Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-WORK, POWER & ENERGY-Archives (integer)
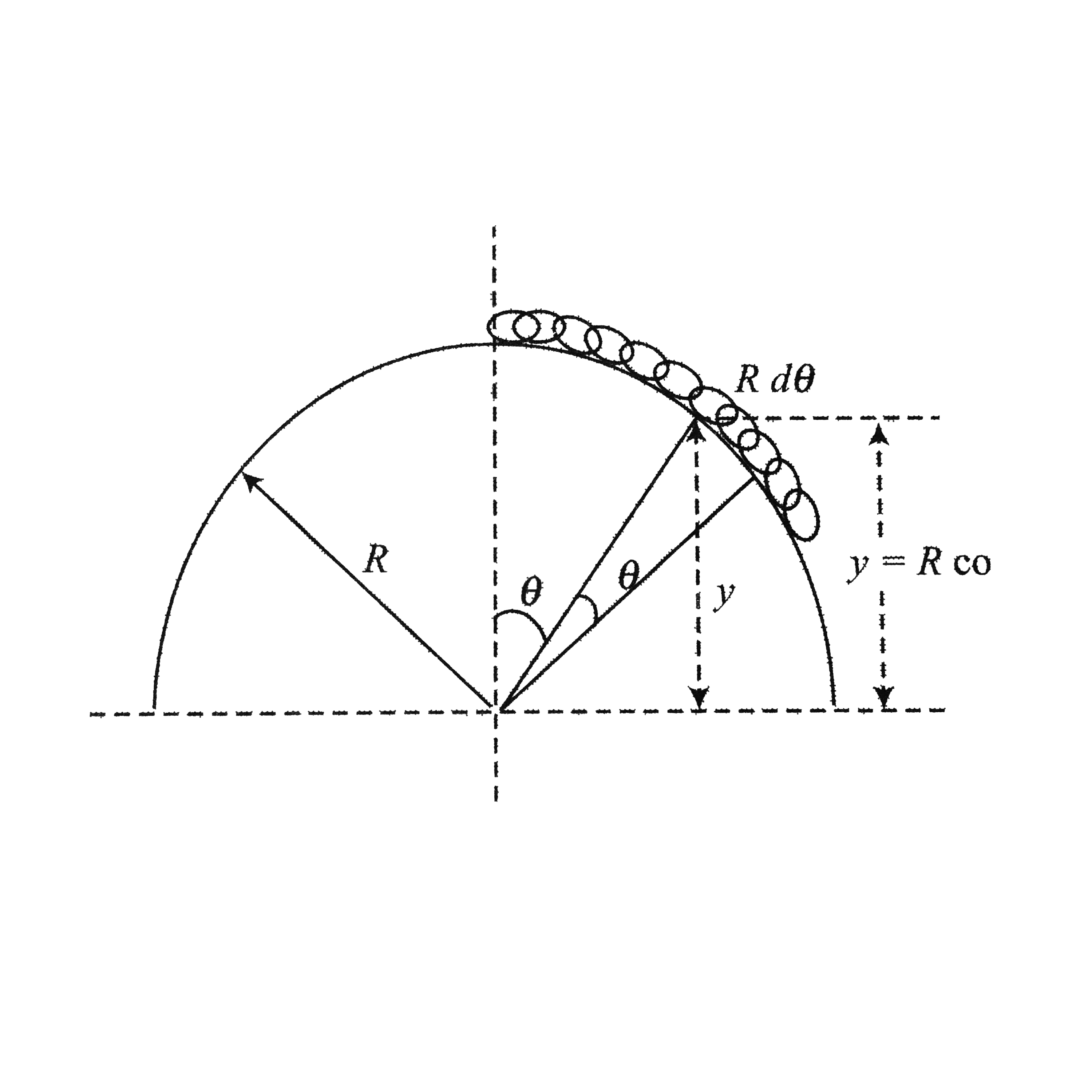
- A chain of length l and mass m lies of the surface of a smooth hemisph...
Text Solution
|
- A light inextensible string that gas over a smooth fixed pulley as sho...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 0.18 kg is attached to a spring of force-constant 2 N/...
Text Solution
|
- A bob of mass m, suspended by a string of length l1 is given a minimum...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass 0.2 kg is moving in one dimension under a force tha...
Text Solution
|