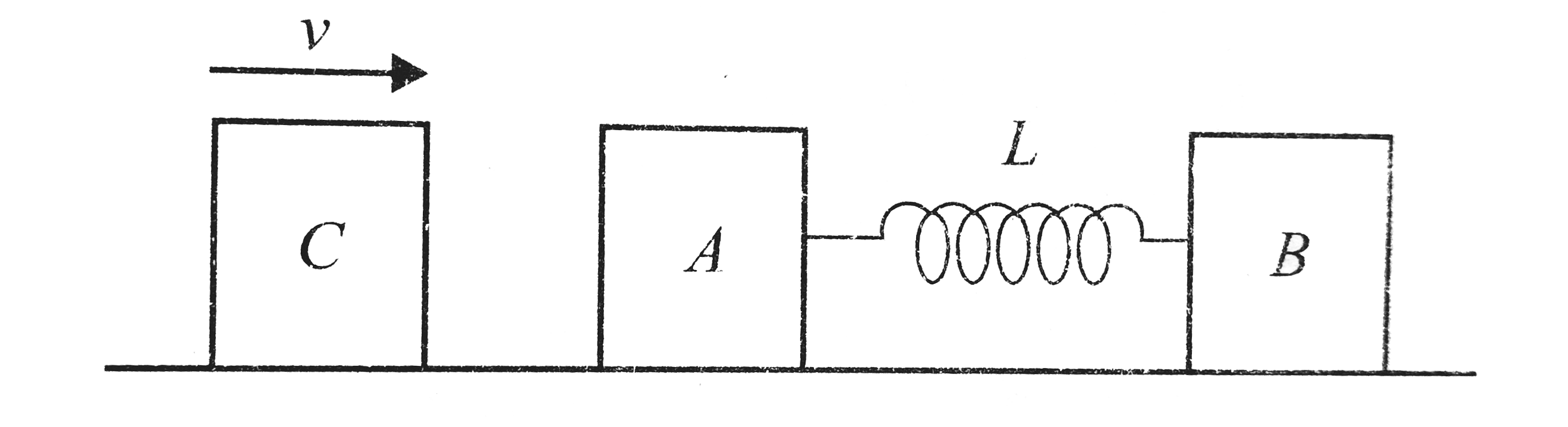
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
WORK, POWER & ENERGY
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Archives (assertion-reasoning)|1 VideosWORK, POWER & ENERGY
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Archives (linked Comprehension)|2 VideosWORK, POWER & ENERGY
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Archives (sinble Correct )|19 VideosVECTORS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Exercise Multiple Correct|5 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems