) , K(1) = 79 Wm^(-1) K^(-...
Text Solution
|
- If L(1) = (3.03 +- 0.02)m and L(2) = (2.01 +- 0.02)m then L(1) + 2L(2)...
Text Solution
|
- चित्र 11.16 में दर्शाए अनुसार लोहे की किसी छड़ (L1 = 0.1m , A1 = 0...
Text Solution
|
- if (5x^(2) +2)/(x^(3)+x)=(A(1))/(x)+(A(2)x+A(3))/(x^(2)+1), then (A(...
Text Solution
|
- यदि bar(a)=l(1)bar(i)+m(1)bar(j)+n(1)bar(k) और bar(b)=l(2)bar(i)+m(2)b...
Text Solution
|
- चित्र में दर्शाए अनुसार लोहे की किसी छड़ (L(1) "=0.1 m ",A(1) =0.02 m^(...
Text Solution
|
- लोहे की किसी छड़ (L(1) "=0.1 m ",A(1) =0.02 m^(2) ,K(1) = 79 Wm^(-1)K^(...
Text Solution
|
- लोहे की किसी छड़ (L(1) "=0.1 m ",A(1) =0.02 m^(2) ,K(1) = 79 Wm^(-1)K^(...
Text Solution
|