Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
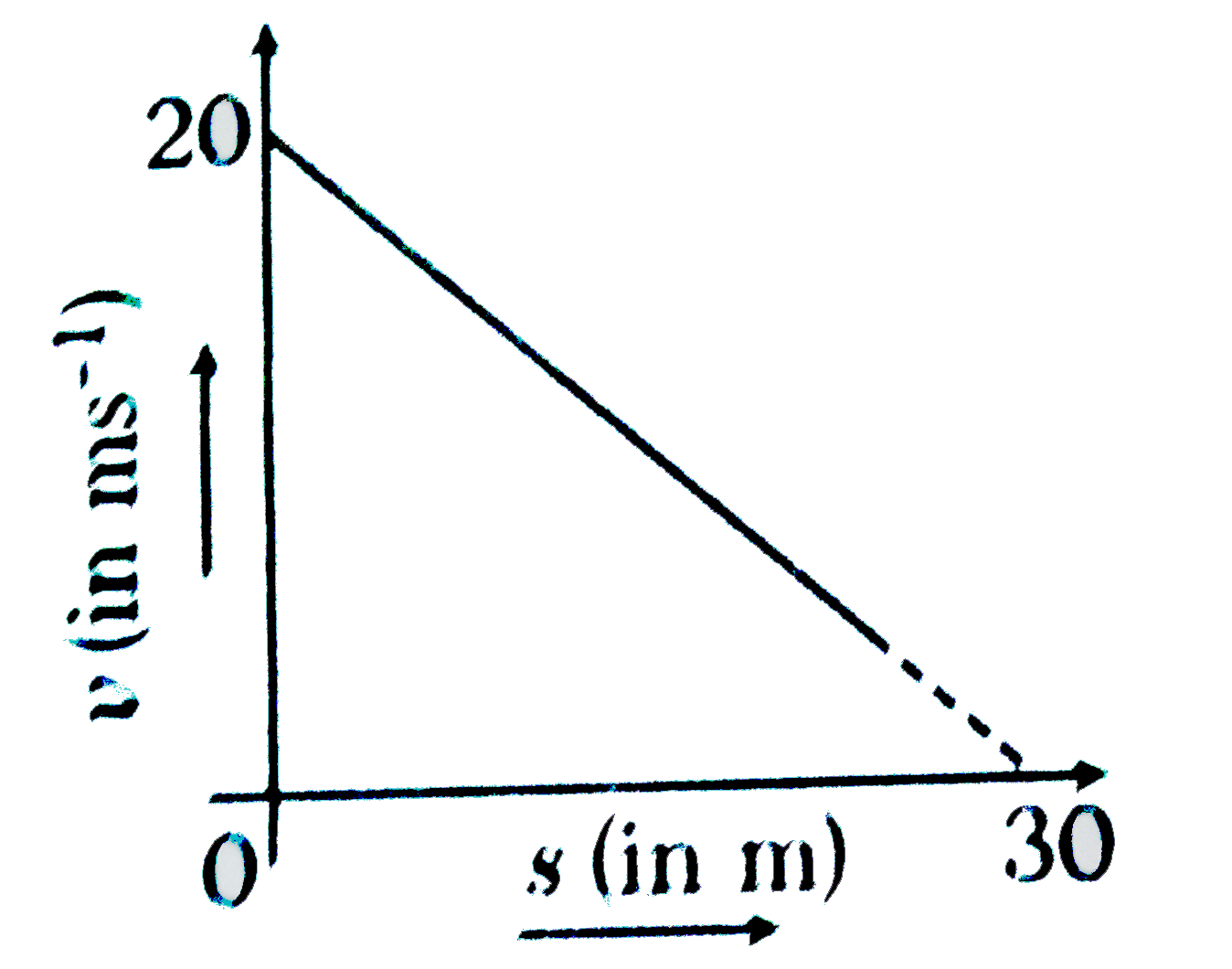
- If the velocity v of particle moving along a straight line decreases l...
Text Solution
|
- Velocity of a particle moving in a straight line varies with its displ...
Text Solution
|
- If the velocity v of a particle moving along a straight line decreases...
Text Solution
|
- The acceleration (a) of a particle moving in a straight line varies wi...
Text Solution
|
- If the velocity v of a particle moving along a straight line decreases...
Text Solution
|
- Acceleration (a) -displacement (s) graph of a particle moving in a str...
Text Solution
|
- A particle moving in a straight in a straight line has velocity and di...
Text Solution
|
- For a particle moving along a straight line, its velocity 'v' and disp...
Text Solution
|
- Adjacent graph is drawn for particle along straight line motion, where...
Text Solution
|