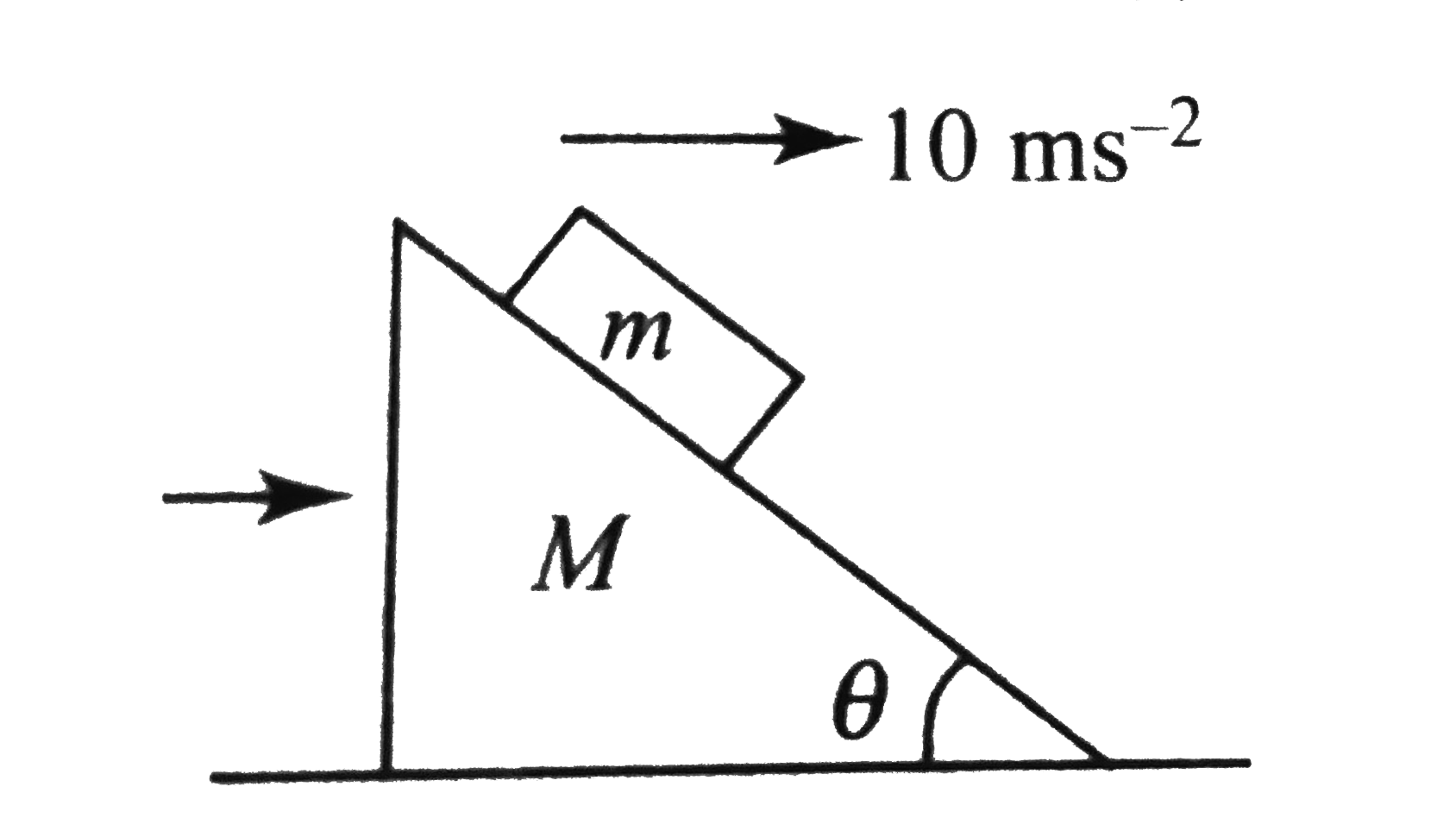
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
WORK, POWER & ENERGY
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Archives (sinble Correct )|19 VideosWORK, POWER & ENERGY
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Archives(multiple Correct)|3 VideosWORK, POWER & ENERGY
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Linked Comprehension|55 VideosVECTORS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Exercise Multiple Correct|5 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-WORK, POWER & ENERGY-Integer
- In the situation shown in figure all contact surfaces are smooth. The ...
Text Solution
|
- An insect jumps from ball A onto ball B, which are suspended from inex...
Text Solution
|
- The PE of a certain spring when streched from natural length through a...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m=0.14kg is moving with velocity v0 towards a mass les...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is released from rest at point A. The compression in...
Text Solution
|
- In figuer, shown all the surfaces are frictionless, and mass of the bl...
Text Solution
|
- A car travelling on a smooth road passes through a curved portion of t...
Text Solution
|
- A man slowly pulls a bucket of water from a well of depth h=20m. The m...
Text Solution
|
- The arrangement shown in figure is at rest. An ideal spring of natural...
Text Solution
|
- In figure, find the velocity of m1 in ms^-1 when m2 falls by 9m. ...
Text Solution
|
- One end of a spring of force constant k1 is attached to the ceiling of...
Text Solution
|
- A system consists of two identical cubes, each of mass 3kg, linked tog...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass 5kg is free to slide on a smooth ring of radius r=2...
Text Solution
|
- A 2144kg freight car roles along rails with negligible friction. The c...
Text Solution
|