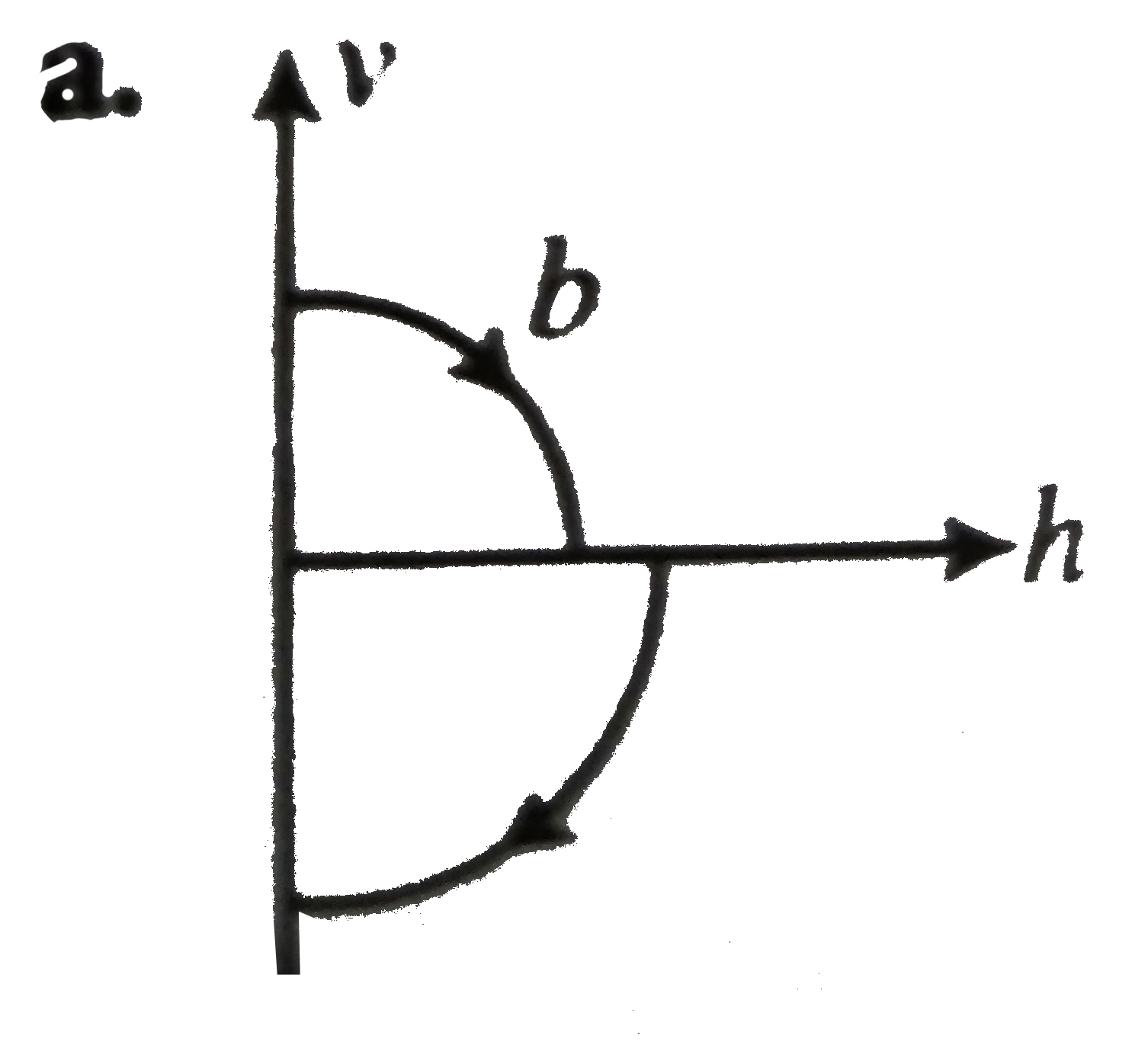
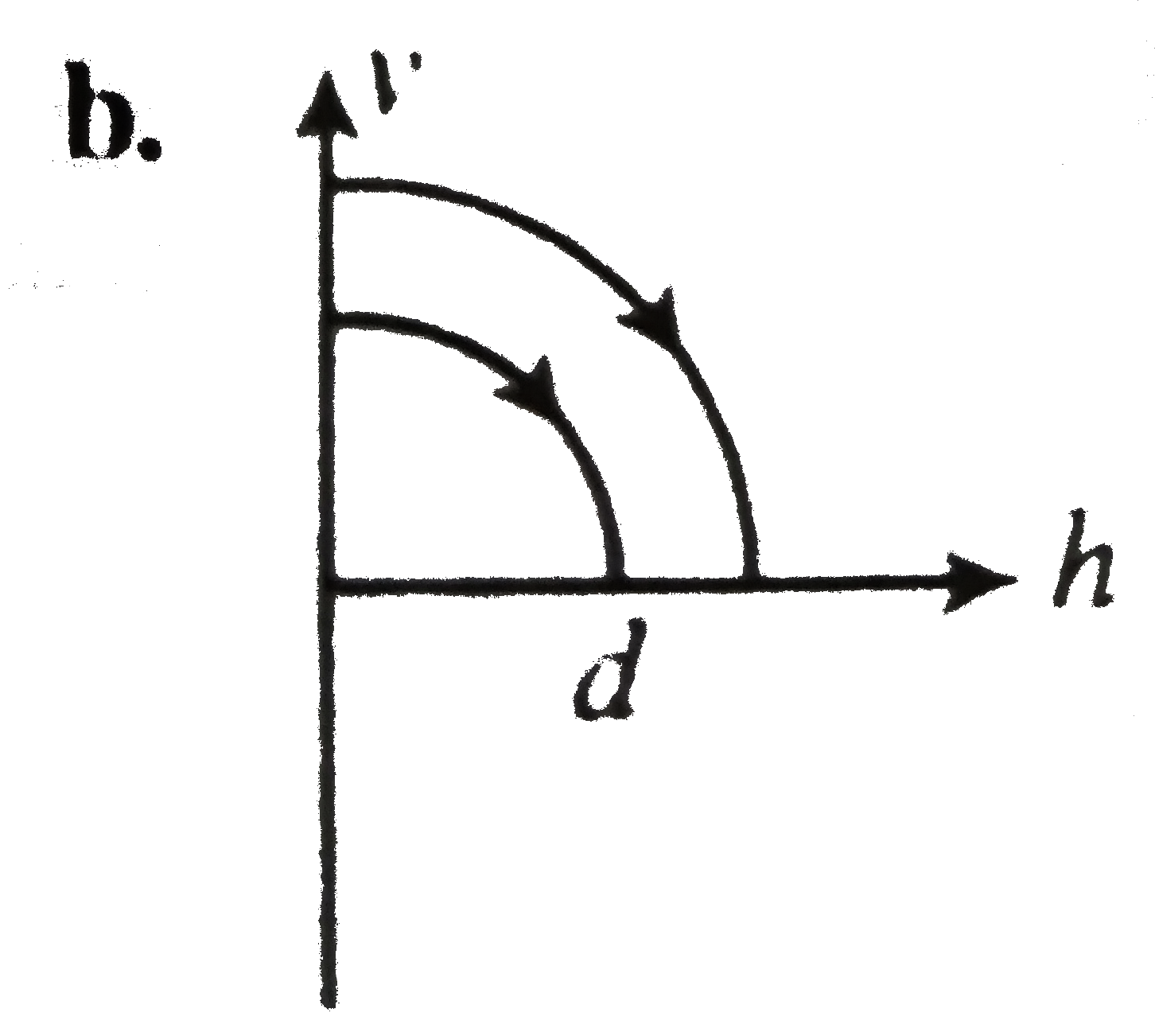
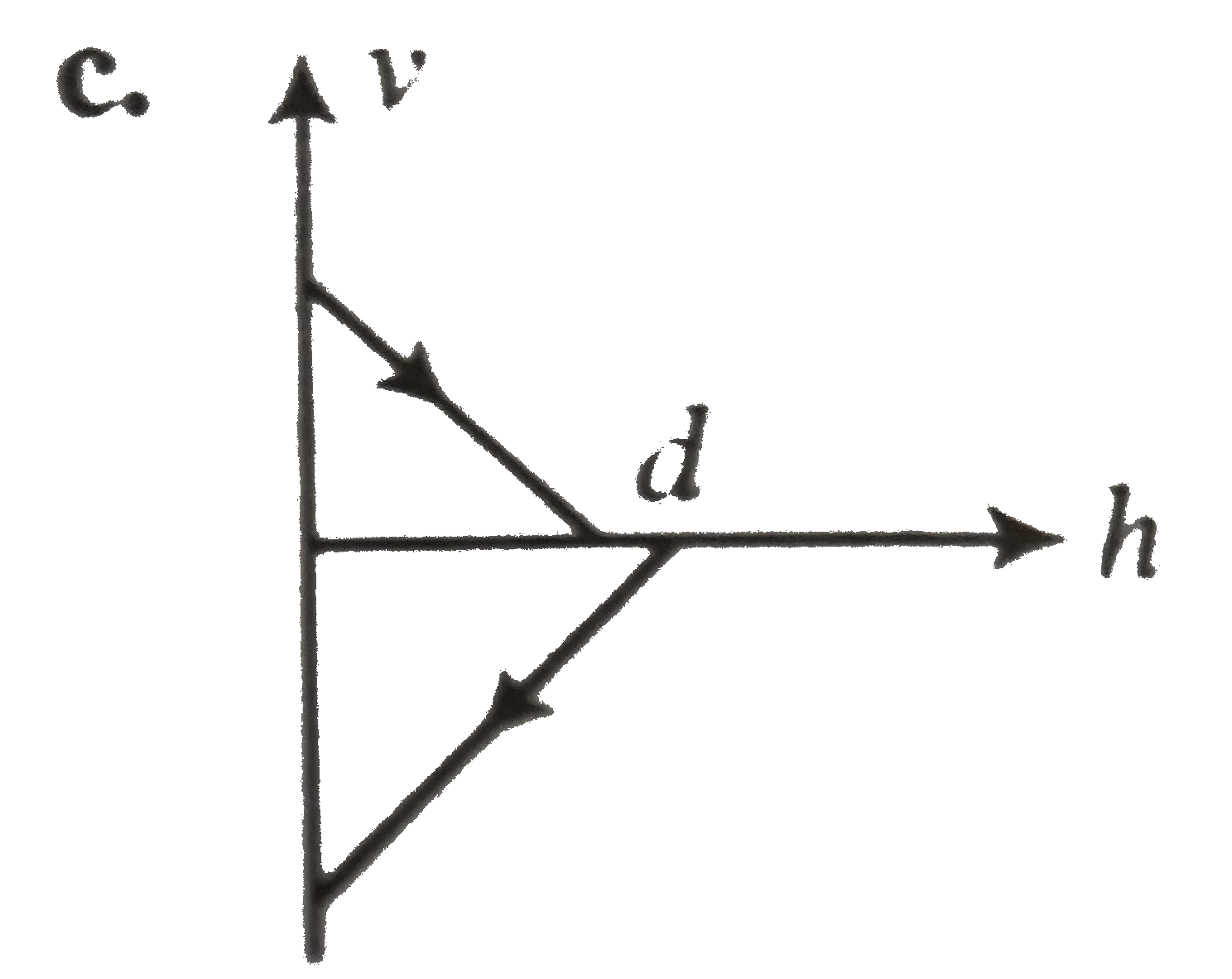
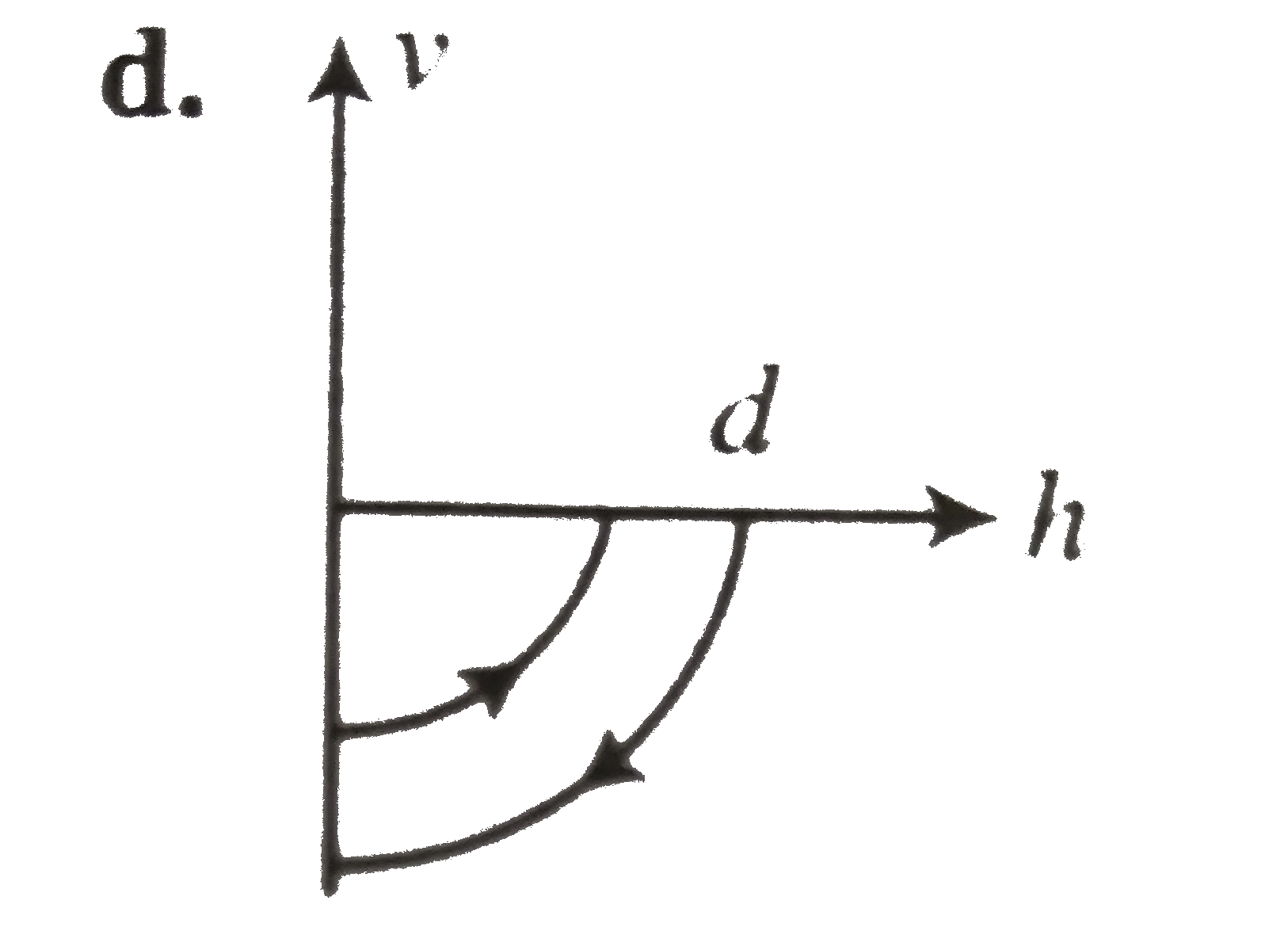
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
MISCELLANEOUS KINEMATICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Multiple Correct Answer Type|26 VideosMISCELLANEOUS KINEMATICS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Linked Comprehension Type|35 VideosLINEAR AND ANGULAR SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Multiple Correct Answer Type|9 VideosMISCELLANEOUS VOLUME 2
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise INTEGER_TYPE|10 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-MISCELLANEOUS KINEMATICS-Interger type
- A ball is dropped vertically from a height d above the ground . It hit...
Text Solution
|
- A train is moving along a straight line with a constant acceleration '...
Text Solution
|
- Airplanes A and B are flying with constant velocity in the same vertic...
Text Solution
|
- A rocket is moving in a gravity free space with a constant acceleratio...
Text Solution
|