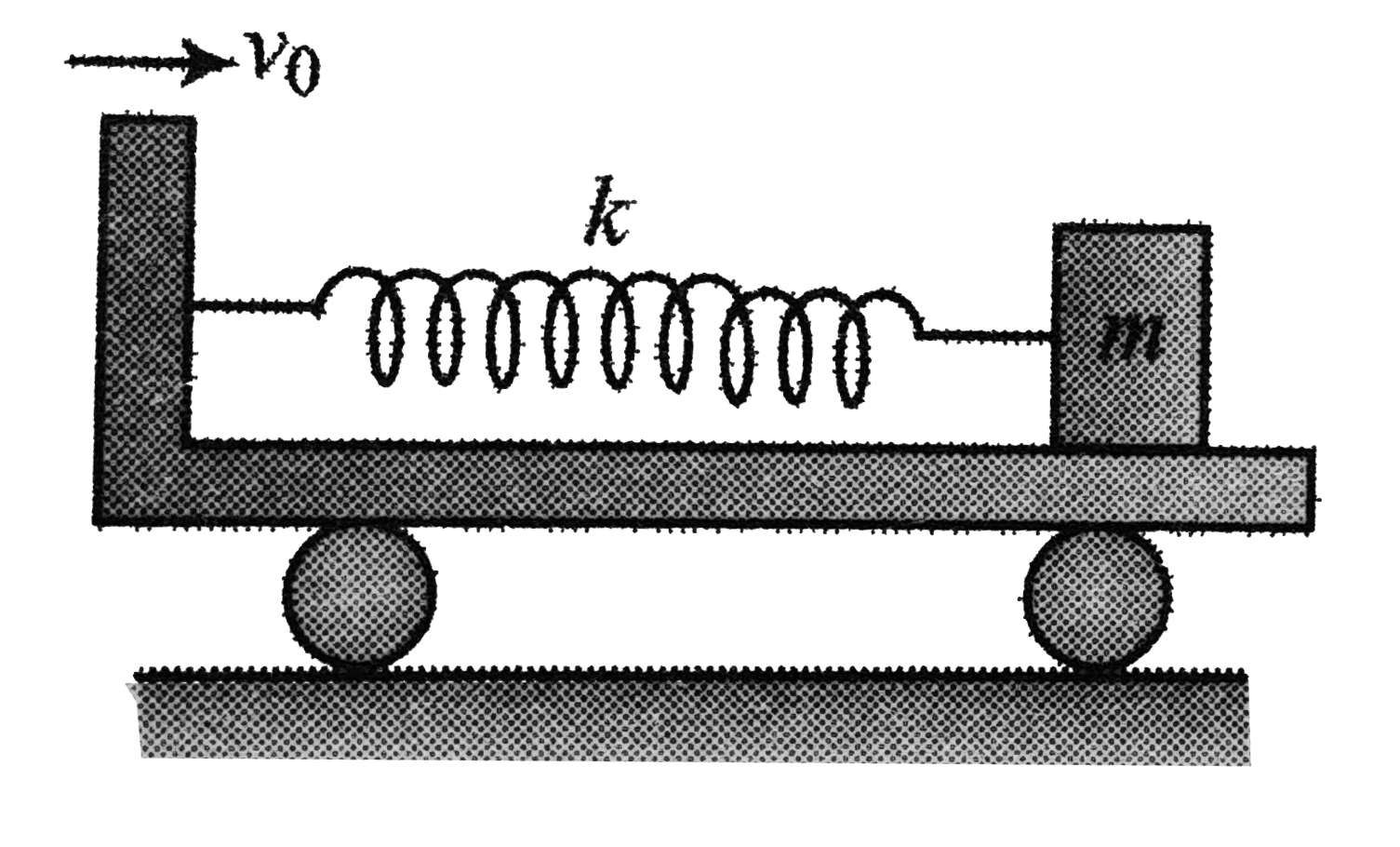
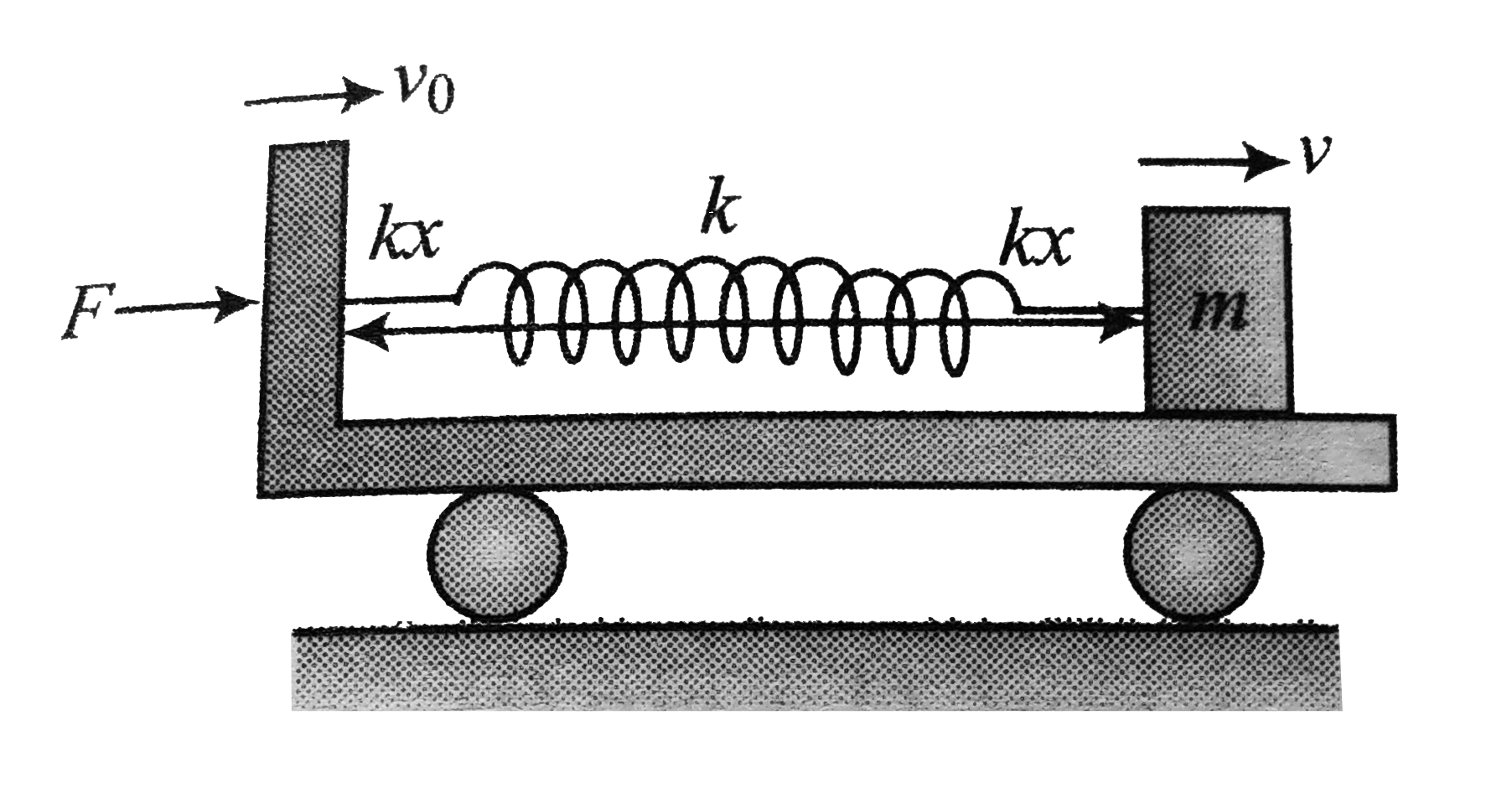
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-WORK, POWER & ENERGY-Solved Examples
- Figure. A smooth circular path of radius R on the horizontal plane whi...
Text Solution
|
- A string with one end fixed on a rigid wall, passing over a fixed fric...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is slowly pulled along a curved surface from positio...
Text Solution
|
- A vertical rod of mass m is kept on a wedge of mass M. If a horizontal...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform chain of mass m and length l is at the verge of sliding unde...
Text Solution
|
- Block of mass m are released from rest and they slide down the incline...
Text Solution
|
- A horizontal plane supports a plank with a bar of mass m placed on it ...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical blocks A and B, each of mass m=2kg are connected to the ...
Text Solution
|
- A small bar A resting on a smooth horizontal plane is attached by thre...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is connected rigidly with a smooth wedge (plank) by ...
Text Solution
|
- A block A of mass m=5kg is attached with a spring having force constan...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is suspended vertically from a point O by an inextensible m...
Text Solution
|
- A loop of mass M with two identical rings of mass m at its top hangs f...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is projected up with a velocity v0 along an inclined...
Text Solution
|
- A spherical balll of mass m is the highest point in the space between ...
Text Solution
|