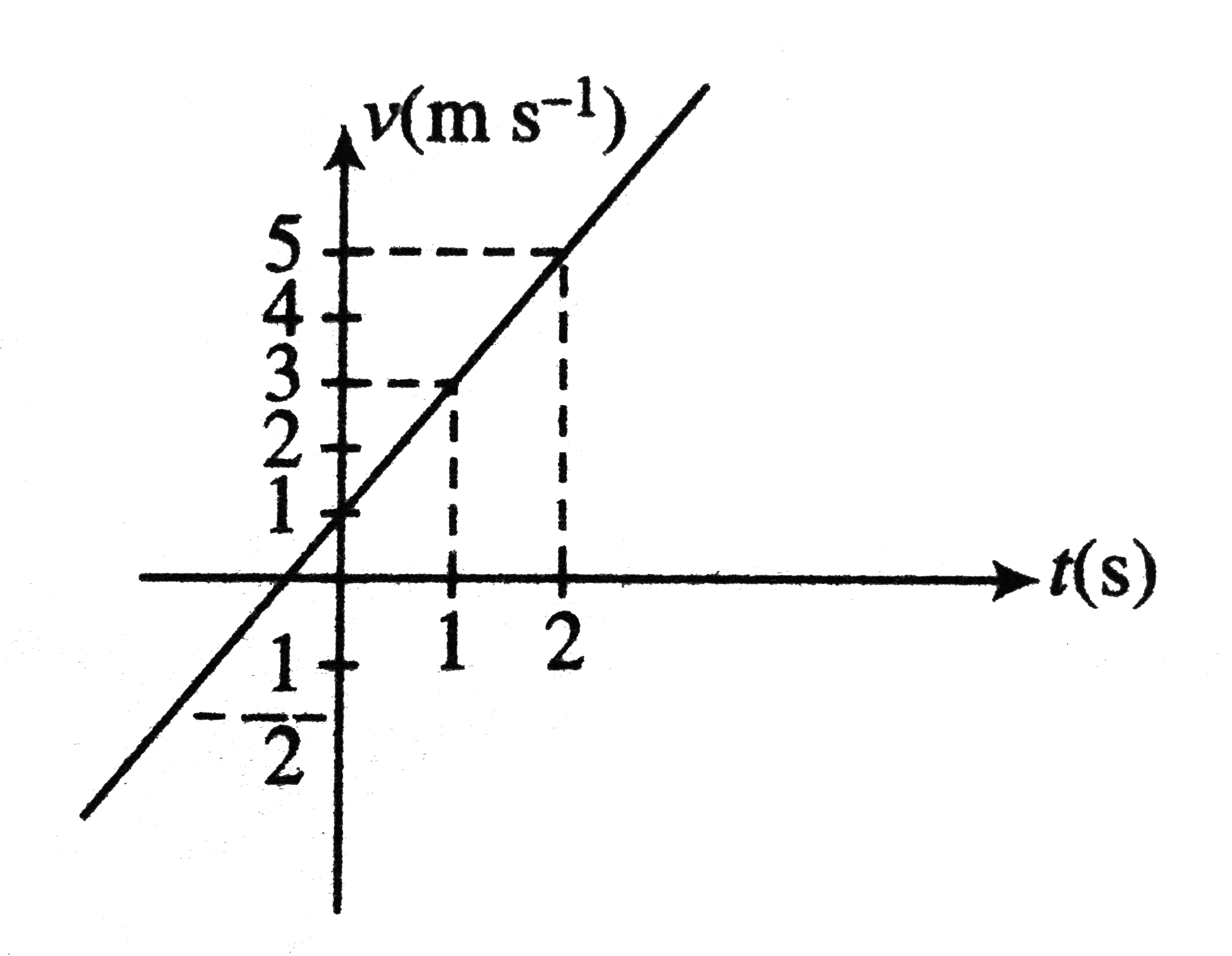
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
BASIC MATHEMATICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Exercise 2.3|2 VideosBASIC MATHEMATICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Exercise 2.4|6 VideosBASIC MATHEMATICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Exercise 2.1|2 VideosARCHIVES 2 VOLUME 6
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Integer|4 VideosCALORIMETRY
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Solved Example|13 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems