Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-WORK, POWER & ENERGY-Subjective
- A small block of mass m=1kg is attached with one end of the spring of ...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical beads, each of m=100g, are connected by an inextensible ...
Text Solution
|
- AB is a quarter of smooth circular track of radius R=6m. A particle P ...
Text Solution
|
- In an ideal pulley particle system, mass m2 is connected with a vertic...
Text Solution
|
- Given k1=1500Nm^-1, k2=500Nm^-1, m1=2kg, m2=1kg. Find: a. potenti...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is dropped onto a spring of constant k from a height...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m attached with a massless spring natural length l ...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks having masses 8kg and 16kg are connected to the two ends of...
Text Solution
|
- a. A 2-kg situated on a smooth fixed incline is connected to a spring ...
Text Solution
|
- A ring of mass m=1kg can slide over a smooth vertical rod. A light str...
Text Solution
|
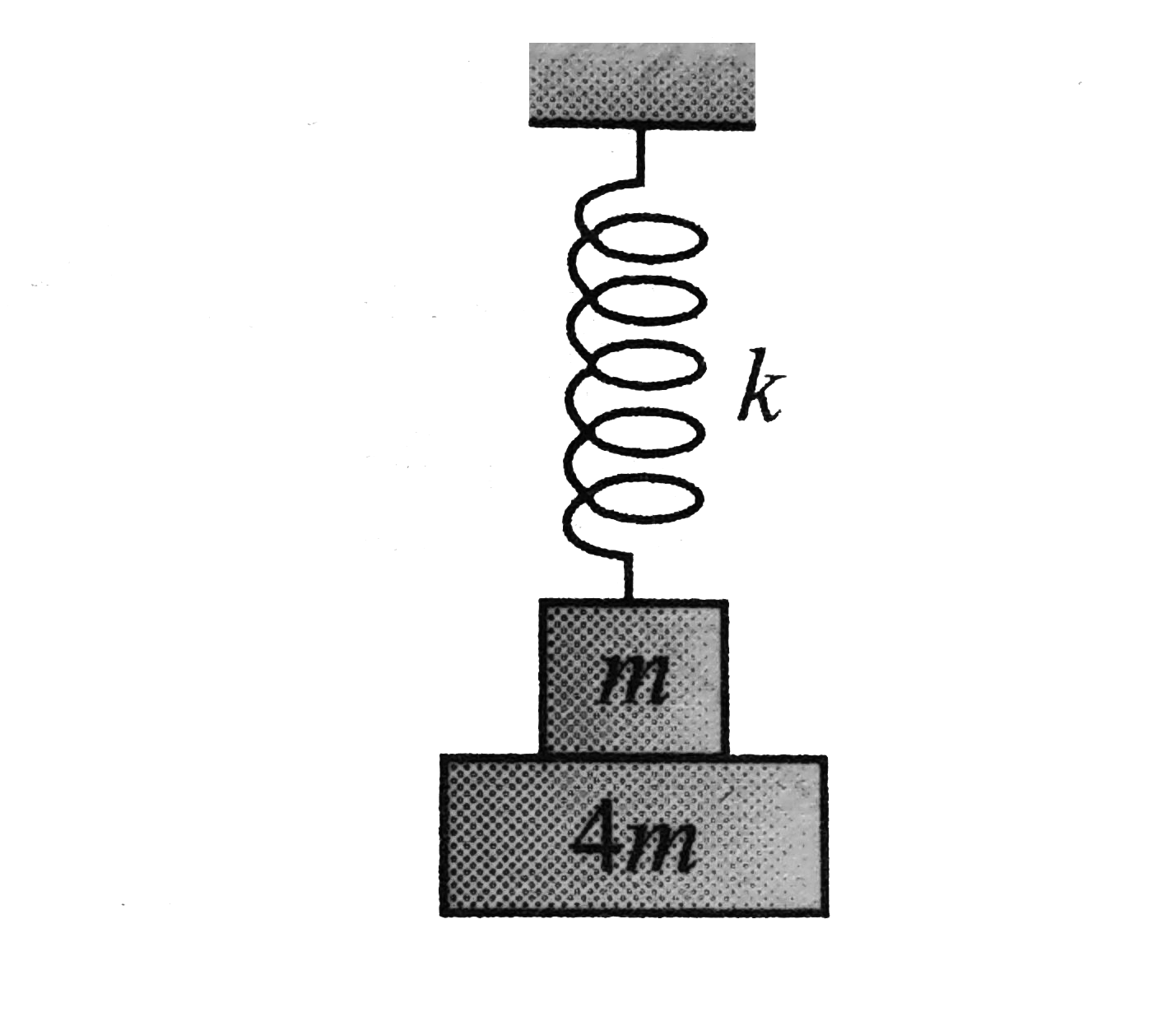
- Find how much mass m will rise if 4m falls away. Blocks are at rest an...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is released from rest onto a spring. A having stiffn...
Text Solution
|
- In figure, the light spring is of force constant k and is on a smooth ...
Text Solution
|
- A vehicle of mass m starts moving along a horizontal circle of radius ...
Text Solution
|
- A block A of mass m is held at rest on a smooth horizontal floor. A li...
Text Solution
|
- A constant force F pushes the block m till the wedge M starts sliding....
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks are connected by a massless string that passes over a frict...
Text Solution
|
- A bob of mass m is projected with a horizontal velocity v=sqrt((gl)/(...
Text Solution
|
- A block is projected with a speed v0 such that it strikes the point of...
Text Solution
|
- A small ball is suspended from point O by a thread of length l. A nail...
Text Solution
|