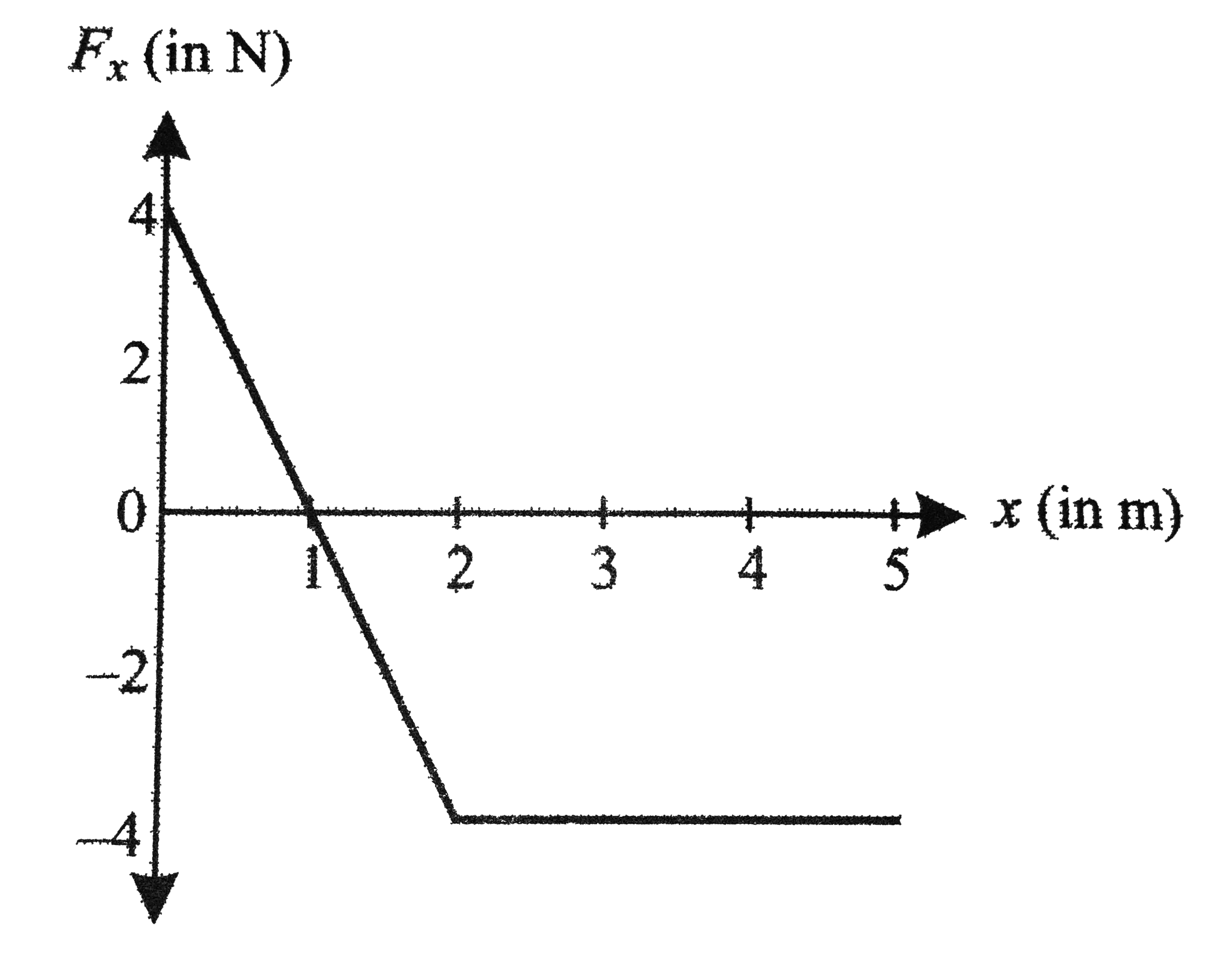
Kinetic energy of the body at `x=0` is
`K_1=1/2xx2.0xx(4.0)^2=16.0J`
Work done by the force on the body is given by the area bounded by the curve and x-axis in figure. From `x=0` to `x=1.0m`, the force decreases linearly from `F_x=4N` to `0`, but it is directed along positive x-axis. Work done by the force is positive. For `1.0mltxle5.0m`, the force is negative, so it is directed along the negative x-axis for any interval in this region. the work done by the force will be negative.
