Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-KINEMATICS-1-Solved Examples
- A particle moving with uniform acceleration along a straight line ABC ...
Text Solution
|
- A balloon in ascending vertically with an acceleration of 1 ms^(-2). T...
Text Solution
|
- A rebber ball is released from a height aboout 1.5 m. If is caught aft...
Text Solution
|
- Determined to test the law of gravity for himself. A student walkd off...
Text Solution
|
- A student is running at her top speed of 5.0 m s^(-1), to catch a bus,...
Text Solution
|
- A particle retards from a velocity v(0) while moving in a straight lin...
Text Solution
|
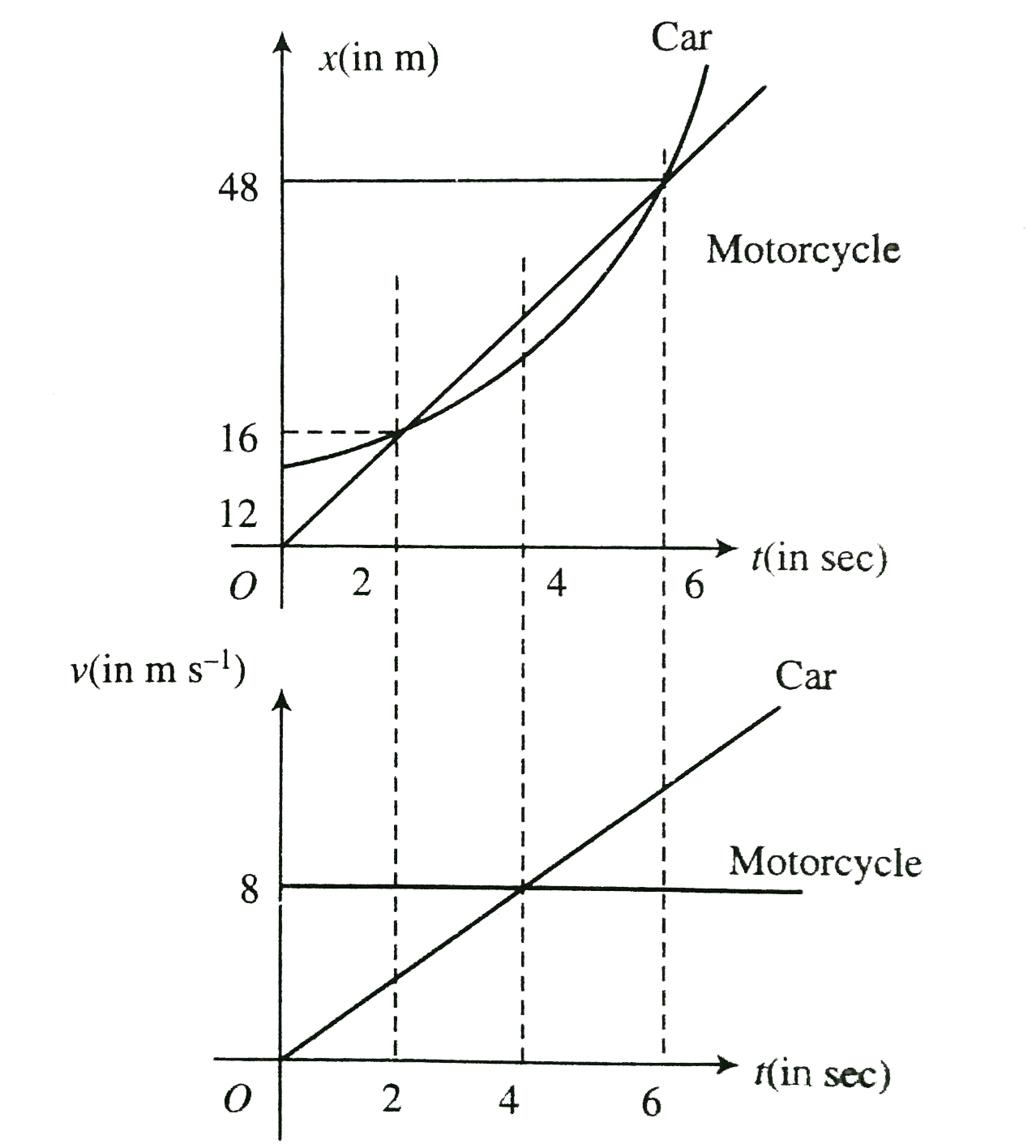
- A motorcyclist situated at origin is located at a distance 12 m. Behin...
Text Solution
|
- A diwali rocket moves vertically up with a constant acceleration a(1) ...
Text Solution
|
- A ball (A) is thrown straight upfrom the edge the roof of a building. ...
Text Solution
|
 .
.  .
.