A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-WORK, POWER & ENERGY-Single Correct
- A block of mass m has initial velocity u having direction towards +x a...
Text Solution
|
- A moving railway compartment has a spring of constant k fixed to its f...
Text Solution
|
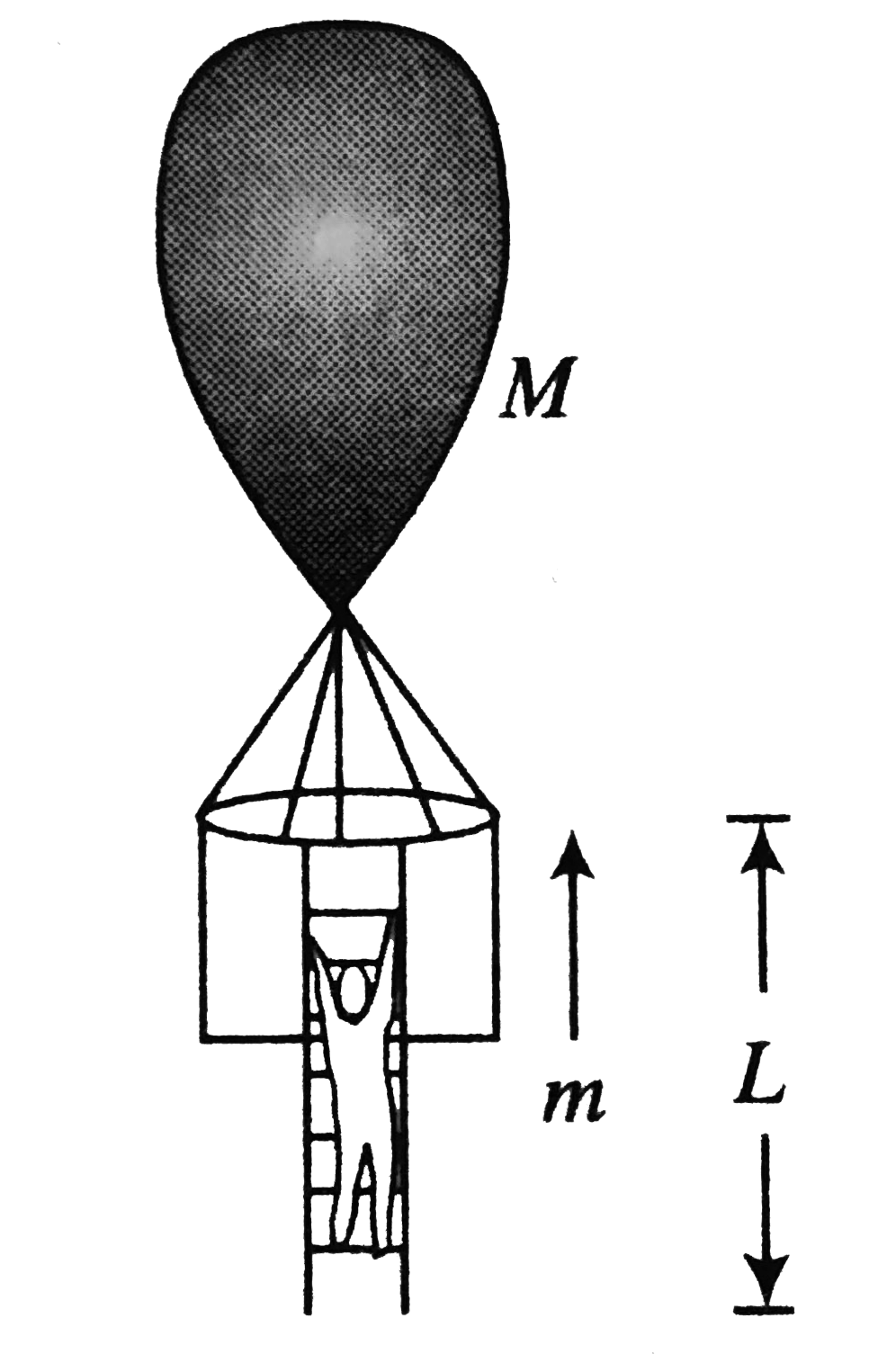
- A rope ladder of length L is attached to a balloon of mass M. As the m...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is lying at rest at point P of a wedge having a smoo...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a smooth vertical circular track AB of radius R. A block ...
Text Solution
|
- A bead of mass m is released from rest at A to move along the fixed sm...
Text Solution
|
- A simple pendulum consisting of a mass M attached to a string of lengt...
Text Solution
|
- Two bodies of masses m and 4m are attached to a light string as shown ...
Text Solution
|
- A 500-kg car, moving with a velocity of 36kmh^-1 on a straight road un...
Text Solution
|
- Two spring P and Q having stiffness constants k1 and k2(ltk1), respect...
Text Solution
|
- In the above question, if equal forces are applied on two springs, the...
Text Solution
|
- Water is drawn from a well in a 5kg drum of capacity 55L by two ropes ...
Text Solution
|
- A bead of mass 1/2 kg starts from rest from A to move in a vertical pl...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is connected to a spring of spring constant k as sho...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a plot of the potential energy as a function of x for a p...
Text Solution
|
- A 20-kg block attached to a spring of spring constant 5Nm^-1 is releas...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical blocks, each having mass M, are placed as shown in figur...
Text Solution
|
- A 1kg stone at the end of 1m long string is whirled in a vertical circ...
Text Solution
|
- A stone at the end of 1m long string is whirled in a vertical circle a...
Text Solution
|
- Ball A of mass m, after sliding from an inclined plane, strikes elasti...
Text Solution
|