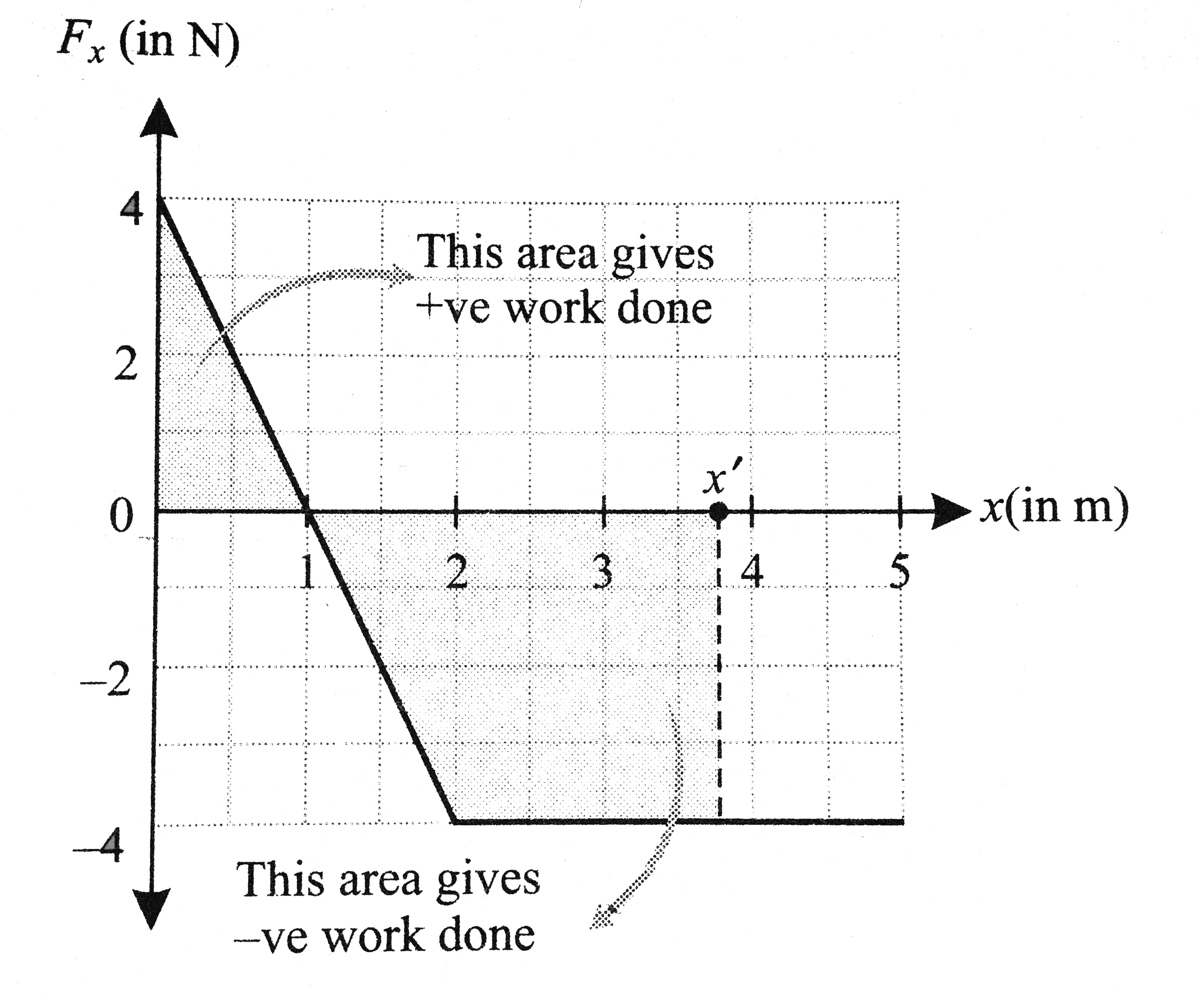
a. From `x=0` to `3.0m`, work done by the force on the body
=Area of `F_x-x` diagram between `x=0` to `x=3.0m` region in figure.
`1/2xx4xx1.0-1/2xx4xx1.0-4xx1.0=-4.0Nm=-4.0J`
Let the kinetic energy of the body at `x=3.0m` be `K_3`. From the work-energy theorem, `W=DeltaK`.
`-4.0=K_3-16.0JimpliesK_3=12.0J`
b. Let the kinetic energy of the body be `8.0J` at `x=x^'`.
From `x=0` to `x^'`, work done by the force=Area of the graph between `x=0` to `x^'` shown in figure, i.e.,
`1/2xx4xx1.0-1/2xx4xx1.0-4xx(x^'-2.0)Nm=-4xx(x^'-2.0)J`
Using the work-energy theorem, we get
`-4xx(x^'-2.0)=8.0-16.0(sumW=K_2-K_1)`
`x^'=4.0m`
Incidentally, in the diagram, `x^'` has been drawn between `3.0m` and `4.0m`. You must not infer from this that `x^'` lies between `3.0m` and `4.0m`
c. From `x=0` to `5.0m`, when the work done by the force is positive, kinetic energy of the block increases. Subsequently, when the work done by the force is negative, kinetic energy of the block decreases. Then, clearly, the kinetic energy of the block is maximum at `x=1.0m`. Using the work-energy theorem again, we get
`1/2xx4xx1.0=K_(max)-K_1`
`K_(max)=K_1+2.0=16.0+2.0=18.0J`