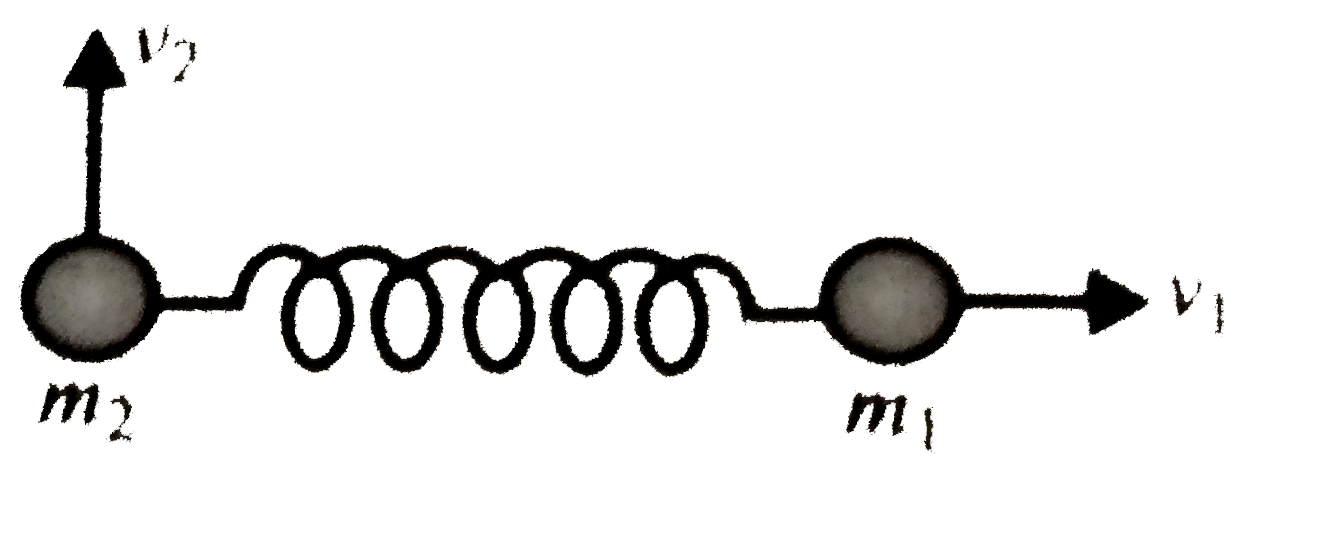
Two small discs of masses `m_(1)` and `m_(2)` are connected by a weightless spring resting on a smooth horizontal plance. The discs are set in motion with initial velocities `v_(1) and v_(2)` whose directions are mutually perpendicular and in the same horizontal plane. Find the total energy `E` of hte system with reference to the frame fixed to the centre of mass.